SparkFun Inventor's Kit for Edison Experiment Guide
Experiment 7: Speaker
Introduction
Many microcontrollers have the ability to create analog voltages using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). DACs are incredibly useful for connecting to a speaker (usually through an amplifier) to make sounds.
Many other microcontrollers and computer modules (like our Edison) do not have an onboard DAC. While separate DAC chips can be added, we are often left with using PWM to approximate sounds with a speaker.
In this experiment, we will read musical note information from a file and use that to create PWM signals. We then amplify the PWM signals and feed it to a small speaker that converts those signals to sound.
Parts Needed
In addition to the Edison and Block Stack, you will need the following parts:
- 1x Breadboard
- 1x Piezo Speaker
- 1x NPN Transistor
- 1x 1kΩ Resistor
- 1x 100Ω Resistor
- 6x Jumper Wires
Intel® Edison
DEV-13024SparkFun Block for Intel® Edison - GPIO
DEV-13038SparkFun Block for Intel® Edison - Base
DEV-13045Suggested Reading
- How a Speaker Works -- Simple electromagnets can be used to create sound waves!
Concepts
Reading a File
The ability to read and write to and from a file in a program can be incredibly useful. Often, we want to store settings and other parameters in a piece of plain text so that users can adjust the configuration of the program without digging through code.
To accomplish that, we will rely on the node module fs. Specifically, we want to use fs.readFileSync().
fs.readFile() will also read the contents of a text file, but it does so asynchronously, which means other parts of the program might execute before the file is completely read. This could result in the variable that's supposed to hold the file contents being undefined.
fs.readFileSync() blocks execution of the program until the file has been completely read.
Sleeping
JavaScript, in its attempt to be as asynchronous (e.g. non-blocking) as possible, does not have a built-in wait() or sleep() function. As JavaScript is primarily intended for use in browsers, telling a client's computer to sleep on a thread is generally considered a bad idea.
As a result (and since we don't care about browser behavior in this Node example), we will write our own sleep function.
We will use the process time, which is found in the Node process object. The "high resolution" time can be found by calling process.hrtime(), which returns the process's run time in seconds and nanoseconds. By doing nothing in a do-while loop, we can effectively sleep for a given number of nanoseconds.
PWM Sounds
While a DAC is normally used to make sounds with a speaker, we can approximate sounds with PWM. Because PWM is a digital signal (a square wave), it contains a lot of harmonic frequencies on top of the original frequency, and thus producing an unclean sound (i.e. not a true representation of the actual frequency). Played through a speaker, a square wave sounds very different from a sine wave.
Without a true DAC on the Edison, we can use a 50% PWM signal (a basic square wave) to create sounds. Played at the correct frequency, we can even make notes!
Based on some testing with an oscilloscope, the fastest the Edison is able to switch a pin on and off is about 475 μs, which translates to about 2.1 kHz. As a result, we need to keep notes to C7 (2093.00 Hz) or lower. A note-to-frequency table can be found here.
Real-Time Operating System
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system (OS), but unlike popular operating systems like Linux, OS X, or Windows, an RTOS is intended to meet strict timing deadlines.
For example, an HDTV receiver often relies on an RTOS within a microcontroller (or microprocessor) to receive a digital signal and decode it within a very small amount of time (every frame!). If deadlines are missed, the TV's picture may be garbled or worse, not displayed at all.
Linux (like the one running in your Edison), generally, is NOT an RTOS! Linux was originally designed as a general-purpose OS with the focus on user experience. If we give Linux several tasks, there is no guarantee as to when those tasks will execute, when they will finish, and in what order. There are several versions of real-time Linux available and in the works, but the default Yocto image on the Edison is not one.
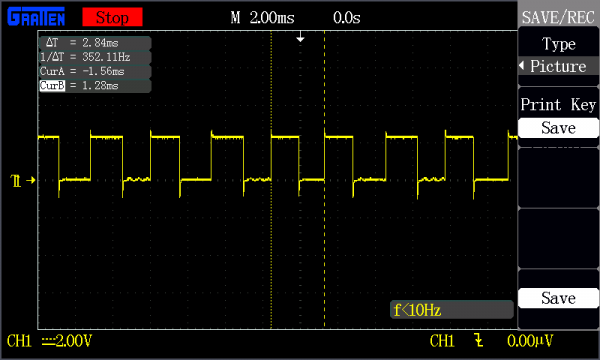
If we create a fast switching signal (a square wave) in our Edison and output it to a pin, we can measure it with an oscilloscope. In this example, we create a square wave with a frequency of 440 Hz.
See anything wrong?
Well, first of all, the measured frequency is WAY off from 440 Hz! The period of a 440 Hz signal is about 2.27 ms, and we measured 2.84 ms. That means Linux is taking its sweet time (around 0.57 ms in this case) to do whatever it needs (switch to some other task, run it for a while, switch back, and then notice that we should toggle that pin). 0.57 ms may not seem like a lot (especially when we are talking about doing things like browsing sites and reading text files), but when it comes to music, that means the difference between reading an A and playing an F note. Talk about tone deaf.
Secondly, not all of the highs and lows in that oscilloscope image are the same width. That means that Linux is not even guaranteeing the frequency will be constant! Unless it is an intentional fluctuation, it often makes a note very unpleasing.
If you still decide to go through with this experiment, please forgive me for assaulting your ears.
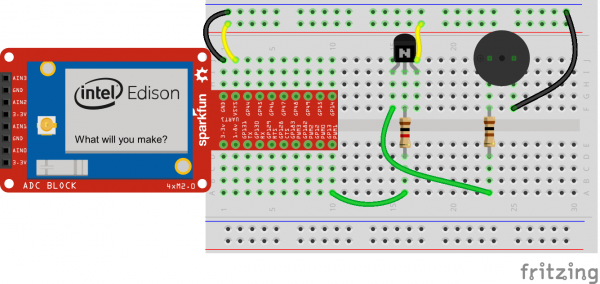
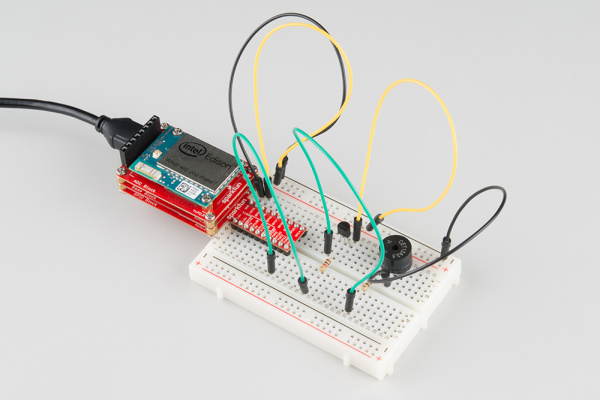
Hardware Hookup
Fritzing Diagram
Tips
Speaker
Note the + marking on the top side of the speaker (there are also + and - markings on the underside).
The pin associated with the positive (+) polarity should be connected to the 100Ω resistor. Negative (-) should be connected to the ground rail on the breadboard.
The Code
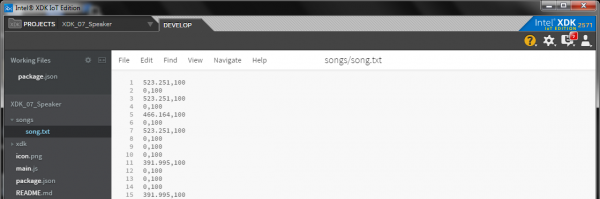
In the XDK, create a new directory named songs in the file browser, and in that, a file named song.txt. In song.txt, copy in the following text:
523.251,100
0,100
523.251,100
0,100
466.164,100
0,100
523.251,100
0,100
0,100
0,100
391.995,100
0,100
0,100
0,100
391.995,100
0,100
523.251,100
0,100
698.456,100
0,100
659.255,100
0,100
523.251,100
0,100
Save that file.
Then, copy the following code into main.js:
language:javascript
/*jslint node:true, vars:true, bitwise:true, unparam:true */
/*jshint unused:true */
// Leave the above lines for propper jshinting
/**
* SparkFun Inventor's Kit for Edison
* Experiment 7: Speaker
* This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics
* November 17, 2015
* Updated: August 1, 2016
* https://github.com/sparkfun/Inventors_Kit_For_Edison_Experiments
*
* Plays a tune using a PWM speaker.
*
* Released under the MIT License(http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
*/
var mraa = require('mraa');
var fs = require('fs');
// Global constants
var MAX_FREQ = 2100;
// Set up a digital output on MRAA pin GP13 for the speaker
var speakerPin = new mraa.Gpio(13, true, true);
speakerPin.dir(mraa.DIR_OUT);
speakerPin.write(0);
// Read and parse song file
var song = fs.readFileSync(__dirname + "/songs/song.txt", 'utf-8');
song = song.replace(/\r/g, '');
song = song.split('\n');
// Play song
console.log("Playing...");
for (var t = 0; t < song.length; t++) {
// Read the frequency and time length of the note
var note = song[t].split(',');
// Play the note
playNote(speakerPin, parseFloat(note[0]), parseInt(note[1], 10));
}
console.log("Done!");
// Play a note with a given frequency for msec milliseconds
function playNote(pin, freq, msec) {
// Check to make sure we actually have valid numbers
if (freq === "NaN" || msec === "NaN") {
return;
}
// Make sure we don't go over the maximum frequency
if (freq >= MAX_FREQ) {
freq = MAX_FREQ;
}
// If the frequency is 0, don't play anything
if (freq === 0) {
console.log("Silence for " + msec + "ms");
delaynsec(msec * 1e6);
return;
}
// Define the note's period and how long we play it for
var period = 1 / freq;
var length = msec / (period * 1000);
console.log("Playing " + freq + "Hz for " + msec + "ms");
// For one period, send pin high and low for 1/2 period each
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
pin.write(1);
delaynsec(Math.round((period / 2) * 1e9));
pin.write(0);
delaynsec(Math.round((period / 2) * 1e9));
}
}
// Delay for a number of given nanoseconds
function delaynsec(nsec) {
var time = process.hrtime();
var diff;
var diffNSec;
// Wait until the specified number of nanoseconds has passed
do {
diff = process.hrtime(time);
diffNSec = (diff[0] * 1e9) + diff[1];
} while (diffNSec < nsec);
}
What You Should See
Well, you shouldn't actually see anything. However, you should hear an awful rendition of a popular '70s song. Bonus points if you can name that tune (and with it being horribly off key, those bonus points really count).
Code to Note
Regular Expressions (Regex)
We get the contents of our song file with fs.readFileSync(), but then we must parse that file to know which notes we need to play and for how long. To do that, we get rid of all the carriage return characters ('\r') by using the regular expression /\r/g, which says "find all \r characters in the string."
We can use the .replace(regex, string), which finds all the occurrences of the regex and replaces it with the given string. In this case, we replace all '\r' with '' (nothing).
String Manipulation
JavaScript plays very nicely with strings. You have just seen the .replace() method, and there are many others.
We also rely on .split() to split up the string containing the file contents into an array of smaller strings. We first split on the newline character \n. We iterate (using a for loop) over that array, and in each case, we split the substring even further.
In each substring, we look for the comma ',' character. As the song.txt file is set up, we list the frequency we want to play first (the note) and for how long (milliseconds) next. They make up the first and second (0 and 1) elements of the array, respectively.
GPIO Raw Pin Numbers
A few pin objects in MRAA (for example, GPIO) allow us to use "raw" pin numbers (e.g. GP13). To do that, we need to pass true to the third parameter. For example:
var speakerPin = new mraa.Gpio(13, true, true);
The second parameter says that we "own" the pin (the descriptor to the pin will automatically close when we exit). The third parameter says that we want to use "raw" values (by default, this value is false, and says that we should treat the first parameter as the MRAA pin number). The number 13 actually corresponds to GP13 on the board!
This does not work for all pin-related objects. For example, PWM does not support raw pin numbers. More about raw pin numbers can be found here.
Troubleshooting
- There is no sound -- Double-check the wiring of the speaker and the transistor. Make sure the + symbol on the speaker is on the same row as the 100Ω resistor in the breadboard.
Going Further
Challenges
- Create a new song! Take a look at how the song.txt file is organized (frequency,time) and generate a new song text file with one of your favorite tunes. Don't forget to change the file location in
fs.readFileSync()!
Digging Deeper
- Node fs API
- How a square wave is created with sine waves
- Piano notes and frequencies
- Regex reference