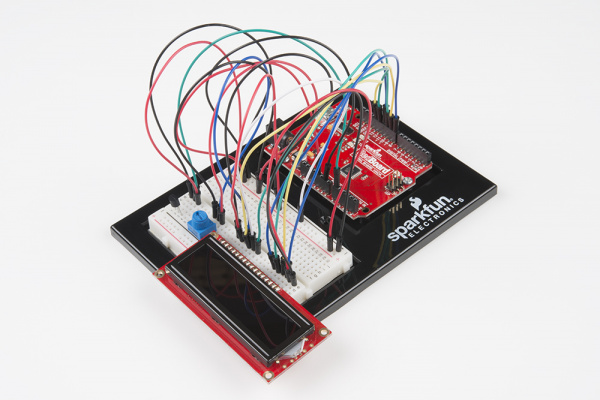
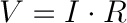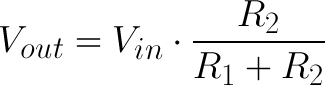SparkFun Inventor's Kit Experiment Guide - v4.0
Introduction
If you have SIK v3.3 or are using parts from the add-on pack, please refer to this tutorial.
The SparkFun Inventor's Kit (SIK) is your map for navigating the waters of beginning embedded electronics. This guide contains all the information you will need to build five projects encompassing the 16 circuits of the SIK. At the center of this guide is one core philosophy: that anyone can (and should) play around with electronics. When you’re done with this guide, you will have built five projects and acquired the know-how to create countless more. Now enough talk — let’s start something!
The print version of this guide is available as a PDF as well. Click the following link to download it. Keep in mind that the original file size used for the printed guidebook was reduced for the web. While the file size was reduced, it is still about a 26MB download.
Choosing a Kit
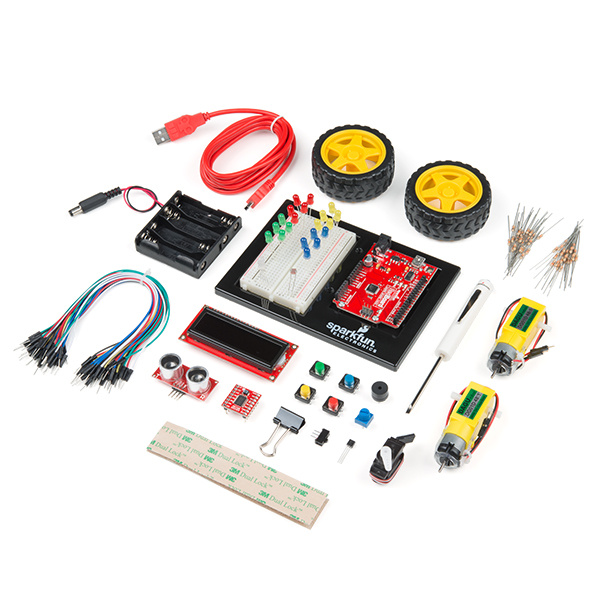
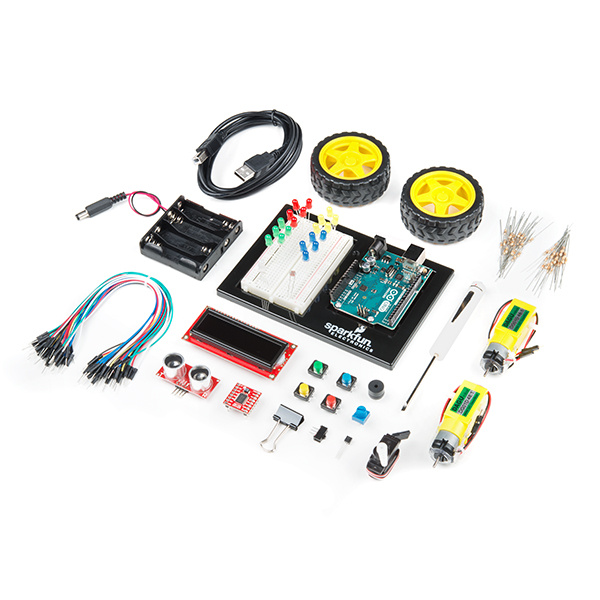
You should have one of the two following versions of the SIK. If you need a overview of the parts included in your kit, please click on the product link below.
SparkFun Inventor's Kit - v4.0
KIT-14265The primary difference between the two kits is the microcontroller included in the kit. The SparkFun Inventor's Kit includes a SparkFun RedBoard, while the SparkFun Inventor's Kit for Arduino Uno includes an Arduino Uno R3. At the heart of each is the ATmega328p microcontroller, giving both the same functionality underneath the hood. Both development boards are capable of taking inputs (such as the push of a button or a reading from a light sensor) and interpreting that information to control various outputs (like a blinking LED light or an electric motor). And much, much more!
If you need more information to determine which microcontroller is right for you, please check out the following tutorials.
What is an Arduino?
RedBoard Hookup Guide
Open Source!
At SparkFun, our engineers and educators have been improving this kit and coming up with new experiments for a long time now. We would like to give attribution to Oomlout, since we originally started working off their Arduino Kit material many years ago. The Oomlut version is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 3.0 Unported License.
The SparkFun Inventor's Kit V4.0 is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 4.0 International License.
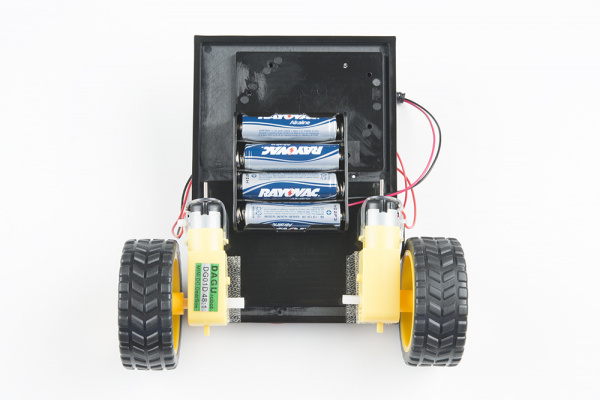
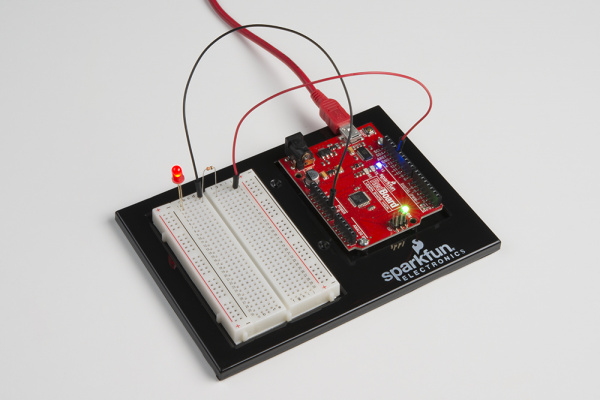
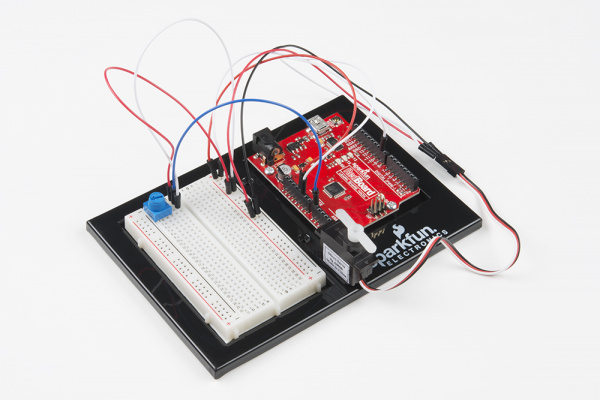
Baseplate Assembly
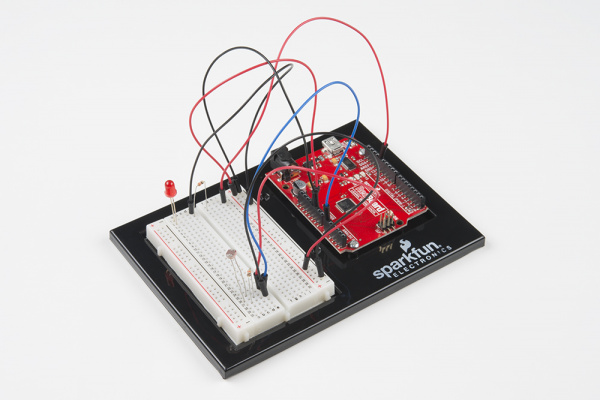
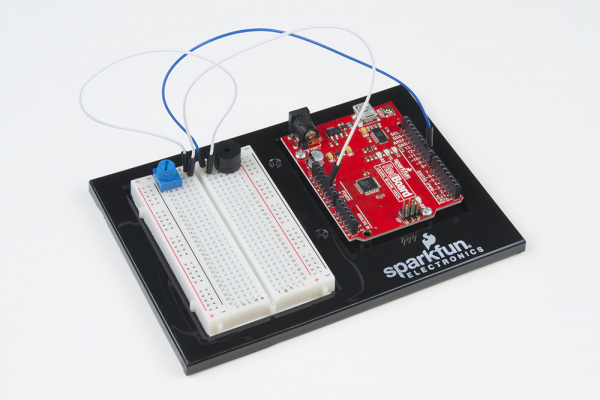
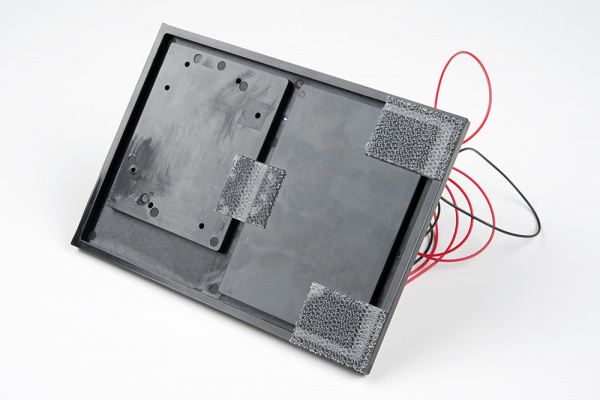
Before you can build circuits, you'll want to first assemble the breadboard baseplate. This apparatus makes circuit building easier by keeping the breadboard and the RedBoard microcontroller connected together without the worry of disconnecting or damaging your circuit. The larger the circuit, the more wires needed to build it. The more wires there are, the easier it is for one of those wires to come undone.
To begin, grab all the parts: the RedBoard, the breadboard, the included screwdriver, the baseplate and the two baseplate screws.
If the screwdriver end is a flathead screwdriver, pull the shaft out, rotate it around to the Phillips head screwdriver side, and reinsert the shaft.
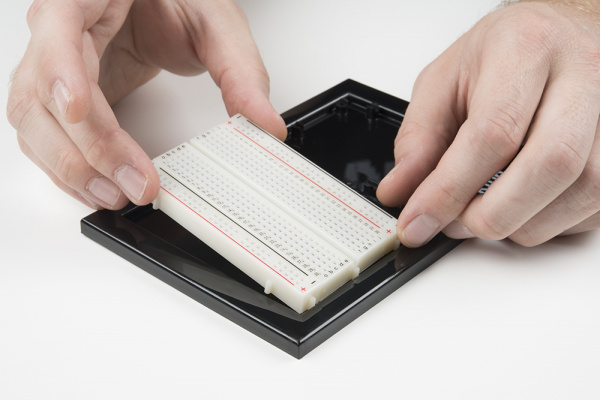
Next, peel the adhesive backing off the breadboard.
Carefully align the breadboard over its spot on the baseplate. The text on the breadboard should face the same direction as the text on the baseplate. Firmly press the breadboard to the baseplate to adhere it.
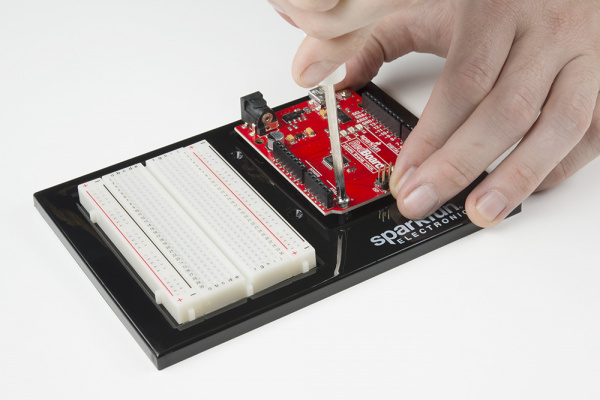
Align the RedBoard with its spot on the baseplate. The text on it should face the same direction as the text on the breadboard and the baseplate. Grab on of the two included screws, and firmly screw it into one of the four stand-off holes found on the RedBoard. The plastic holes are not threaded, so you will need to apply pressure as you twist the screwdriver.
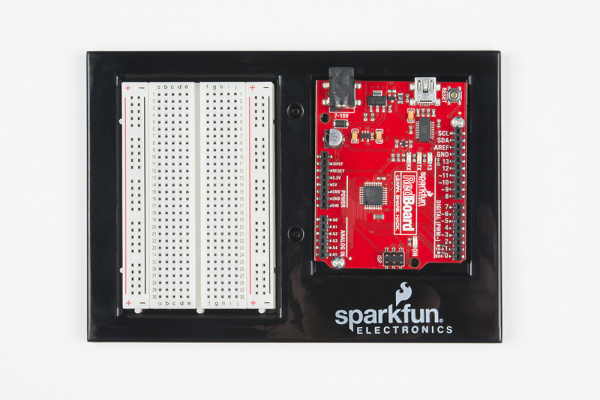
Screw the second screw in the stand-off hole diagonally across from the first. With that, your baseplate is now assembled.
Arduino Uno Baseplate Assembly
Newer versions of the Arduino Uno come with a clear, plastic baseplate of their own. It will need to be removed before the Uno can be attached to the breadboard baseplate. To remove it, pull it from the Uno.
You may now attach the Uno to the baseplate as shown in the instructions above.
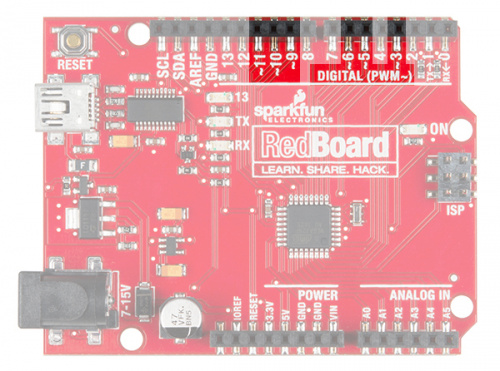
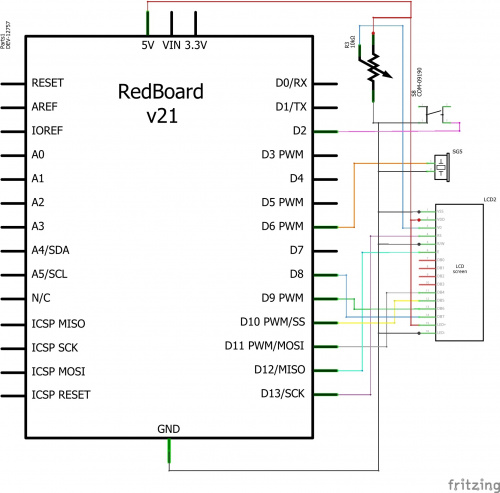
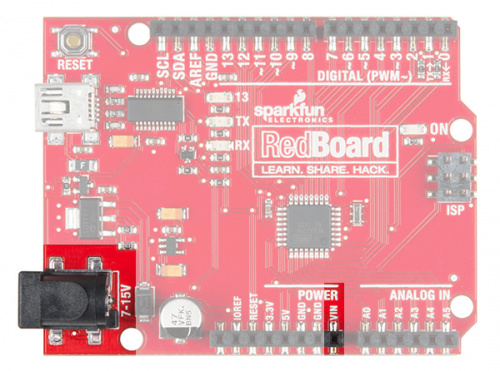
The SparkFun RedBoard
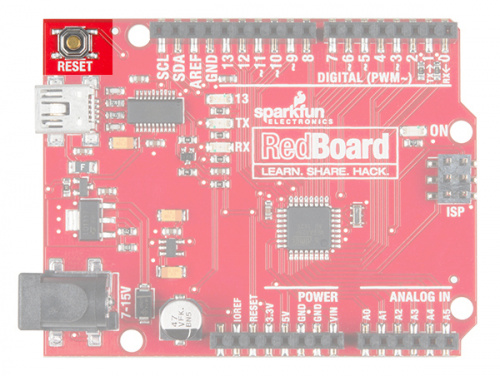
The SparkFun RedBoard is your development platform. At its roots, the RedBoard is essentially a small, portable computer, also known as a microcontroller. It is capable of taking inputs (such as the push of a button or a reading from a light sensor) and interpreting that information to control various outputs (like blinking an LED light or spinning an electric motor). That’s where the term “physical computing” comes in; this board is capable of taking the world of electronics and relating it to the physical world in a real and tangible way.
The SparkFun RedBoard is one of a multitude of development boards based on the ATmega328 microprocessor. It has 14 digital input/output pins (six of which can be PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16MHz crystal oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, and a reset button. You’ll learn more about each of the RedBoard's features as you progress through this guide.
Check out the guide below to learn more about the SparkFun RedBoard.
RedBoard Hookup Guide
Understanding Breadboards
A breadboard is a circuit-building platform that allows you to connect multiple components without using a soldering iron.
If you have never seen or used a breadboard before, it is highly recommended you read the following guide that explains the breadboards anatomy and how to use one.
How to Use a Breadboard
Install the Arduino IDE and SIK Code
The following steps are a basic overview of getting started with the Arduino IDE. For more detailed, step-by-step instructions for setting up the Arduino IDE on your computer, please check out the following tutorial.
Installing Arduino IDE
Download the Arduino IDE
In order to get your microcontroller up and running, you'll need to download the newest version of the Arduino software first (it's free and open source!).
This software, known as the Arduino IDE, will allow you to program the board to do exactly what you want. It’s like a word processor for writing code.
Download Arduino Code
You are so close to to being done with setup! Download the SIK Guide Code. You can also download the code from GitHub or click the following link to download the code:
Place the SIK-Guide-Code folder in the Arduino IDE examples directory:
- Windows: drag the
SIK-Guide-Code-V4.0afolder intoC:\Program Files\Arduino-x\examples
Note: For those that automatically installed the Arduino IDE on a Windows 64-bit computer, the Arduino program folder may be located in the "C:\Program Files (x86)..." folder. - MacOS: Right-click on the Arduino IDE app and click "Show Package Contents...". Drag the
SIK-Guide-Code-V4.0afolder intoContents/Resources/Java - Linux: see http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Learning/Linux
Connect the Microcontroller to your Computer
Use the USB cable provided in the SIK kit to connect the included microcontroller (RedBoard or Arduino Uno) to one of your computer’s USB inputs.
Install FTDI Drivers
Depending on your computer’s operating system, you will need to follow specific instructions. Please go to How to Install FTDI Drivers, for specific instructions on how to install the FTDI drivers onto your RedBoard.
USB Serial Driver Quick Install
Select your Board: Arduino/Genuino Uno
Before we can start jumping into the experiments, there are a couple adjustments we need to make. This step is required to tell the Arduino IDE which of the many Arduino boards we have. Go up to the Tools menu. Then hover over Board and make sure Arduino Uno is selected.
Select a Serial Port
Next up we need to tell the Arduino IDE which of our computer's serial ports the microcontroller is connected to. For this, again go up to Tools, then hover over Port (Serial Port in older Arduino versions) and select your RedBoard or Arduino's serial port. This will be the same serial port seen when installing FTDI drivers.
With that, you're now ready to begin building your first circuit!
Project 1: Light
Welcome to your first SparkFun Inventor's Kit project. Each project is broken up into several circuits, each designed to help you learn about new technologies and concepts. The knowledge gained from each circuit will play a part in building each project. This first project will set the foundation for the rest of the projects in the guide and will aid in helping you understand the basic fundamentals of circuit building and electricity!
In Project 1, you will learn about light-emitting diodes (LEDs), resistors, inputs and sensors --- using all of those technologies to build and program your own multicolored night-light! The night-light uses a sensor to turn on an RGB (Red, Green, Blue) LED when it gets dark, and you will be able to change the color using an input knob.
New Components Introduced in This Project
Each of the components listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each project.
- LEDs
- Resistors
- Potentiometers
- Photoresistors
New Concepts Introduced in This Project
Each of the concepts listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each project.
- Polarity
- Ohm's Law
- Digital Output
- Analog vs. Digital
- Analog Input
- Analog to Digital Conversion
- Voltage Divider
- Pulse-width Modulation
- Functions
You Will Learn
- How to upload a program to your RedBoard or Arduino Uno
- Circuit building basics
- How to control LEDs with digital outputs
- How to read sensors you analog inputs
Circuit 1A: Blink an LED
Light-Emitting Diodes, or LEDs (pronounced el-ee-dees), are small, powerful lights that are used in many different applications. You can find LEDs in just about any source of light nowadays, from the bulbs lighting your home to the tiny status lights flashing on your home electronics. Blinking an LED is the classic starting point for learning how to program embedded electronics. It's the "Hello, World!" of microcontrollers.
In this circuit, you’ll write code that makes an LED flash on and off. This will teach you how to build a circuit, write a short program and upload that program to your RedBoard.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
LED (Light Emitting Diode)
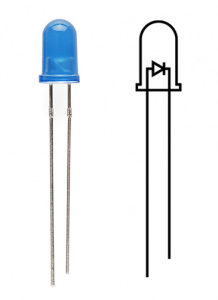
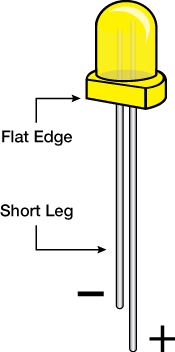
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are small lights made from a silicon diode. They come in different colors, brightnesses and sizes. LEDs have a positive (+) leg and a negative (-) leg, and they will only let electricity flow through them in one direction. LEDs can also burn out if too much electricity flows through them, so you should always use a resistor to limit the current when you wire an LED into a circuit.
Resistors
Resistors resist the flow of electricity. You can use them to protect sensitive components like LEDs. The strength of a resistor (measured in ohms) is marked on the body of the resistor using small colored bands. Each color stands for a number, which you can look up using a resistor chart.
New Concepts
Polarity
Many electronics components have polarity, meaning electricity can only flow through them in one direction. Components like resistors do not have polarity; electricity can flow through them in either direction. However, components like an LED that do have polarity only work when electricity flows through them in one direction.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's law describes the relationship between the three fundamental elements of electricity: voltage, resistance and current. This relationship can be represented by the following equation:
Where
- V = Voltage in volts
- I = Current in amps
- R = Resistance in ohms (Ω)
This equation is used to calculate what resistor values are suitable to sufficiently limit the current flowing to the LED so that it does not get too hot and burn out.
Digital Output
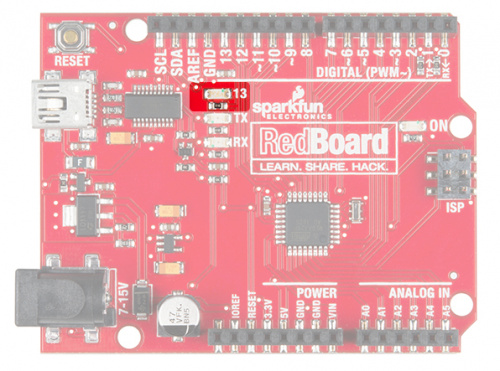
When working with microcontrollers such as the RedBoard, there are a variety of pins to which you can connect electronic components. Knowing which pins perform which functions is important when building your circuit. In this circuit, we will be using what is known as a digital output. There are 14 of these pins found on the RedBoard and Arduino Uno. A digital output only has two states: ON or OFF. These two states can also be thought of as HIGH or LOW or TRUE or FALSE. When an LED is connected to one of these pins, the pin can only perform two jobs: turning the LED on and turning the LED off. We'll explore the other pins and their functions in later circuits.
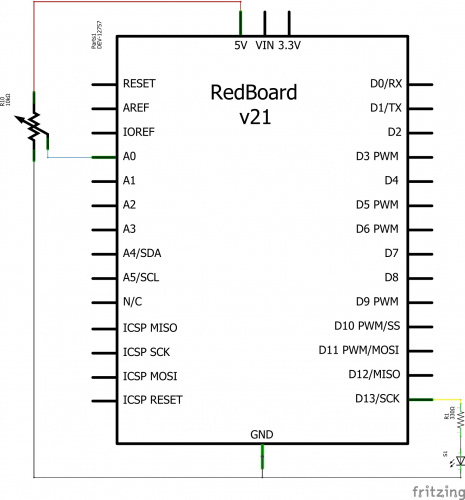
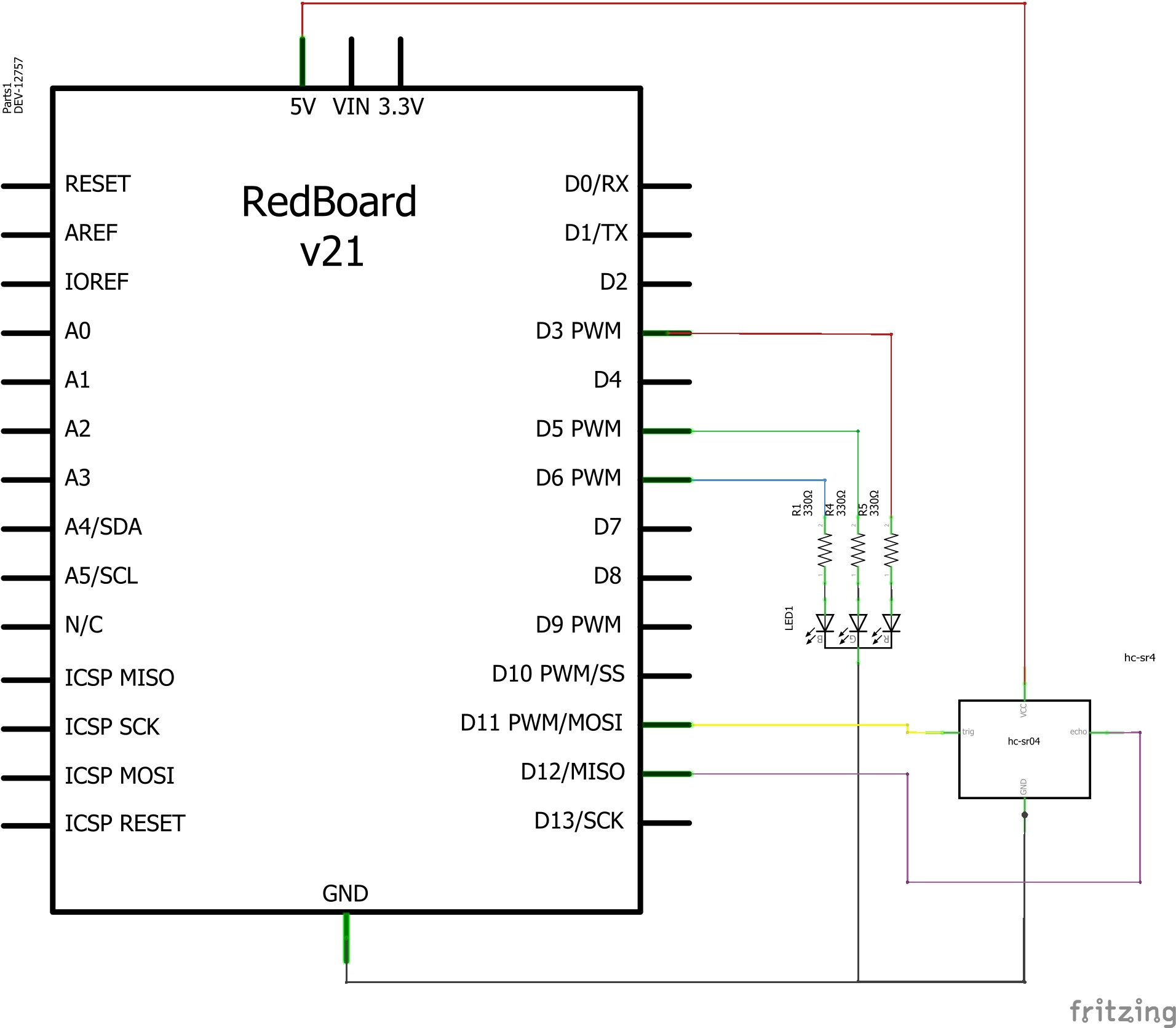
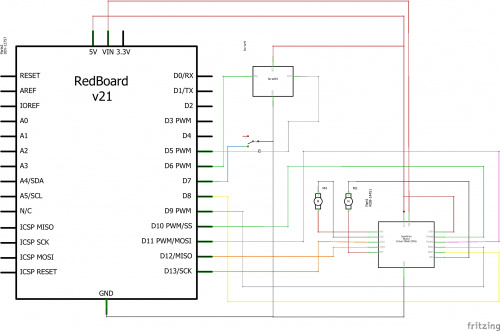
Hardware Hookup
We recommend familiarizing yourself with each of the components used in each circuit first.
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
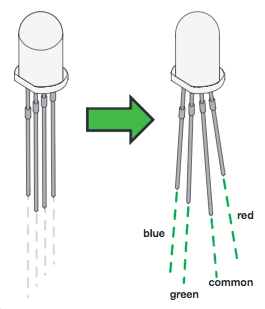
**Pay close attention to the LED. It is polarized. The negative side of the LED is the short leg, marked with a flat edge. **
Components like resistors need to have their legs bent into 90° angles in order to correctly fit the breadboard sockets.
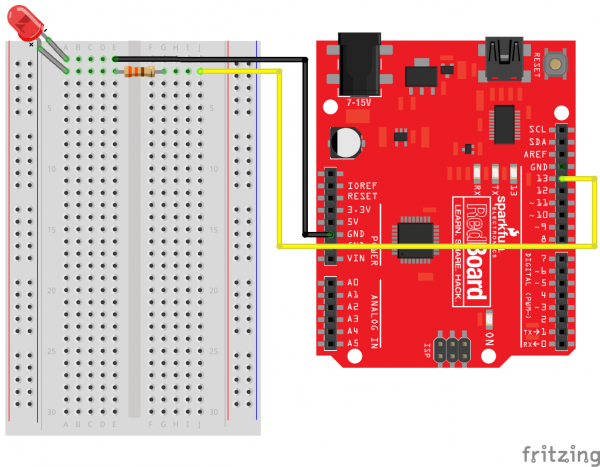
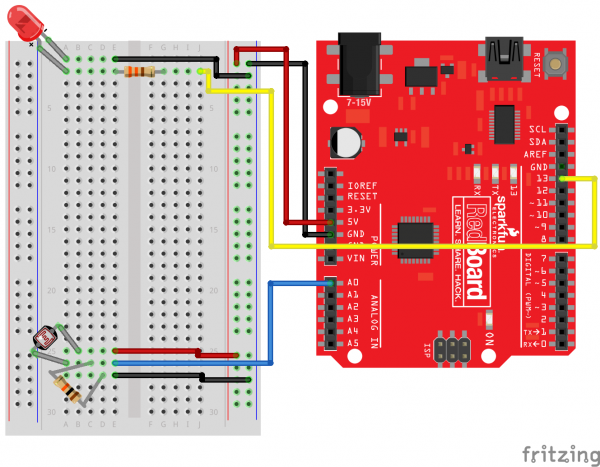
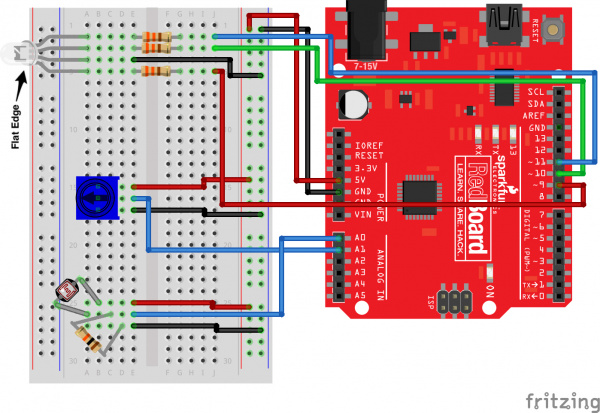
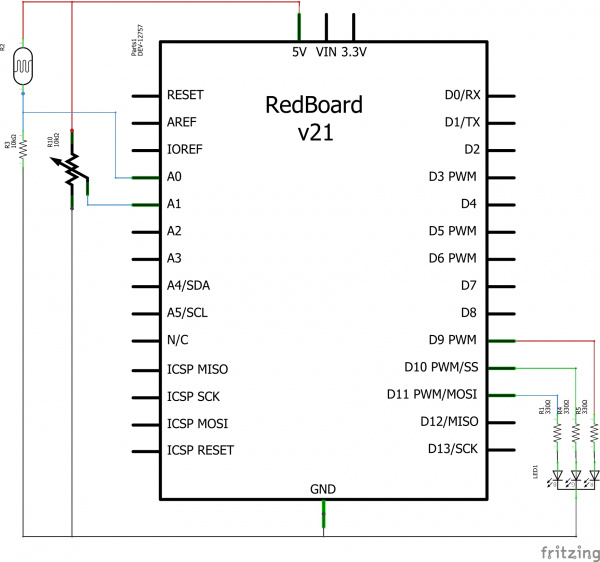
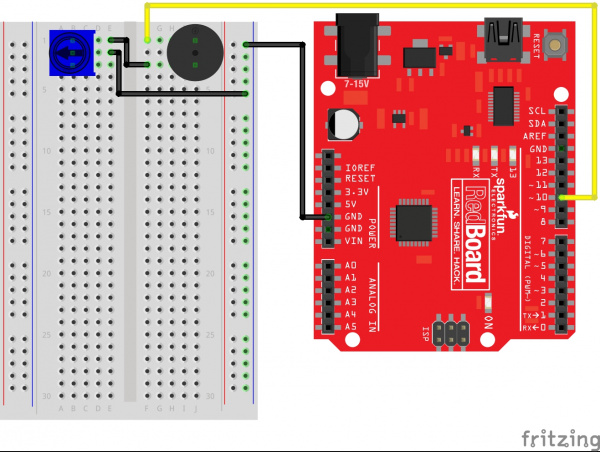
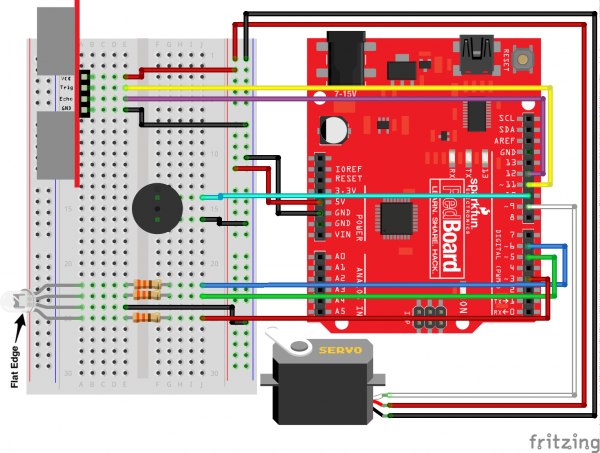
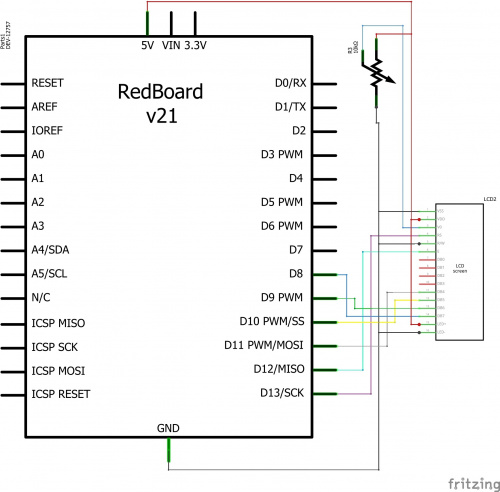
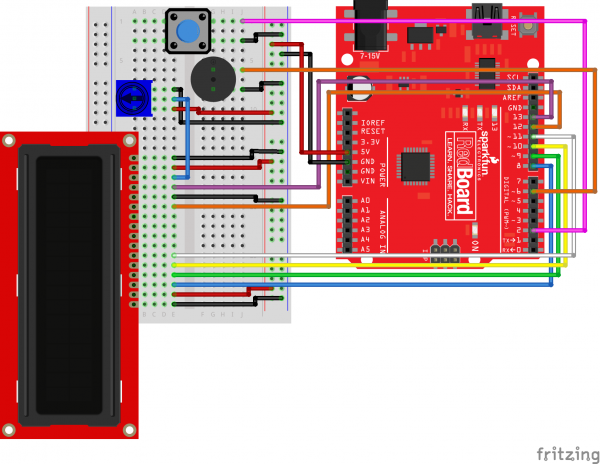
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below, to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED | A1 LED ( - ) | A2 LED ( + ) | |
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E2 | F2 | |
| Jumper Wire | GND | E1 | |
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | J2 |
Open Your First Sketch
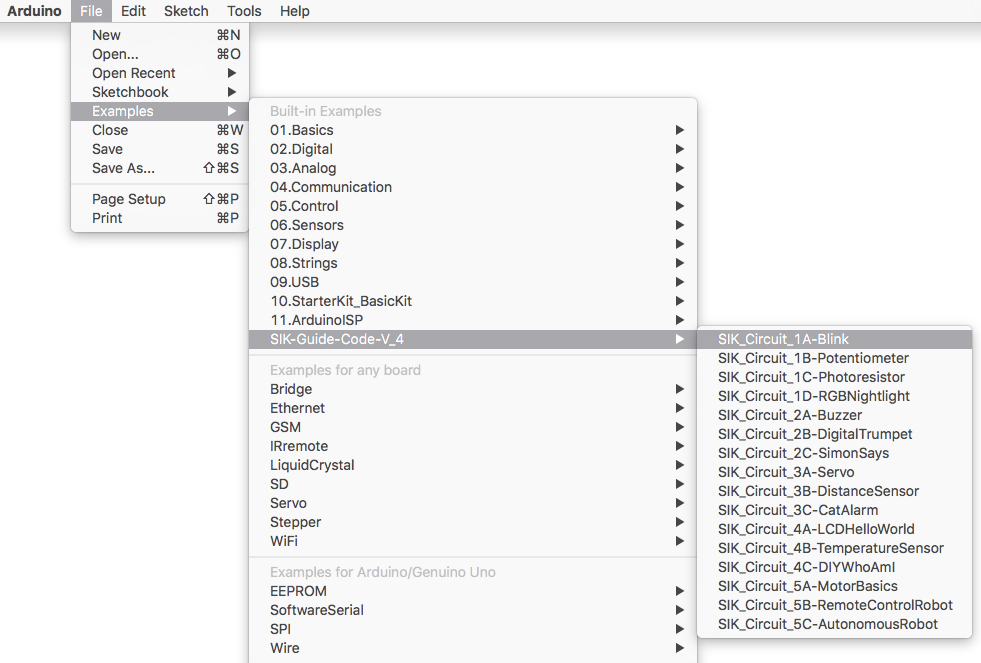
Open the Arduino IDE software on your computer. Open the code for Circuit 1A by accessing the SIK Guide Code you downloaded and placed into your examples folder earlier.
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_1A-Blink
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 1A-Blink
Turns an LED connected to pin 13 on and off. Repeats forever.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 to output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
delay(2000); // Wait for two seconds
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn off the LED
delay(2000); // Wait for two seconds
}
What You Should See
The LED will flash on for two seconds, off for two seconds, then repeat. If it doesn't, make sure you have assembled the circuit correctly and verified and uploaded the code to your board, or see the Troubleshooting section at the end of this section.
Program Overview
- Turn the LED on by sending power to Pin 13.
- Wait 2 seconds (2000 milliseconds).
- Turn the LED off by cutting power to Pin 13.
- Wait 2 seconds (2000 milliseconds).
- Repeat.
One of the best ways to understand the code you just uploaded is to change something and see how it affects the behavior of your circuit. For this first circuit, try changing the number found in these lines of code: delay(2000);. What happens if you change both to 100? What happens if you change both to 5000? What happens if you change just one delay and not the other?
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Setup and Loop:void setup(){code to run once} & void loop(){code to run forever} | Every Arduino program needs these two functions. Code that goes in between the curly brackets of setup() runs once, then the code in between the loop() curly brackets runs over and over until the RedBoard is reset or powered off. |
Input or Output?:pinMode(13, OUTPUT); | Before you can use one of the digital pins, you need to tell the RedBoard whether it is an INPUT or OUTPUT. We use a built-in "function" called pinMode() to make pin 13 a digital output. You'll learn more about digital inputs in Project 2. |
Digital Output:digitalWrite(13, HIGH); | When you're using a pin as an OUTPUT, you can command it to be HIGH (output 5 volts) or LOW (output 0 volts). |
Delay:delay(time in milliseconds); | Causes the program to wait on this line of code for the amount of time in between the brackets. After the time has passed, the program will continue to the next line of code. |
Comments://This is a comment | Comments are a great way to leave notes in your code explaining why you wrote it the way you did. You'll find many comments in the examples that further explain what the code is doing and why. Comments can be single line using //, or they can be multi-line using /* */. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Persistence of Vision | Computer screens, movies and the lights in your house all flicker so quickly that they appear to be on all of the time but are actually blinking faster than the human eye can detect. See how much you can decrease the delay time in your program before the light appears to be on all the time but is still blinking. |
| Morse Code | Try changing the delays and adding more digitalWrite() commands to make your program blink a message in Morse code. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| I get an error when uploading my code | The most likely cause is that you have the wrong board selected in the Arduino IDE. Make sure you have selected Tools > Board > Arduino/Genuino Uno. |
| I still get an error when uploading my code | If you're sure you have the correct Board selected but you still can't upload, check that you have selected the correct Serial Port. You can change this in Tools > Serial Port > your_serial_port. |
| Which Serial Port is the right one? | Depending on how many devices you have plugged into your computer, you may have several active Serial Ports. Make sure you are selecting the correct one. A simple way to determine this is to look at your list of Serial Ports. Unplug your RedBoard from your computer. Look at the list again. Whichever Serial Port has disappeared from the list is the one you want to select once you plug your board back in to your computer. |
| My code uploads, but my LED won’t turn on | LEDs will only work in one direction. Try taking it out of your breadboard, turning it 180 degrees, and reinserting it. |
| Still not working? | Jumper wires unfortunately can go "bad" from getting bent too much. The copper wire inside can break, leaving an open connection in your circuit. If you are certain that your circuit is wired correctly and that your code is error-free and uploaded but you are still encountering issues, try replacing one or more of the jumper wires for the component that is not working. |
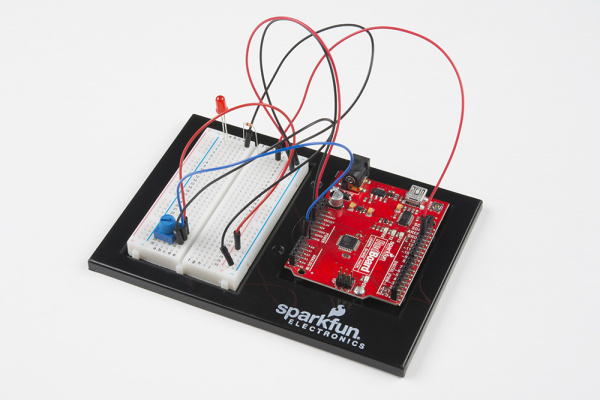
Circuit 1B: Potentiometer
Potentiometers (also known as “pots” or “knobs”) are one of the basic inputs for electronics devices. By tracking the position of the knob with your RedBoard, you can make volume controls, speed controls, angle sensors and a ton of other useful inputs for your projects. In this circuit, you'll use a potentiometer as an input device to control the speed at which your LED blinks.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
Potentiometer
A potentiometer (trimpot for short) is a variable resistor. When powered with 5V, the middle pin outputs a voltage between 0V and 5V, depending on the position of the knob on the potentiometer. Internal to the trimpot is a single resistor and a wiper, which cuts the resistor in two and moves to adjust the ratio between both halves. Externally, there are usually three pins: two pins connect to each end of the resistor, while the third connects to the pot's wiper.
New Concepts
Analog vs. Digital
Understanding the difference between analog and digital is a fundamental concept in electronics.
We live in an analog world. There is an infinite number of colors to paint an object (even if the difference is indiscernible to our eye), an infinite number of tones we can hear, and an infinite number of smells we can smell. The common theme among all of these analog signals is their infinite possibilities.
Digital signals deal in the realm of the discrete or finite, meaning there is a limited set of values they can be. The LED from the previous circuit had only two states it could exist in, ON or OFF, when connected to a Digital Output.
Analog Inputs
So far, we've only dealt with outputs. The RedBoard also has inputs. Both inputs and outputs can be analog or digital. Based on our definition of analog and digital above, that means an analog input can sense a wide range of values versus a digital input, which can only sense two states.
You may have noticed some pins labeled Digital and some labeled Analog In on your RedBoard. There are only six pins that function as analog inputs; they are labeled A0--A5.
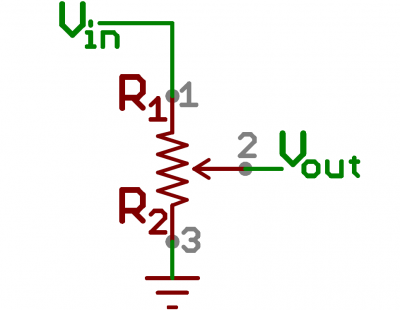
Voltage Divider
A voltage divider is a simple circuit that turns some voltage into a smaller voltage using two resistors. The following is a schematic of the voltage divider circuit. Schematics are a universally agreed upon set of symbols that engineers use to represent electric circuits.
A potentiometer is a variable resistor that can be used to create an adjustable voltage divider.
If the outside pins connect to a voltage source (one to ground, the other to Vin), the output (Vout) at the middle pin will mimic a voltage divider. Turn the trimpot all the way in one direction, and the voltage may be zero; turned to the other side, the output voltage approaches the input. A wiper in the middle position means the output voltage will be half of the input.
Voltage dividers will be covered in more detail in the next circuit.
Hardware Hookup
The potentiometer has three legs. Pay close attention into which pins you're inserting it on the breadboard, as they will be hard to see once inserted.
Potentiometers are not polarized. You can attach either of the outside pins to 5V and the opposite to GND. However, the values you get out of the trimpot will change based on which pin is 5V and which is GND.
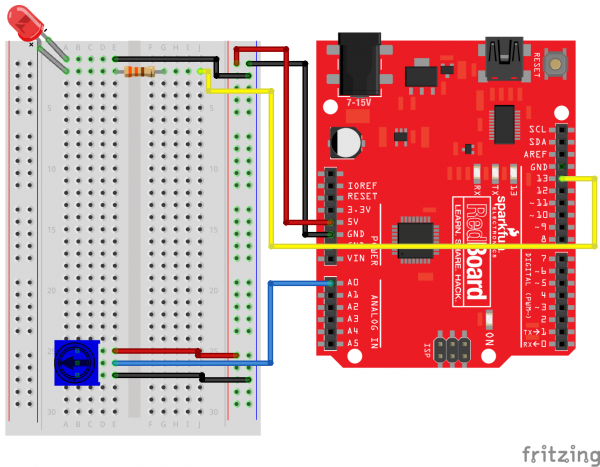
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| LED | A1 LED ( - ) | A2 LED ( + ) | ||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E2 | F2 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E1 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | J2 | ||
| Potentiometer | B25 | B26 | B27 | |
| Jumper Wire | Analog Pin 0 (A0) | E26 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E25 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E27 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_1B-Potentiometer
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 1B-Potentiometer
Changes how fast an LED connected to pin 13 blinks, based on a potentiometer connected to pin A0
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
int potPosition; //this variable will hold a value based on the position of the potentiometer
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //start a serial connection with the computer
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); //set pin 13 as an output that can be set to HIGH or LOW
}
void loop()
{
//read the position of the pot
potPosition = analogRead(A0); //set potPosition to a number between 0 and 1023 based on how far the knob is turned
Serial.println(potPosition); //print the value of potPosition in the serial monitor on the computer
//change the LED blink speed based on the pot value
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
delay(potPosition); // delay for as many milliseconds as potPosition (0-1023)
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn off the LED
delay(potPosition); // delay for as many milliseconds as potPosition (0-1023)
}
What You Should See
You should see the LED blink faster or slower in accordance with your potentiometer. The delay between each flash will change based on the position of the knob. If it isn't working, make sure you have assembled the circuit correctly and verified and uploaded the code to your board, or see the Troubleshooting section.
Program Overview
- Read the position of the potentiometer (from 0 to 1023) and store it in the variable
potPosition. - Turn the LED on.
- Wait from 0 to 1023 milliseconds, based on the position of the knob and the value of
potPosition. - Turn the LED off.
- Wait from 0 to 1023 milliseconds, based on the position of the knob and the value of
potPosition. - Repeat.
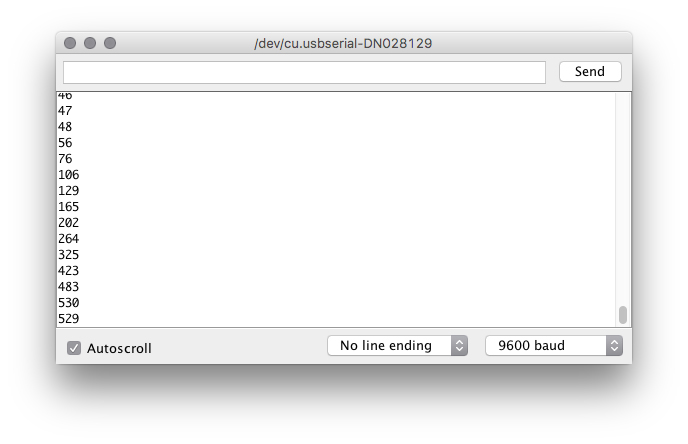
You should then see numeric values print out on the monitor. Turn the potentiometer, and you should see the values change as well as the delay between each print.
If you are having trouble seeing the values, ensure that you have selected 9600 baud in the dropdown menu and have auto scroll checked.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Integer Variables:int potPosition; | A variable is a placeholder for values that may change in your code. You must introduce, or "declare" variables before you use them. Here we're declaring a variable called potPosition of type int (integer). We will cover more types of variables in later circuits. Don't forget that variable names are case-sensitive! |
Serial Begin:Serial.begin(9600); | Serial commands can be used to send and receive data from your computer. This line of code tells the RedBoard that we want to "begin" that communication with the computer, the same way we would say "Hi" to initiate a conversation. Notice that the baud rate, 9600, is the same as the one we selected in the monitor. This is the speed at which the two devices communicate, and it must match on both sides. |
Analog Input:potPosition = analogRead(A0); | We use the analogRead() function to read the value on an analog pin. analogRead() takes one parameter, the analog pin you want to use, A0 in this case, and returns a number between 0 (0 volts) and 1023 (5 volts), which is then assigned to the variable potPosition |
Serial Print:Serial.println(potPosition); | This is the line that actually prints the trimpot value to the monitor. It takes the variable potPosition and prints whatever value it equals at that moment in the loop(). The ln at the end of print tells the monitor to print a new line at the end of each value; otherwise the values would all run together on one line. Try removing the ln to see what happens. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Changing the Range | Try multiplying, dividing or adding to your sensor reading so that you can change the range of the delay in your code. For example, can you multiply the sensor reading so that the delay goes from 0–2046 instead of 0–1023? |
| Adding More LEDs | Add more LEDs to your circuit. Don't forget the current limiting resistor for each one. Try making multiple LEDs blink at different rates by changing the range of each using multiplication or division. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The potentiometer always reads as 0 or 1023 | Make sure that your 5V, A0 and GND pins are properly connected to the three pins on your potentiometer. It is easy to misalign a wire with the actual trimpot pin. |
| No values in Serial Monitor | Make sure that you have selected the correct baud rate, 9600. Also ensure that you are on the correct Serial Port. The same Serial Port you use when uploading code to your board is the same Serial Port you use to print values to the Serial Monitor. |
Circuit 1C: Photoresistor
In circuit 1B, you got to use a potentiometer, which varies resistance based on the twisting of a knob. In this circuit you’ll be using a photoresistor, which changes resistance based on how much light the sensor receives. Using this sensor you can make a simple night-light that turns on when the room gets dark and turns off when it is bright.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
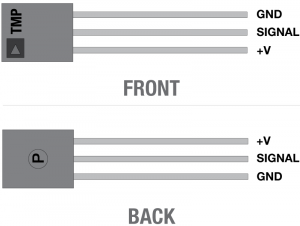
Photoresistor
Photoresistors, or photocells, are light-sensitive, variable resistors. As more light shines on the sensor’s head, the resistance between its two terminals decreases. They’re an easy-to-use component in projects that require ambient-light sensing.
New Concepts
Analog to Digital Conversion
The world we live in is analog, but the RedBoard lives in a digital world. In order to have the RedBoard sense analog signals, we must first pass them through an Analog to Digital Converter (or ADC). The six analog inputs (A0--A5) covered in the last circuit all use an ADC. These pins "sample" the analog signal and create a digital signal for the microcontroller to interpret. The "resolution" of this signal is based on the resolution of the ADC. In the case of the RedBoard, that resolution is 10-bit. With a 10-bit ADC, we get 2 ^ 10 = 1024 possible values, which is why the analog signal varies between 0 and 1023.
Voltage Divider Continued
Since the RedBoard can’t directly interpret resistance (rather, it reads voltage), we need to use a voltage divider to use our photoresistor, a part that doesn't output voltage. The resistance of the photoresistor changes as it gets darker or lighter. That changes the amount of voltage that is read on the analog pin, which "divides" the voltage, 5V in this case. That divided voltage is then read on the analog to digital converter.
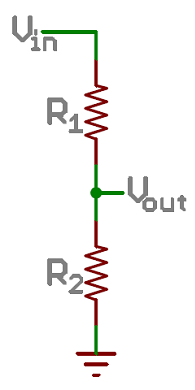

The voltage divider equation assumes that you know three values of the above circuit: the input voltage (Vin), and both resistor values (R1 and R2). Given those values, we can use this equation to find the output voltage (Vout):
If R1 is a constant value (the resistor) and R2 fluctuates (the photoresistor), the amount of voltage measured on the Vout pin will also fluctuate.
Hardware Hookup
Note that the photoresistor is not polarized. It can be inserted in either direction.
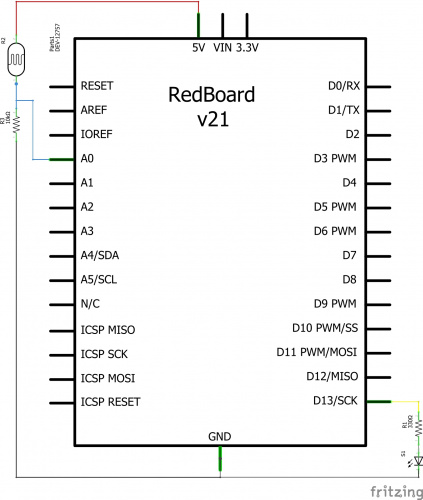
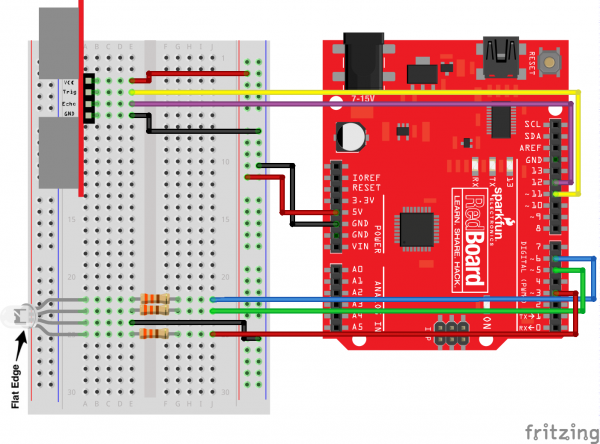
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | |
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | |
| LED | A1 LED ( - ) | A2 LED ( + ) | |
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E2 | F2 | |
| Jumper Wire | E1 | GND Rail ( - ) | |
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | J2 | |
| Photoresistor | A26 | B25 | |
| 10kΩ Resistor (brown, black, orange) |
C26 | D27 | |
| Jumper Wire | Analog Pin 0 (A0) | E26 | |
| Jumper Wire | E25 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |
| Jumper Wire | E27 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_1C-Photoresistor
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 1C-Photoresistor
Use a photoresistor to monitor how bright a room is, and turn an LED on when it gets dark.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
int photoresistor = 0; //this variable will hold a value based on the brightness of the ambient light
int threshold = 750; //if the photoresistor reading is below this value the the light will turn on
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //start a serial connection with the computer
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); //set pin 13 as an output that can be set to HIGH or LOW
}
void loop()
{
//read the brightness of the ambient light
photoresistor = analogRead(A0); //set photoresistor to a number between 0 and 1023 based on how bright the ambient light is
Serial.println(photoresistor); //print the value of photoresistor in the serial monitor on the computer
//if the photoresistor value is below the threshold turn the light on, otherwise turn it off
if (photoresistor < threshold) {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
} else {
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn off the LED
}
delay(100); //short delay to make the printout easier to read
}
What You Should See
The program stores the light level in a variable, photoresistor. Then, using an if/else statement, the program checks to see what it should do with the LED. If the variable is above the threshold (it’s bright), turn the LED off.
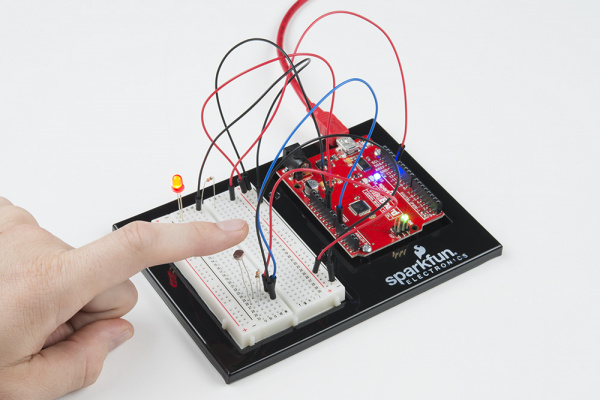
If the variable is below the threshold (it’s dark), turn the LED on. You now have just built your own night-light!
Open the Serial Monitor in Arduino. The value of the photoresistor should be printed every so often. When the photoresistor value drops below the threshold value set in the code, the LED should turn on (you can cover the photoresistor with your finger to make the value drop).
Program Overview
- Store the light level in the variable
photoresistor. - If the value of
photoresistoris above thethreshold(it’s bright), turn the LED off. - If the value of
photoresistoris below thethreshold(it’s dark), turn the LED on.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
If/else Statements:if(logic statement) {code to be run if the logic statement is true}else {code to be run if the logic statement is false
} |
The if/else statement lets your code react to the world by running one set of code when the logic statement in the round brackets is true and another set of code when the logic statement is false. For example, this sketch uses an if statement to turn the LED on when it is dark, and turn the LED off when it is light. |
Logical Operators:(photoresistor < threshold) |
Programmers use logic statements to translate things that happen in the real world into code. Logic statements use logical operators such as 'equal to' (==), 'greater than' (>), and 'less than' (<), to make comparisons. When the comparison is true (e.g., 4 < 5) then the logic statement is true. When the comparison is false (e.g., 5 < 4) then the logic statement is false. This example is asking whether the variable photoresistor is less than the variable threshold. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Response Pattern | Right now your if statement turns the LED on when it gets dark, but you can also use the light sensor like a no-touch button. Try using digitalWrite() and delay() to make the LED blink a pattern when the light level drops, then calibrate the threshold variable in the code so that the blink pattern triggers when you wave your hand over the sensor. |
| Replace 10KΩ Resistor with LED | Alter the circuit be replacing the 10KΩ resistor with an LED (the negative leg should connect to GND). Now what happens when you place your finger over the photoresistor? This is a great way to see Ohm's law in action by visualizing the change in resistance's affect on the current flowing through the LED. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The light never turns on or always stays on | Start the Serial Monitor in Arduino. Look at the value that the photoresistor is reading in a bright room (e.g., 915). Cover the photoresistor, or turn the lights off. Then look at the new value that the photoresistor is reading (e.g., 550). Set the threshold in between these two numbers (e.g., 700) so that the reading is above the threshold when the lights are on and below the threshold when the lights are off. |
| Nothing is printing in the Serial Monitor | Try unplugging your USB cable and plugging it back in. In the Arduino IDE, go to Tools > Port, and make sure that you select the right port. |
Circuit 1D: RGB Night-Light
In this circuit, you'll take the night-light concept to the next level by adding an RGB LED, which is three differently colored Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) built into one component. RGB stands for Red, Green and Blue, and these three colors can be combined to create any color of the rainbow!
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
RGB LED
An RGB LED is actually three small LEDs --- one red, one green and one blue --- inside a normal LED housing. The RGB LED included in this kit has all the internal LEDs share the same ground wire, so there are four legs in total. To turn one color on, ensure ground is connected, then power one of the legs just as you would a regular LED. If you turn on more than one color at a time, you will see the colors start to blend together to form a new color.
New Concepts
Analog Output (Pulse-width Modulation)
You can use the digitalWrite() command to turn pins on the RedBoard on (5V) or off (0V), but what if you want to output 2.5V? The RedBoard doesn't have an Analog Output, but it is really good at switching some digital pins on and off fast enough to simulate an analog output. analogWrite() can output 2.5 volts by quickly switching a pin on and off so that the pin is only on 50 percent of the time (50% of 5V is 2.5V). By changing the percent of time that a pin is on, from 0 percent (always off) to 100 percent (always on), analogWrite() can output any voltage between 0 and 5V. This is what is known as pulse-width modulation (or PWM). By using PWM, you can create many different colors with the RGB LED.
analogWrite() on these pins.
Creating Your Own Simple Functions
When programmers want to use a piece of code over and over again, they write a function. The simplest functions are just chunks of code that you give a name to. When you want to run that code, you can “call” the function by typing its name, instead of writing out all of the code. More complicated functions take and return pieces of information from the program (we call these pieces of information parameters). In this circuit, you'll write functions to turn the RGB LED different colors by just typing that color's name.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Just like a regular LED, an RGB LED is polarized and only allows electricity to flow in one direction. Pay close attention to the flat edge and to the different length leads. Both are indicators to help orient the LED correctly.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGB LED | A5 (RED) | A4 (GND) | A3 (GREEN) | A2 (BLUE) | |
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E2 | F2 | |||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E3 | F3 | |||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E5 | F5 | |||
| Jumper Wire | E4 | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | J5 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | J3 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | J2 | |||
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Potentiometer | B15 | B16 | B17 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Analog Pin 1 (A1) | E16 | |||
| Jumper Wire | E15 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E17 | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Photoresistor | A26 | B25 | |||
| 10kΩ Resistor (brown, black, orange) |
C26 | D27 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Analog Pin 0 (A0) | E26 | |||
| Jumper Wire | E25 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E27 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_1D-RGBNightlight
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 1D-RGB Nightlight
Turns an RGB LED on or off based on the light level read by a photoresistor.
Change colors by turning the potentiometer.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
int photoresistor = A0; //variable for storing the photoresistor value
int potentiometer = A1; //this variable will hold a value based on the position of the knob
int threshold = 700; //if the photoresistor reading is lower than this value the light will turn on
//LEDs are connected to these pins
int RedPin = 9;
int GreenPin = 10;
int BluePin = 11;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //start a serial connection with the computer
//set the LED pins to output
pinMode(RedPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(GreenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BluePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
photoresistor = analogRead(A0); //read the value of the photoresistor
potentiometer = analogRead(A1);
Serial.print("Photoresistor value:");
Serial.print(photoresistor); //print the photoresistor value to the serial monitor
Serial.print(" Potentiometer value:");
Serial.println(potentiometer); //print the potentiometer value to the serial monitor
if (photoresistor < threshold) { //if it's dark (the photoresistor value is below the threshold) turn the LED on
//These nested if statements check for a variety of ranges and
//call different functions based on the current potentiometer value.
//Those functions are found at the bottom of the sketch.
if (potentiometer > 0 && potentiometer <= 150)
red();
if (potentiometer > 150 && potentiometer <= 300)
orange();
if (potentiometer > 300 && potentiometer <= 450)
yellow();
if (potentiometer > 450 && potentiometer <= 600)
green();
if (potentiometer > 600 && potentiometer <= 750)
cyan();
if (potentiometer > 750 && potentiometer <= 900)
blue();
if (potentiometer > 900)
magenta();
}
else { //if it isn't dark turn the LED off
turnOff(); //call the turn off function
}
delay(100); //short delay so that the printout is easier to read
}
void red () {
//set the LED pins to values that make red
analogWrite(RedPin, 100);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 0);
analogWrite(BluePin, 0);
}
void orange () {
//set the LED pins to values that make orange
analogWrite(RedPin, 100);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 50);
analogWrite(BluePin, 0);
}
void yellow () {
//set the LED pins to values that make yellow
analogWrite(RedPin, 100);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 100);
analogWrite(BluePin, 0);
}
void green () {
//set the LED pins to values that make green
analogWrite(RedPin, 0);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 100);
analogWrite(BluePin, 0);
}
void cyan () {
//set the LED pins to values that make cyan
analogWrite(RedPin, 0);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 100);
analogWrite(BluePin, 100);
}
void blue () {
//set the LED pins to values that make blue
analogWrite(RedPin, 0);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 0);
analogWrite(BluePin, 100);
}
void magenta () {
//set the LED pins to values that make magenta
analogWrite(RedPin, 100);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 0);
analogWrite(BluePin, 100);
}
void turnOff () {
//set all three LED pins to 0 or OFF
analogWrite(RedPin, 0);
analogWrite(GreenPin, 0);
analogWrite(BluePin, 0);
}
What You Should See
This sketch is not dissimilar from the last. It reads the value from the photoresistor, compares it to a threshold value, and turns the RGB LED on or off accordingly. This time, however, we've added a potentiometer back into the circuit. When you twist the pot, you should see the color of the RGB LED change based on the pot's value.
Open the Serial Monitor. The value being read by the light sensor should be printed several times a second. When you turn out the lights or cover the sensor, the LED will shine whatever color your programmed in your color function. Next to the light value, you'll see the potentiometer value print out as well.
Program Overview
- Store the light level from pin A0 in the variable
photoresistor. - Store the potentiometer value from pin A1 in the variable
potentiometer. - If the light level variable is above the
threshold, call the function that turns the RGB LED off. - If the light level variable is below the
threshold, call one of the color functions to turn the RGB LED on. - If
potentiometeris between 0 and 150, turn the RGB LED on red. - If
potentiometeris between 151 and 300, turn the RGB LED on orange. - If
potentiometeris between 301 and 450, turn the RGB LED on yellow. - If
potentiometeris between 451 and 600, turn the RGB LED on green. - If
potentiometeris between 601 and 750, turn the RGB LED on cyan. - If
potentiometeris between 751 and 900, turn the RGB LED on blue. - If
potentiometeris greater than 900, turn the RGB LED on magenta.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Analog Output (PWM):analogWrite(RedPin, 100); |
The analogWrite() function outputs a voltage between 0 and 5V on a pin. The function breaks the range between 0 and 5V into 255 little steps. Note that we are not turning the LED on to full brightness (255) in this code so that the night-light is not too bright. Feel free to change these values and see what happens. |
Nested if Statements:if(logic statement) {if(logic statement) {code to be run if the logic statement is true}if(logic statement) {code to be run if the logic statement is true}} |
A nested if statement is one or more if statements "nested" inside of another if statement. If the parent if statement is true, then the code looks at each of the nested if statements and executes any that are true. If the parent if statement is false, then none of the nested statements will execute. |
More Logical Operators:if(potentiometer > 0 && potentiometer <= 150) |
These if statements are checking for two conditions by using the AND (&&) operator. In this line, the if statement will only be true if the value of the variable potentiometer is greater than 0 AND if the value is less than or equal to 150. By using &&, the program allows the LED to have many color states. |
Defining a Function:void function_name () {
code to run inside function
}
|
This simple version of a function executes the code inside the curly brackets whenever the name is written in the main program. |
Calling a Function:function_name();
|
Calls a function that you have created. In a later circuit, you will learn how to make more complicated functions that take data from the main program (these pieces of data are called parameters). |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Add more colors | You can create many more colors with the RGB LED. Use the analogWrite() function to blend different values of red, green and blue together to make even more colors. You can divide the potentiometer value up more and make more nested if statements so that you can have more colors as you twist the knob. |
| Multi color blink | Try using delays and multiple color functions to have your RGB LED change between multiple colors. |
| Change the threshold | Try setting your threshold variable by reading the value of a potentiometer with analogRead(). By turning the potentiometer, you can then change the threshold level and adjust your night-light for different rooms. |
| Fading the LED | Try using a loop with the analogWrite() to get your LED to pulse gently or smoothly transition between colors. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The LED never turns on or off | Open the Serial Monitor in Arduino and make sure that your photoresistor is returning values between 0 and 1023. Try covering the photoresistor; the values should change. If they do not change, check the wiring of the photoresistor.
If your photoresistor is working correctly, make sure that your threshold variable sits in between the value that the photoresistor reads when it is bright and the value that the photoresistor reads when it is dark (e.g., bright = 850, dark = 600, threshold = 700). |
| My LED doesn’t show the colors that I expect | Make sure that all three of the pins driving your RGB LED are set to OUTPUT, using the pinMode() command in the setup section of the code. Then make sure that each LED is wired properly. |
| Nothing is printing in the Serial Monitor | Try unplugging your USB cable and plugging it back in. In the Arduino IDE, go to Tools > Port, and make sure that you select the right port. |
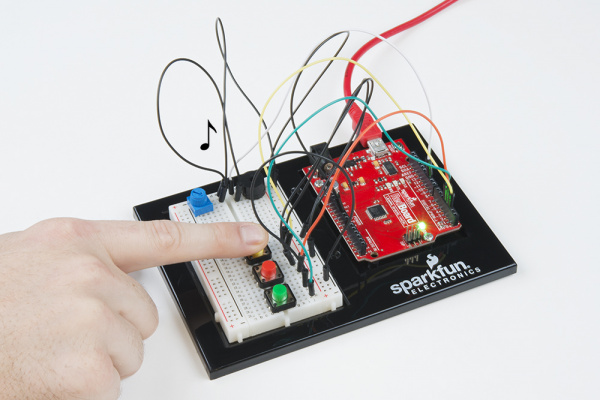
Project 2: Sound
In Project 2, you will venture into the world of buttons and buzzers while building your own Simon Says game! Simon Says is a game in which the LEDs flash a pattern of red, green, yellow and blue blinks, and the user must recreate the pattern using color-coded buttons before the timer runs out.
New Components Introduced in This Project
Each of the components listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- Buzzer
- Buttons
New Concepts Introduced in This Project
Each of the concepts listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- Arrays
- Binary
- Digital Inputs
- Pull-up Resistors
- For Loops
- Measuring Elapsed Time
You Will Learn
- How to make tones with a buzzer
- How to read a button using digital inputs
- How to program a game
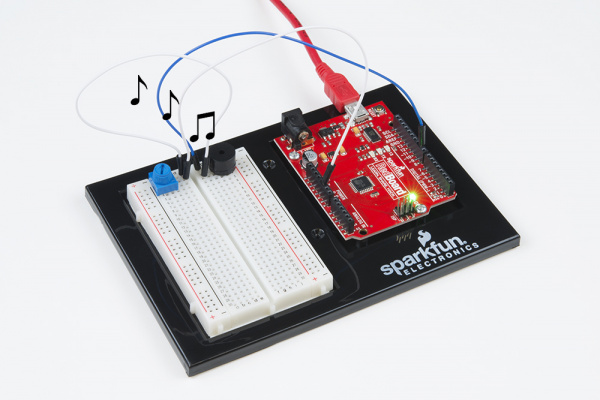
Circuit 2A: Buzzer
In this circuit, you'll use the RedBoard and a small buzzer to make music, and you'll learn how to program your own songs using arrays.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
Buzzer
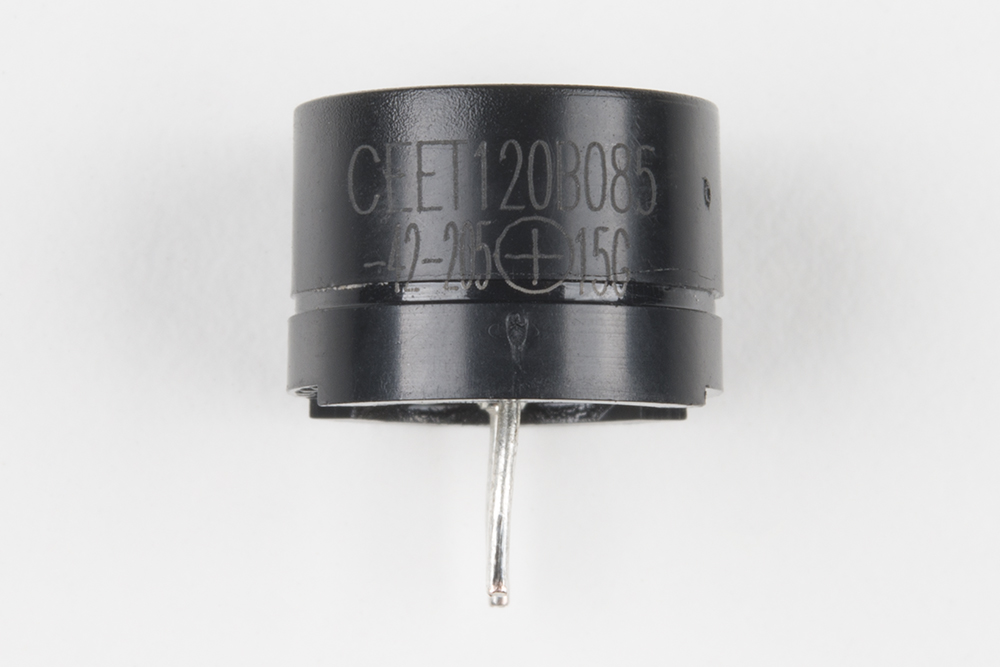
The buzzer uses a small magnetic coil to vibrate a metal disc inside a plastic housing. By pulsing electricity through the coil at different rates, different frequencies (pitches) of sound can be produced. Attaching a potentiometer to the output allows you to limit the amount of current moving through the buzzer and lower its volume.
New Concepts
Reset Button
The RedBoard has a built-in reset button. This button will reset the board and start the code over from the beginning, running what is in setup() and then loop().
Tone Function
To control the buzzer, you will use the tone function. This function is similar to PWM in that it generates a wave that is of a certain frequency on the specified pin. The frequency and duration can both be passed to the tone() function when calling it. To turn the tone off, you need to call noTone() or pass a duration of time for it to play and then stop. Unlike PWM, tone() can be used on any digital pin.
Arrays
Arrays are used like variables, but they can store multiple values. The simplest array is just a list. Imagine that you want to store the frequency for each note of the C major scale. We could make seven variables and assign a frequency to each one, or we could use an array and store all seven in the same array, as shown below. To refer to a specific value in the array, an index number is used. Arrays are indexed from 0. For example, to call the first element in the array, use array_name[0];; to call the second element, use array_name[1]; and so on.
| Musical Note | Frequency (Hz) | Using Variables | Using an Array |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 220 | aFrequency | frequency[0] |
| B | 247 | bFrequency | frequency[1] |
| C | 261 | cFrequency | frequency[2] |
| D | 294 | dFrequency | frequency[3] |
| E | 330 | eFrequency | frequency[4] |
| F | 349 | fFrequency | frequency[5] |
| G | 392 | gFrequency | frequency[6] |
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
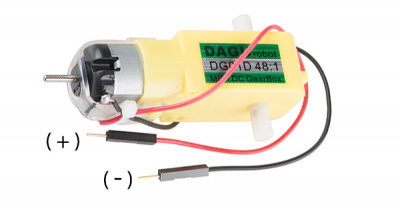
The buzzer is polarized. To see which leg is positive and which is negative, flip the buzzer over and look at the markings underneath. Keep track of which pin is where, as they will be hard to see once inserted into the breadboard. There is also text on the positive side of the buzzer, along with a tiny (+) symbol.


Volume Knob
All of the circuits in Project 2 make use of a potentiometer as a rudimentary volume knob. Notice that only two of the potentiometer's legs are used in these circuits. In these instances, the potentiometer is acting as a variable resistor, limiting the amount of current flowing to the speaker and thus affecting the volume as you turn the knob. This is similar to the current-limiting resistor used to limit current to the LED in circuit 1A --- only this time the resistance is variable.
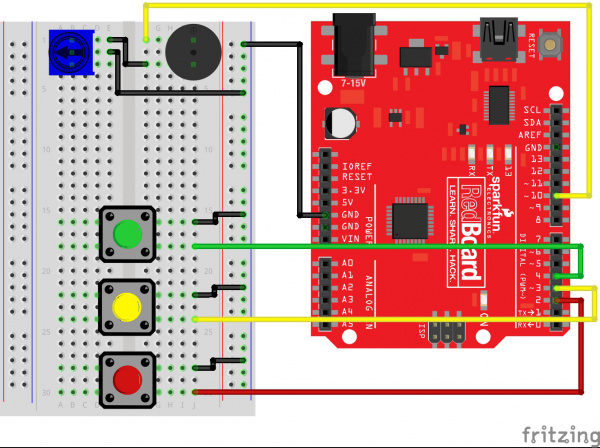
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buzzer | J1 (Buzzer + ) | J3 (Buzzer - ) | ||
| Potentiometer | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | F1 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E2 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E1 | F3 |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_2A-Buzzer
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 2A - Buzzer
Play notes using a buzzer connected to pin 10
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
int speakerPin = 10; //the pin that buzzer is connected to
void setup()
{
pinMode(speakerPin, OUTPUT); //set the output pin for the speaker
}
void loop()
{
play('g', 2); //ha
play('g', 1); //ppy
play('a', 4); //birth
play('g', 4); //day
play('C', 4); //to
play('b', 4); //you
play(' ', 2); //pause for 2 beats
play('g', 2); //ha
play('g', 1); //ppy
play('a', 4); //birth
play('g', 4); //day
play('D', 4); //to
play('C', 4); //you
play(' ', 2); //pause for 2 beats
play('g', 2); //ha
play('g', 1); //ppy
play('G', 4); //birth
play('E', 4); //day
play('C', 4); //dear
play('b', 4); //your
play('a', 6); //name
play(' ', 2); //pause for 2 beats
play('F', 2); //ha
play('F', 1); //ppy
play('E', 4); //birth
play('C', 4); //day
play('D', 4); //to
play('C', 6); //you
while (true) {} //get stuck in this loop forever so that the song only plays once
}
void play( char note, int beats)
{
int numNotes = 14; // number of notes in our note and frequency array (there are 15 values, but arrays start at 0)
//Note: these notes are C major (there are no sharps or flats)
//this array is used to look up the notes
char notes[] = { 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'a', 'b', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'A', 'B', ' '};
//this array matches frequencies with each letter (e.g. the 4th note is 'f', the 4th frequency is 175)
int frequencies[] = {131, 147, 165, 175, 196, 220, 247, 262, 294, 330, 349, 392, 440, 494, 0};
int currentFrequency = 0; //the frequency that we find when we look up a frequency in the arrays
int beatLength = 150; //the length of one beat (changing this will speed up or slow down the tempo of the song)
//look up the frequency that corresponds to the note
for (int i = 0; i < numNotes; i++) // check each value in notes from 0 to 14
{
if (notes[i] == note) // does the letter passed to the play function match the letter in the array?
{
currentFrequency = frequencies[i]; // Yes! Set the current frequency to match that note
}
}
//play the frequency that matched our letter for the number of beats passed to the play function
tone(speakerPin, currentFrequency, beats * beatLength);
delay(beats * beatLength); //wait for the length of the tone so that it has time to play
delay(50); //a little delay between the notes makes the song sound more natural
}
/* CHART OF FREQUENCIES FOR NOTES IN C MAJOR
Note Frequency (Hz)
c 131
d 147
e 165
f 175
g 196
a 220
b 247
C 262
D 294
E 330
F 349
G 392
A 440
B 494
*/
What You Should See
When the program begins, a song will play from the buzzer once. To replay the song, press the reset button on the RedBoard. Use the potentiometer to adjust the volume.
Program Overview
Inside the main loop:
- Play the first note for x number of beats using the play function. a. (Inside the play function:) Take the note passed to the play function and compare it to each letter in the notes array. When you find a note that matches, remember the index position of that note (e.g., 6th entry in the notes array). b. Get a frequency from the frequency array that has the same index as the note that matched (e.g., the 6th frequency). c. Play that frequency for the number of beats passed to the play function.
- Play the second note using the play function
...and so on.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Character Variables:void play( char note, int beats) | The char, or character, variable to store character values. For example, in this sketch, the play() function gets passed two variables, a character variable that represents the mucial note we want to play and an integer variable that represents how long to play that note. A second array takes the character variable and associates a frequency value to it. This makes programming a song easier as you can just reference the character and not the exact frequency. |
Tone Function:tone(pin, frequency, duration); | The tone() function will pulse power to a pin at a specific frequency. The duration controls how long the sound will play. Tone can be used on any digital pin. |
Declaring an Array:arrray_name[array_size]; or arrray_name[] = {array elements}; | To declare an array, you must give it a name, then either tell Arduino how many positions the array will have or assign a list of values to the array. |
Calling an Array:array_name[index #]; | To call one of the values in an array, simply type the name of the array and the index of the value. You can use a variable instead of a number in between the square brackets. Don't forget the index starts at 0, not 1, so to call the first element, use array_name[0];. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the tempo of the song | Experiment with the beatLength; variable to change the tempo of the song. |
| Make your own song | Try changing the notes to make a different song. Spaces " " can be used for rests in the song. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The song is too quiet or too loud | Turn the potentiometer to adjust the volume. |
| No sound is playing | Try pressing the reset button on the RedBoard. If that doesn’t work, check your wiring of the buzzer. It's easy to misalign a pin with a jumper wire. |
Circuit 2B: Digital Trumpet
Learn about digital inputs and buttons as you build your own digital trumpet!
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
Buttons
Buttons, also known as momentary switches, are switches that only remain in their on state as long as they’re being actuated, or pressed. Most often momentary switches are best used for intermittent user-input cases: reset button and keypad buttons. These switches have a nice, tactile, “clicky” feedback when you press them.
Note that the different colors are just aesthetic. All of the buttons included behave the same no matter their color.
New Concepts
Binary Number System
Number systems are the methods we use to represent numbers. We’ve all been mostly operating within the comfy confines of a base-10 number system, but there are many others. The base-2 system, otherwise known as binary, is common when dealing with computers and electronics. There are really only two ways to represent the state of anything: ON or OFF, HIGH or LOW, 1 or 0. And so, almost all electronics rely on a base-2 number system to store and manipulate numbers. The heavy reliance electronics places on binary numbers means it’s important to know how the base-2 number system works.
Digital Input
In circuit 1A, you worked with digital outputs. This circuit focuses on digital inputs. Digital inputs only care if something is in one of two states: TRUE or FALSE, HIGH or LOW, ON or OFF. Digital inputs are great for determining if a button has been pressed or if a switch has been flipped.
Pull-up Resistors
A pull-up resistor is a small circuit that holds the voltage HIGH (5V) on a pin until a button is pressed, pulling the voltage LOW (0V). The most common place you will see a pull-up resistor is when working with buttons. A pull-up resistor keeps the button in one state until it is pressed. The RedBoard has built-in pull-up resistors, but they can also be added to a circuit externally. This circuit uses the internal pull-up resistors, covered in more detail in the Code to Note section.
Hardware Hookup
Buttons are not polarized. However, they do merit a closer look. Buttons make momentary contact from one connection to another, so why are there four legs on each button? The answer is to provide more stability and support to the buttons in your breadboard circuit. Each row of legs is connected internally. When the button is pressed, one row connects to the other, making a connection between all four pins.
If the button's legs don't line up with the slots on the breadboard, rotate it 90 degrees.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buzzer | J1 (Buzzer + ) | J3 (Buzzer - ) | ||
| Potentiometer | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | F1 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E2 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E1 | F3 | ||
| Push Button | D16/D18 | G16/G18 | ||
| Push Button | D22/D24 | G22/G24 | ||
| Push Button | D28/D30 | G28/G30 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 4 | J18 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 3 | J24 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 2 | J30 | ||
| Jumper Wire | J16 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | J22 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | J28 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_2B-ButtonTrumpet
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 2B-ButtonTrumpet
Use 3 buttons plugged to play musical notes on a buzzer.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
//set the pins for the button and buzzer
int firstKeyPin = 2;
int secondKeyPin = 3;
int thirdKeyPin = 4;
int buzzerPin = 10;
void setup() {
//set the button pins as inputs
pinMode(firstKeyPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(secondKeyPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(thirdKeyPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
//set the buzzer pin as an output
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(firstKeyPin) == LOW) { //if the first key is pressed
tone(buzzerPin, 262); //play the frequency for c
}
else if (digitalRead(secondKeyPin) == LOW) { //if the second key is pressed
tone(buzzerPin, 330); //play the frequency for e
}
else if (digitalRead(thirdKeyPin) == LOW) { //if the third key is pressed
tone(buzzerPin, 392); //play the frequency for g
}
else {
noTone(buzzerPin); //if no key is pressed turn the buzzer off
}
}
/*
note frequency
c 262 Hz
d 294 Hz
e 330 Hz
f 349 Hz
g 392 Hz
a 440 Hz
b 494 Hz
C 523 Hz
*/
What You Should See
Different tones will play when you press different keys. Turning the potentiometer will adjust the volume.
Program Overview
- Check to see if the first button is pressed. a. If it is, play the frequency for c. b. If it isn’t, skip to the next else if statement.
- Check to see if the second button is pressed. a. If it is, play the frequency for e. b. If it isn’t, skip to the next else if statement.
- Check to see if the second button is pressed. a. If it is, play the frequency for g. b. If it isn’t, skip to the next else if statement.
- If none of the if statements are true a. Turn the buzzer off.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Internal Pull-Up Resistor:pinMode(firstKeyPin, INPUT_PULLUP); | To declare a standard input, use the line pinMode(pin_name, INPUT). If you would like to use one of the RedBoard's built-in pull-up 20kΩ resistors, it would look like this: pinMode(firstKeyPin, INPUT_PULLUP);. The advantage of external pull-ups is being able to choose a more exact value for the resistor. |
Digital Input:digitalRead(pin); | Check to see if an input pin is reading HIGH (5V) or LOW (0V). Returns TRUE (1) or FALSE (0) depending on the reading. |
Is Equal to:if(digitalRead(firstKeyPin) == LOW) | This is another logical operator. The 'is equal to' symbol (==) can be confusing. Two equals signs are equivalent to asking, "Are these two values equal to one another?" On the other hand, one equals sign in code is assigning a particular variable to a value. Don't forget to add the second equals sign if you are comparing two values. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the key of each button | Use the frequency table in the comment section at the end of the code to change the notes that each button plays. |
| Play more than three notes with if statements | By using combinations of buttons, you can play up to seven notes of the scale. You can do this in a few ways. To get more practice with if statements, try adding seven if statements and using the Boolean AND (&&) operator to represent all of the combinations of keys. |
| Play more than three notes with binary math | You can use a clever math equation to play more than three notes with your three keys. By multiplying each key by a different number, then adding up all of these numbers, you can make a math equation that produces a different number for each combination of keys. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The buzzer is too loud or too quiet | Turn the potentiometer to adjust the volume. |
| The RedBoard thinks one key is always pressed | Check your wiring. You may have ground and 5V backward if one or more buttons behave as though they're pressed all the time. |
| The buttons are not working | First, make sure that the wiring is correct. It is easy to misalign a wire with a button leg. Second, make sure that you have declared your buttons as inputs and have enabled the internal pull-up resistors with INPUT_PULLUP. |
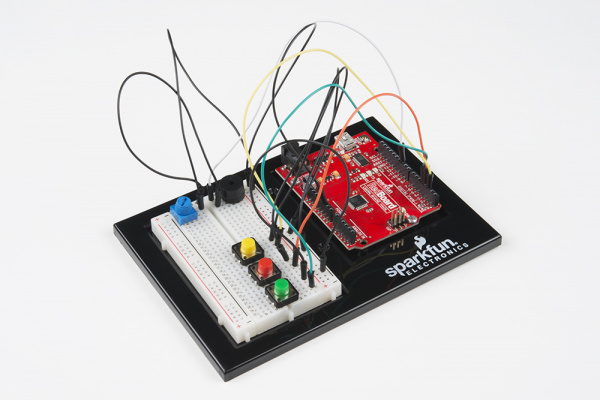
Circuit 2C: Simon Says Game
The Simon Says game uses LEDs to flash a pattern, which the player must remember and repeat using four buttons. The classic Simon) game has been a hit since the 1980s. Now you can build your own!
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Concepts
For Loops
For loops repeat a section of code a set number of times. The loop works by using a counter (usually programmers use the letter “i” for this variable) that increases each loop until it reaches a stop value. Here’s an example of a simple for loop:
language:c
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
Serial.print(i);
}
The for loop takes three parameters in the brackets, separated by semicolons. The first parameter is the start value. In this case, integer i starts at 0. The second value is the stop condition. In this case, we stop the loop when i is no longer less than 5 (i < 5 is no longer true). The final parameter is an increment value. i++ is shorthand for increase i by 1 each time, but you could also increase i by different amounts. This loop would repeat five times. Each time it would run the code in between the brackets, which prints the value of i to the serial monitor.
Measuring Durations of Time With millis()
The RedBoard has a built-in clock that keeps accurate time. You can use the millis() command to see how many milliseconds have passed since the RedBoard was last powered. By storing the time when an event happens and then subtracting the current time, you can measure the number of milliseconds (and thus seconds) that have passed. This sketch uses this function to set a time limit for repeating the pattern.
Custom Functions
This sketch uses several user-defined functions. These functions perform operations that are needed many times in the program (for example, reading which button is currently pressed or turning all of the LEDs off). Functions are essential to make more complex programs readable and compact.
Hardware Hookup
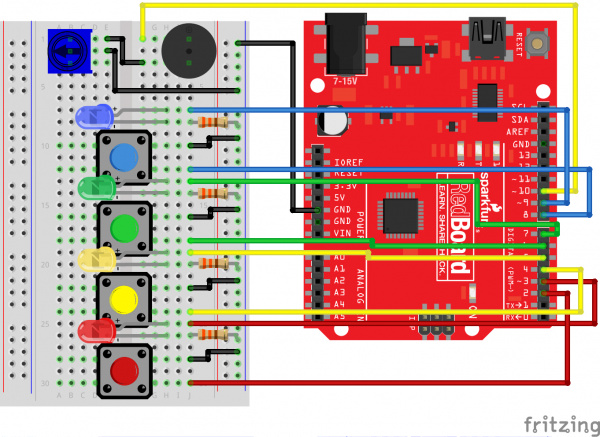
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buzzer | J1 (Buzzer + ) | J3 (Buzzer - ) | ||
| Potentiometer | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | F1 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E2 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E1 | F3 | ||
| Push Button | D10/D12 | G10/G12 | ||
| Push Button | D16/D18 | G16/G18 | ||
| Push Button | D22/D24 | G22/G24 | ||
| Push Button | D28/D30 | G28/G30 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 8 | J12 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 6 | J18 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 4 | J24 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 2 | J30 | ||
| Jumper Wire | J10 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | J16 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | J22 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | J28 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Blue LED | H7 LED ( + ) | H8 LED ( - ) | ||
| Green LED | H13 LED ( + ) | H14 LED ( - ) | ||
| Yellow LED | H19 LED ( + ) | H20 LED ( - ) | ||
| Red LED | H25 LED ( + ) | H26 LED ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | J7 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 7 | J13 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 5 | J19 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 3 | J25 | ||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
J8 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
J14 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
j20 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
J26 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_2C-SimonSays
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 2C-Simon Says
The Simon Says game flashes a pattern using LED lights, then the player must repeat the pattern.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
//set the pins where the buttons, LEDs and buzzer connect
int button[] = {2, 4, 6, 8}; //red is button[0], yellow is button[1], green is button[2], blue is button[3]
int led[] = {3, 5, 7, 9}; //red is led[0], yellow is led[1], green is led[2], blue is led[3]
int tones[] = {262, 330, 392, 494}; //tones to play with each button (c, e, g, b)
int roundsToWin = 10; //number of rounds the player has to play before they win the game (the array can only hold up to 16 rounds)
int buttonSequence[16]; //make an array of numbers that will be the sequence that the player needs to remember
int buzzerPin = 10; //pin that the buzzer is connected to
int pressedButton = 4; //a variable to remember which button is being pressed. 4 is the value if no button is being pressed.
int roundCounter = 1; //keeps track of what round the player is on
long startTime = 0; //timer variable for time limit on button press
long timeLimit = 2000; //time limit to hit a button
boolean gameStarted = false; //variable to tell the game whether or not to play the start sequence
void setup() {
//set all of the button pins to input_pullup (use the built-in pull-up resistors)
pinMode(button[0], INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(button[1], INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(button[2], INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(button[3], INPUT_PULLUP);
//set all of the LED pins to output
pinMode(led[0], OUTPUT);
pinMode(led[1], OUTPUT);
pinMode(led[2], OUTPUT);
pinMode(led[3], OUTPUT);
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT); //set the buzzer pin to output
}
void loop() {
if (gameStarted == false) { //if the game hasn't started yet
startSequence(); //flash the start sequence
roundCounter = 0; //reset the round counter
delay(1500); //wait a second and a half
gameStarted = true; //set gameStarted to true so that this sequence doesn't start again
}
//each round, start by flashing out the sequence to be repeated
for (int i = 0; i <= roundCounter; i++) { //go through the array up to the current round number
flashLED(buttonSequence[i]); //turn on the LED for that array position and play the sound
delay(200); //wait
allLEDoff(); //turn all of the LEDs off
delay(200);
}
//then start going through the sequence one at a time and see if the user presses the correct button
for (int i = 0; i <= roundCounter; i++) { //for each button to be pressed in the sequence
startTime = millis(); //record the start time
while (gameStarted == true) { //loop until the player presses a button or the time limit is up (the time limit check is in an if statement)
pressedButton = buttonCheck(); //every loop check to see which button is pressed
if (pressedButton < 4) { //if a button is pressed... (4 means that no button is pressed)
flashLED(pressedButton); //flash the LED for the button that was pressed
if (pressedButton == buttonSequence[i]) { //if the button matches the button in the sequence
delay(250); //leave the LED light on for a moment
allLEDoff(); //then turn off all of the lights and
break; //end the while loop (this will go to the next number in the for loop)
} else { //if the button doesn't match the button in the sequence
loseSequence(); //play the lose sequence (the loose sequence stops the program)
break; //when the program gets back from the lose sequence, break the while loop so that the game can start over
}
} else { //if no button is pressed
allLEDoff(); //turn all the LEDs off
}
//check to see if the time limit is up
if (millis() - startTime > timeLimit) { //if the time limit is up
loseSequence(); //play the lose sequence
break; //when the program gets back from the lose sequence, break the while loop so that the game can start over
}
}
}
if (gameStarted == true) {
roundCounter = roundCounter + 1; //increase the round number by 1
if (roundCounter >= roundsToWin) { //if the player has gotten to the 16th round
winSequence(); //play the winning song
}
delay(500); //wait for half a second between rounds
}
}
//----------FUNCTIONS------------
//FLASH LED
void flashLED (int ledNumber) {
digitalWrite(led[ledNumber], HIGH);
tone(buzzerPin, tones[ledNumber]);
}
//TURN ALL LEDS OFF
void allLEDoff () {
//turn all the LEDs off
digitalWrite(led[0], LOW);
digitalWrite(led[1], LOW);
digitalWrite(led[2], LOW);
digitalWrite(led[3], LOW);
//turn the buzzer off
noTone(buzzerPin);
}
//CHECK WHICH BUTTON IS PRESSED
int buttonCheck() {
//check if any buttons are being pressed
if (digitalRead(button[0]) == LOW) {
return 0;
} else if (digitalRead(button[1]) == LOW) {
return 1;
} else if (digitalRead(button[2]) == LOW) {
return 2;
} else if (digitalRead(button[3]) == LOW) {
return 3;
} else {
return 4; //this will be the value for no button being pressed
}
}
//START SEQUENCE
void startSequence() {
randomSeed(analogRead(A0)); //make sure the random numbers are really random
//populate the buttonSequence array with random numbers from 0 to 3
for (int i = 0; i <= roundsToWin; i++) {
buttonSequence[i] = round(random(0, 4));
}
//flash all of the LEDs when the game starts
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
tone(buzzerPin, tones[i], 200); //play one of the 4 tones
//turn all of the leds on
digitalWrite(led[0], HIGH);
digitalWrite(led[1], HIGH);
digitalWrite(led[2], HIGH);
digitalWrite(led[3], HIGH);
delay(100); //wait for a moment
//turn all of the leds off
digitalWrite(led[0], LOW);
digitalWrite(led[1], LOW);
digitalWrite(led[2], LOW);
digitalWrite(led[3], LOW);
delay(100); //wait for a moment
} //this will repeat 4 times
}
//WIN SEQUENCE
void winSequence() {
//turn all the LEDs on
for (int j = 0; j <= 3; j++) {
digitalWrite(led[j], HIGH);
}
//play the 1Up noise
tone(buzzerPin, 1318, 150); //E6
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 1567, 150); //G6
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 2637, 150); //E7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 2093, 150); //C7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 2349, 150); //D7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 3135, 500); //G7
delay(500);
//wait until a button is pressed
do {
pressedButton = buttonCheck();
} while (pressedButton > 3);
delay(100);
gameStarted = false; //reset the game so that the start sequence will play again.
}
//LOSE SEQUENCE
void loseSequence() {
//turn all the LEDs on
for (int j = 0; j <= 3; j++) {
digitalWrite(led[j], HIGH);
}
//play the 1Up noise
tone(buzzerPin, 130, 250); //E6
delay(275);
tone(buzzerPin, 73, 250); //G6
delay(275);
tone(buzzerPin, 65, 150); //E7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 98, 500); //C7
delay(500);
//wait until a button is pressed
do {
pressedButton = buttonCheck();
} while (pressedButton > 3);
delay(200);
gameStarted = false; //reset the game so that the start sequence will play again.
}
What You Should See
The circuit will flash all of the LEDs and play a melody. After a few seconds, it will flash the first light in the pattern. If you repeat the pattern correctly by pressing the corresponding colored button, then the game will move to the next round and add another color to the pattern sequence. If you make a mistake, the loss melody will play. If you get to round 10, the win melody will play. Press any button to start a new game.
Program Overview
- Check if a new game is starting. If it is, play the start sequence. Reset the counter that keeps track of rounds, and randomly generate a sequence of numbers from 0 to 3 that control which LEDs the user will have to remember.
- The game works in rounds that progress from 0 to 10. Each round the game will flash LEDs in a pattern, then the player has to recreate the pattern by pressing the button(s) that match the LED(s). In the first round, one LED will flash, and the player will have to press one button. In the eighth round, eight LEDs will flash, and the player will have to press eight buttons.
- Use a loop to flash LEDs from the sequence until you have flashed the number of LEDs that matches the round number (1 for round 1, 2 for round 2, etc).
- Start a timer, and wait for the player to press a button. The player has 1.5 seconds to press the correct button. a. If the time limit runs out before a button is pressed, the player loses. b. If the player presses the wrong button, the player loses. c. If the player presses the right button, move on to the next number in the sequence. d. Repeat this process until the player has lost or correctly repeated the sequence for this round.
- If the player repeats the entire sequence for that round. Increase the round number by one (this will add one extra item to the end of the pattern). Then go back to step 3.
- Keep incrementing the round until the player loses or the player finishes 10 rounds. If the player finishes 10 rounds, play the winning sequence.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Elapsed Time:millis(); | The millis function returns the number of milliseconds that have passed since the RedBoard was last turned on. |
Boolean Variables:boolean variable_name; | The name for these variables comes from Boolean logic. The Boolean variable type only has two values: 1 or 0, HIGH or LOW, TRUE or FALSE. Using Boolean variables helps save memory on your microcontroller if you only need to know if something is true or false. Space in your microcontroller's memory is reserved when a variable is declared. How much memory is reserved depends on the type of variable. |
Storing pin numbers in Arrays:int led[] = {3,5,7,9}; | Sometimes you will want to cycle through all of the LEDs or buttons connected to a project. You can do this by storing a sequence of pin numbers in an array. The advantage of having pins in an array instead of a sequence of variables is that you can use a loop to easily cycle through each pin. |
| User Functions | Description |
flashLED(# for LED to flash); | This turns one of the four LEDs on and plays the tone associated with it. 0 = Red, 1 = Yellow, 2 = Green, 3 = Blue. |
allLEDoff(); | Turns all four LEDs off. |
buttonCheck(); | Uses digitalRead() to check which button is pressed. Returns 0, 1, 2 or 3 if one of the buttons is pressed. Returns 4 if no button is pressed.
|
startSequence(); | Flashes the LEDs and plays tones in a sequence. Resets the round counter and generates a new random sequence for the user to remember. |
winSequence(); | Plays a sequence of tones, turns all of the LEDs on, then waits for the player to press a button. If a button is pressed, restarts the game. |
loseSequence(); | Plays a sequence of tones, turns all of the LEDs on, then waits for the player to press a button. If a button is pressed, restarts the game. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the difficulty of the game | Change the difficulty of the game by changing how fast the player has to press each button or by increasing or decreasing the number of rounds needed to win.
Note that if you increase the number of rounds to be larger than 16, you will need to change the size of the “buttonSequence” array (it is set at the top of the code in a line that looks like this: int buttonSequence[16];.
|
| Change the sound effects | Try changing the sequence of notes that play when you start, win or lose the game. |
| 2-Player mode | Ready for a real coding challenge? Try changing the code so that two players can play head-to-head. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| One of the LEDs isn’t lighting up | Make sure your LED is flipped around in the right direction. If the LED still doesn’t work, try wiggling the resistor and the wires that connect to the LED. |
| The buzzer is too loud or too quiet | Turn the potentiometer to adjust the volume |
| One of the buttons isn’t working | Carefully check your wiring for each button. One leg of the button should connect to a pin on the RedBoard; the other leg should connect to the ground rail on the breadboard. |
| None of the buttons or LEDs is working | Make sure you don't have 5V and GND mixed up. Double check that you have a GND connection from the RedBoard to the GND rail on the breadboard. |
| Still not working? | Jumper wires unfortunately can go "bad" from getting bent too much. The copper wire inside can break, leaving an open connection in your circuit. If you are certain that your circuit is wired correctly and that your code is error-free and uploaded, but you are still encountering issues, try replacing one or more of the jumper wires for the component that is not working. |
Project 3: Motion
Tired of your cat walking all over the kitchen counter? How about the dog getting into the garbage? Need a way to stop your little brother from sneaking into your bedroom? Learn how to protect against all of these annoyances as you build a multipurpose alarm. The alarm detects distance and motion using an ultrasonic distance sensor, and creates motion using a servo motor.
New Components Introduced in This Project
Each of the components listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- Servo Motor
- Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
New Concepts Introduced in This Project
Each of the concepts listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- PWM Duty Cycle
- Arduino Libraries
- Objects and Methods
- Datasheets
- Digital Sensors
- Servo Mechanisms
You Will Learn
- How to control a servo motor
- How to use an ultrasonic distance sensor
- How to move objects using servo mechanisms
Circuit 3A: Servo Motors
In this circuit, you will learn how to wire a servo and control it with code. Servo motors can be told to move to a specific position and stay there. Low-cost servo motors were originally used to steer remote-controlled airplanes and cars, but they have become popular for any project where precise movement is needed.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
Additional Materials
- Scissors (NOT INCLUDED)
New Components
Servo Motors
Regular DC motors have two wires. When you hook the wires up to power, the motor spins around and around. Servo motors, on the other hand, have three wires: one for power, one for ground and one for signal. When you send the right signal through the signal wire, the servo will move to a specific angle and stay there. Common servos rotate over a range of 0° to 180°. The signal that is sent is a PWM signal, the same used to control the RGB LED in Project 1.
New Concepts
Duty Cycle
The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) hardware available on a microcontroller is a great way to generate servo control signals. When talking about how long a PWM signal is on, this is referred to as duty cycle. Duty cycle is measured in percentage. The percentage of duty cycle specifically describes the percentage of time a digital signal is on over an interval or period of time. The variation in the duty cycle tells the servo which position to go to in its rotation.
Arduino Libraries
Writing code that sends precise PWM signals to the servo would be time consuming and would require a lot more knowledge about the servo. Luckily, the Arduino IDE has hundreds of built-in and user-submitted containers of code that are called libraries. One of the built-in libraries, the Servo Library, allows us to control a servo with just a few lines of code!
To use one of the built-in Arduino libraries, all you have to do is "include" a link to its header file. A header file is a smaller code file that contains definitions for all the functions used in that library. By adding a link to the header file in your code, you are enabling your code to use all of those library functions. To use the Servo Library, you would add the following line to the top of your sketch.
language:cpp
#include <Servo.h>
Objects and Methods
To use the Servo Library, you will have to start by creating a servo object, like this:
language:cpp
Servo myServo;
Objects look a lot like variables, but they can do much more. Objects can store values, and they can have their own functions, which are called methods.
The most used method that a servo object has is .write().
language:cpp
myServo.write(90);
The write method takes one parameter, a number from 0 to 180, and moves the servo arm to the specified position (in this case, degree 90).
Why would we want to go to the trouble of making an object and a method instead of just sending a servo control signal directly over a pin? First, the servo object does the work of translating our desired position into a signal that the servo can read. Second, using objects makes it easy for us to add and control more than one servo.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Servo motor connectors are polarized, but there is no place to attach them directly. Instead, connect three jumper wires to the female 3-pin header on the servo. This will make it so you can connect the servo to the breadboard.
The servo wires are color coded to make hookup simple. The pin-out is as follows:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| White | Signal - PWM In |
| Red | Power (5V) |
| Black | Ground (GND) |
Included with your servo motor you will find a variety of motor mounts that connect to the shaft of your servo. You may choose to attach any mount you wish for this circuit. It will serve as a visual aid, making it easier to see the servo spin. The mounts will also come in handy at the end of this project.
Affix the Servo (optional)
Included in your SIK is a strip of Dual Lock™. Cut a piece off the strip that is about ⅝ inch or 1.6cm. Then cut that strip in half to get two pieces that are roughly ⅝ inch x 1/2 inch or 1.6cm x 1.3cm.
Peel off the adhesive backing, and stick one half on the bottom of the servo motor.
Stick the other half anywhere on the breadboard baseplate you want. Firmly press the bottom of the servo to the baseplate to temporarily adhere the two pieces of Dual Lock together. This will help stabilize the servo motor as it moves about.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the Fritzing diagram below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Servo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potentiometer | B1 | B2 | B3 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Analog Pin 0 | E2 | |||
| Jumper Wire | E1 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E3 | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | White Servo Pin | |||
| Jumper Wire | 5V Rail ( + ) | Red Servo Pin | |||
| Jumper Wire | GND Rail ( - ) | Black Servo Pin |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_3A-Servo.
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 3A-Servo
Move a servo attached to pin 9 so that it's angle matches a potentiometer attached to A0.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
#include <Servo.h> //include the servo library
int potPosition; //this variable will store the position of the potentiometer
int servoPosition; //the servo will move to this position
Servo myservo; //create a servo object
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); //tell the servo object that its servo is plugged into pin 9
}
void loop() {
potPosition = analogRead(A0); //use analog read to measure the position of the potentiometer (0-1023)
servoPosition = map(potPosition, 0, 1023, 20, 160); //convert the potentiometer number to a servo position from 20-160
//Note: its best to avoid driving the little SIK servos all the
//way to 0 or 180 degrees it can cause the motor to jitter, which is bad for the servo.
myservo.write(servoPosition); //move the servo to the 10 degree position
}
What You Should See
Turning the potentiometer will cause the servo to turn.
Program Overview
- Read the value of the potentiometer.
- Convert the potentiometer value (0--1023) to an angle (20--160).
- Tell the servo to go to this angle.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Including Libraries:#include <Servo.h> |
The #include command adds a library to your Arduino program. After you include a library, you can use the commands in the library in your program. This line adds the Servo library. |
Creating Servo Objects:Servo myServo; |
The Servo command creates a new servo object and assigns a name to it, myServo in this case. If you make more than one servo object, you will need to give them different names. |
Servo Attach:myServo.attach(9); |
The .attach() method tells the servo object to which pin the signal wire of its servo is attached. It will send position signals to this pin. In this sketch, pin 9 is used. Remember to only use digital pins that are capable of PWM. |
Range Mapping:map(potPosition, 0,1023,20,160); |
As shown in previous circuits, the analog pin values on your microcontroller vary from 0-1023. However, what if we want those values to control a servo motor that only accepts a value from 0-180? The answer is to use the map function. The map() function takes a range of values and outputs a different range of values that can contain more or less values than the original. In this case, we are taking the range 0-1023 and mapping it to the range 20-160. |
Servo Write:myServo.write(90); |
The .write() method moves the servo to a specified angle. In this example, the servo is being told to go to angle 90. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Reverse the direction | Try making the servo move in the opposite direction to the potentiometer. |
| Change the range | Try altering the map function so that moving the potentiometer a lot only moves the servo a little. |
| Swap in a different sensor | Try swapping a light sensor in for the potentiometer. You have just made a dial that reads how much light is present! |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The servo doesn’t move | Check the wiring on your servo. Make sure that the red wire on the servo cord is connected to 5V, the black wire is connected to GND and the white signal wire is connected to pin 9. |
| The servo is twitching | Although these servos are supposed to move from 0 to 180 degrees, sometimes sending them to the extremes of their range causes them to twitch (the servo is trying to move farther than it can). Make sure that you aren’t telling the servo to move outside of the 20-160 degree range. |
Circuit 3B: Distance Sensor
Distance sensors are amazing tools with all kinds of uses. They can sense the presence of an object, they can be used in experiments to calculate speed and acceleration, and they can be used in robotics to avoid obstacles. This circuit will walk you through the basics of using an ultrasonic distance sensor, which measures distance using sound waves!
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
Distance sensors work by sending pulses of light or sound out from a transmitter, then timing how long it takes for the signals to bounce off an object and return to a receiver (just like sonar). Some sensors use infrared light, some use lasers, and some, like the HC-SR04 included in your kit, use ultrasonic sound (sound so high-pitched that you can’t hear it).
New Concepts
Datasheets
When working with electronics, datasheets are your best friend. Datasheets contain all the relevant information needed to get you up and running with a part. In this circuit, we are calculating distance based on the time it takes sound waves to be transmitted, bounce off an object and then be received. But, how can we tell distance from that information? The answer lies in the datasheet for the distance sensor. In it, you can find the equation the program needs to interpret distance from the time it takes the sound wave to travel.
Else If Statement
In the night-light circuit, you used an if/else statement to run one set of code when a logic statement was true, and a different set of code when it was false. What if you wanted to have more than two options? Else if statements let you run as many logical tests as you want in one if statement. For example, in the code for this circuit, there is an if statement that flows like this:
- If the distance is less than 10, make the RGB LED red.
- Else if the distance is more than 10 but less than 20, make the RGB LED yellow.
- Else make the RGB LED green.
If you wanted to have four or five colors for different distances, you could add more else if statements.
Else if statements are different from nested if statements in that only one of the statements above can be true, whereas you could have multiple nested if statements that could true.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
The distance sensor is polarized. Take note of the pin labels when connecting your circuit.
The following table describes the function of each pin on the distance sensor:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power (5V) |
| Trig | Trigger Pulse Input: Sends bursts of ultrasound at 40kHz. |
| Echo | Echo Pulse Output: Receives echo signal. Range is calculated by the proportion of trigger signal sent and echo signal received. |
| GND | Ground (0V) |
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the Fritzing diagram below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| RGB LED | A25 (RED) | A24 (GND) | A23 (GREEN) | A22 (BLUE) | |
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E22 | F22 | |||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E23 | F23 | |||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E25 | F25 | |||
| Jumper Wire | E24 | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 3 | J25 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 5 | J23 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 6 | J22 | |||
| Distance Sensor | A3 (Vcc) | A4 (Trig) | A5 (Echo) | A6 (GND) | |
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | E4 (Trig) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | E5 (Echo) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E3 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E6 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_3B-DistanceSensor
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 3B-Distance Sensor
Control the color of an RGB LED using an ultrasonic distance sensor.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
const int trigPin = 11; //connects to the trigger pin on the distance sensor
const int echoPin = 12; //connects to the echo pin on the distance sensor
const int redPin = 3; //pin to control the red LED inside the RGB LED
const int greenPin = 5; //pin to control the green LED inside the RGB LED
const int bluePin = 6; //pin to control the blue LED inside the RGB LED
float distance = 0; //stores the distance measured by the distance sensor
void setup()
{
Serial.begin (9600); //set up a serial connection with the computer
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); //the trigger pin will output pulses of electricity
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); //the echo pin will measure the duration of pulses coming back from the distance sensor
//set the RGB LED pins to output
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
distance = getDistance(); //variable to store the distance measured by the sensor
Serial.print(distance); //print the distance that was measured
Serial.println(" in"); //print units after the distance
if (distance <= 10) { //if the object is close
//make the RGB LED red
analogWrite(redPin, 255);
analogWrite(greenPin, 0);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
} else if (10 < distance && distance < 20) { //if the object is a medium distance
//make the RGB LED yellow
analogWrite(redPin, 255);
analogWrite(greenPin, 50);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
} else { //if the object is far away
//make the RGB LED green
analogWrite(redPin, 0);
analogWrite(greenPin, 255);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
}
delay(50); //delay 50ms between each reading
}
//------------------FUNCTIONS-------------------------------
//RETURNS THE DISTANCE MEASURED BY THE HC-SR04 DISTANCE SENSOR
float getDistance()
{
float echoTime; //variable to store the time it takes for a ping to bounce off an object
float calculatedDistance; //variable to store the distance calculated from the echo time
//send out an ultrasonic pulse that's 10ms long
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
echoTime = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); //use the pulsein command to see how long it takes for the
//pulse to bounce back to the sensor
calculatedDistance = echoTime / 148.0; //calculate the distance of the object that reflected the pulse (half the bounce time multiplied by the speed of sound)
return calculatedDistance; //send back the distance that was calculated
}
What You Should See
Move your hand or a large, flat object closer and farther away from the distance sensor. As the object approaches, the light will change from green to yellow to red.
Open the Serial Monitor, and you should see the distance printed to the window.
Program Overview
- Check what distance the sensor is reading. a. If the distance is less than 10 inches, make the RGB LED red. b. If the distance is between 10 and 20 inches, make the RGB LED yellow. c. If the distance value is not equal to the fist two conditions, make the RGB LED green.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Float Variables:float echoTime; |
The float variable, short for floating-point number, is similar to an integer except it can represent numbers that contain a decimal point. Floats are good for representing values that need to be more precise than an int. Floats allow us to measure precise distances such as 9.33 inches instead of just 9 inches. |
Else if Statement:if(logic statement){else(default logic statement){ |
Else if statements let you combine more than one logic statement. Arduino will test each logic statement in order; if one is true it will run the code in that section and then skip all of the other sections of code in the if statement. |
User-Defined Function:getDistance(); |
This function tells the distance sensor to send out an ultrasonic wave form, measures the time it takes to bounce back to the sensor, then calculates the distance based on the speed of sound. This calculation is based off information found in the distance sensor's datasheet. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the limits of the distance sensor | Try editing the values in the logic statements so that the RGB LED changes color at different distances. |
| Change the units of the distance sensor | Try editing the code so that the distance sensor outputs a different unit of length, such as centimeters or feet. |
| Add a fourth color | Try adding another else if statement so that there are four different colors instead of three. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The RGB LED colors aren't working or a color is missing | Check the connection for the wire and resistor connected to each leg of the LED. Ensure the RGB LED is inserted in the correct orientation. |
| The distance sensor doesn’t seem to work | Open up the serial monitor on your computer. You should see a stream of distances being printed in the monitor. If they are all reading 0 or jump around, then check the wiring on your sensor. |
| The distance sensor still doesn’t work | Ultrasonic noise pollution will interfere with your distance sensor readings. If you aim two distance sensors at each other, they will confuse each other. Some air-conditioning systems may also emit noises in the ultrasonic range. Try pointing your sensor away from the other distance sensors or changing to a different location. |
Circuit 3C: Motion Alarm
Time to take your distance sensor project to the next level. Let’s imagine that you want to stop your cat from prowling around your countertop. This circuit will use light, sound and motion to scare away your cat when it is detected by the distance sensor. Using a servo motor, you can add a moving pop-up to animate your alarm.
Don’t have a cat? No problem! This circuit can be adapted for a variety of projects such as a room alarm, an automated pop-up story, an automatic treat dispenser and so much more. Let your imagination run wild with this project.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
Additional Materials (NOT INCLUDED)
The following materials are optional. The circuit can be completed without these items.
- Paper
- Scissors
- Scotch™ Tape
- Markers/Pen
- Paper Clip
- Needle-Nose Pliers
New Concepts
Getting Creative With Mechanisms
This circuit gets really fun when you start to use your servo to animate the world around you. To do this, you’ll need to connect your servo to some physical mechanisms. Tape and hot glue are easy ways to connect things to your servo. You can also loop a paper clip through the small holes in the servo arm to serve as a linkage. See the Hardware Hookup section below for more information.
Hardware Hookup
If you have opted for the extra materials, use the following instructions to create the moving pop-up for your cat alarm.
To begin, attach your servo to the baseplate using Dual Lock, as described in Circuit 3A.
Attach the servo mount of your choice. It is recommended you wait until after you have uploaded your code to ensure the mount is in the best position before screwing on the mount. The screw is optional, but it will make for a more robust mechanism.
Next, use needle-nose pliers to bend the paper clip straight. Imagine a 3D space. The straight clip is the X-axis. Bend one end of the paper clip 90 degrees along the Y-axis. The bent segment should be about 1 inch or 2.5cm long. Then bend the other end along the Z-axis. This bend should be about 1/8 inch or 3mm long. Repeat this bend once more back toward the X-axis, making a hook shape. You should now have a linkage rod that looks something like this:
Attach the hook end of the linkage rod to the end hole on your servo mount.
Cut out the pop-up image of your choice. We chose this public domain menacing cat image (http://bit.ly/2vinyE1). The image you choose should be about 2.5 inches x 2.5 inches and can be drawn or printed. Leave a rectangular strip of paper under the image that is about 2 inches long. Fold along the bottom of the image. Tape the pop-up to the underside of the breadbaord baseplate on the same side to which the servo is connected.
Last, tape the free end of the rod to the back of your pop-up image.
Once you have the rest of the circuit built and the code uploaded, you can fine-tune your moving pop-up and make any necessary adjustments. Remember to wait until these adjustments have been made before you screw the servo mount onto the motor.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the Fritzing diagram below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Servo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) |
||||
| RGB LED | A25 (RED) | A24 (GND) | A23 (GREEN) | A22 (BLUE) | ||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E22 | F22 | ||||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E23 | F23 | ||||
| 330Ω Resistor (orange, orange, brown) |
E25 | F25 | ||||
| Jumper Wire | E24 | GND Rail ( - ) |
||||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 3 | J25 | ||||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 5 | J23 | ||||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 6 | J22 | ||||
| Distance Sensor | A3 (Vcc) | A4 (Trig) | A5 (Echo) | A6 (GND) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | E4 (Trig) | ||||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | E5 (Echo) | ||||
| Jumper Wire | E3 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||||
| Jumper Wire | E6 | GND Rail ( - ) |
||||
| Buzzer | F14 (Buzzer +) |
F16 (Buzzer -) |
||||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | J14 | ||||
| Jumper Wire | J16 | GND Rail ( - ) |
||||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | White Servo Pin | ||||
| Jumper Wire | 5V Rail ( + ) | Red Servo Pin | ||||
| Jumper Wire | GND Rail ( - ) |
Black Servo Pin |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_3C-CatAlarm
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 3C-Motion Alarm
Control the color of an RGB LED using an ultrasonic distance sensor. When an object is close to the sensor, buzz the buzzer and wiggle the servo motor.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
#include <Servo.h> //include the servo library
const int trigPin = 11; //connects to the trigger pin on the distance sensor
const int echoPin = 12; //connects to the echo pin on the distance sensor
const int redPin = 3; //pin to control the red LED inside the RGB LED
const int greenPin = 5; //pin to control the green LED inside the RGB LED
const int bluePin = 6; //pin to control the blue LED inside the RGB LED
const int buzzerPin = 10; //pin that will drive the buzzer
float distance = 0; //stores the distance measured by the distance sensor
Servo myservo; //create a servo object
void setup()
{
Serial.begin (9600); //set up a serial connection with the computer
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); //the trigger pin will output pulses of electricity
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); //the echo pin will measure the duration of pulses coming back from the distance sensor
//set the RGB LED pins to output
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT); //set the buzzer pin to output
myservo.attach(9); //use pin 9 to control the servo
}
void loop() {
distance = getDistance(); //variable to store the distance measured by the sensor
Serial.print(distance); //print the distance that was measured
Serial.println(" in"); //print units after the distance
if (distance <= 10) { //if the object is close
//make the RGB LED red
analogWrite(redPin, 255);
analogWrite(greenPin, 0);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
//this code wiggles the servo and beeps the buzzer
tone(buzzerPin, 272); //buzz the buzzer pin
myservo.write(10); //move the servo to 45 degrees
delay(100); //wait 100 milliseconds
noTone(buzzerPin); //turn the buzzer off
myservo.write(150); //move the servo to 135 degrees
delay(100); //wait 100 milliseconds
} else if (10 < distance && distance < 20) { //if the object is a medium distance
//make the RGB LED yellow
analogWrite(redPin, 255);
analogWrite(greenPin, 50);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
} else { //if the object is far away
//make the RGB LED green
analogWrite(redPin, 0);
analogWrite(greenPin, 255);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
}
delay(50); //delay 50ms between each reading
}
//------------------FUNCTIONS-------------------------------
//RETURNS THE DISTANCE MEASURED BY THE HC-SR04 DISTANCE SENSOR
float getDistance()
{
float echoTime; //variable to store the time it takes for a ping to bounce off an object
float calculatedDistance; //variable to store the distance calculated from the echo time
//send out an ultrasonic pulse that's 10ms long
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
echoTime = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); //use the pulsein command to see how long it takes for the
//pulse to bounce back to the sensor
calculatedDistance = echoTime / 148.0; //calculate the distance of the object that reflected the pulse (half the bounce time multiplied by the speed of sound)
return calculatedDistance; //send back the distance that was calculated
}
What You Should See
The RGB LED will behave as in your last circuit. It will be green when objects are far, yellow when they are midrange and red when they are close. When an object is close the buzzer will also beep, and the servo will rotate back and forth.
Program Overview
- Check what distance the sensor is reading. a. If the distance is less than 10 inches, make the RGB LED red. Then make the servo rotate back and forth and make the buzzer beep. b. If the distance is between 10 and 20 inches, make the RGB LED yellow. c. If the distance value is not equal to the fist two conditions, make the RGB LED green.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Constants: const int trigPin = 11; |
Constants are variables that have been marked as "read-only" and cannot have their value changed as the program progresses. Constants are great for declaring pin number variables that will not change throughout the program. |
No Tone Function: |
In circuit 2A you made songs using a buzzer and the tone function, but you gave the tone function three parameters: a pin number, a frequency and a duration. You can leave out the third parameter, and the tone will play until you change it or turn it off. noTone() turns off a pin that has been activated with the tone command.
|
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the servo behavior | Try changing the way that your servo behaves when the distance sensor is triggered. |
| Change the alarm settings | Try altering the code so the alarm goes off from much farther or closer distances. |
| Create a different mechanism | Try your hand at making different objects move with your servo motor. Make an interactive pop-up story. Make an automatic fish feeder. Time to use your imagination! |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The RGB LED colors aren't working or a color is missing | Check the connection for the wire and resistor connected to each leg of the LED. Ensure the RGB LED is inserted in the correct orientation. |
| The distance sensor doesn’t seem to work | Open up the Serial Monitor on your computer. You should see a stream of distances being printed in the monitor. If they are all reading 0 or jumping around, then check the wiring on your sensor. |
| The distance sensor still doesn’t work | Ultrasonic noise pollution will interfere with your distance sensor readings. If you aim two distance sensors at each other, they will confuse each other. Some air conditioning systems may also emit noises in the ultrasonic range. Try pointing your sensor away from the other distance sensors or changing to a different location. |
| The servo doesn’t work | Make sure all of your servo wires are connected. Be sure that the black wire is connected to the negative rail and the red wire is connected to the positive rail. Make sure you are using a digital pin that is capable of PWM. |
| The pop-up is moving too much or not enough | The two lines of code that pass angles to the servo motor are myservo.write(45); and myservo.write(135);. Try changing these angle values to fine-tune your mechanism. |
Project 4: Display
Printing data to the Arduino Serial Monitor is a great way to see data from the RedBoard. But, what if you want to make your project mobile and see sensor values away from your computer? This project will show you how to do exactly that. You'll learn about liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and how to print things like sensor data and strings of words to the display.
New Components Introduced in This Project
Each of the components listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
- TMP36 Digital Temperature Sensor
- 4xAA Battery Holder
New Concepts Introduced in This Project
Each of the concepts listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- Contrast
- Pixels
- Algorithms
- Button Debouncing
- Strings
- Pointers
You Will Learn
- How to print simple messages to an LCD
- How to use a temperature sensor
- How to print sensor data to an LCD
- How to make an interactive game that incorporates the LCD
Circuit 4A: LCD "Hello, World!"
Printing “Hello, world!” is usually the first thing that programming tutorials will have you do in a new language. This guide starts by blinking an LED, but now we’re going to print out real text using a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD).
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
Character Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
Character LCDs are designed to show a grid of letters, numbers and a few special characters. This makes them great for printing data and showing values. When current is applied to this special kind of crystal, it turns opaque. This is used in a lot of calculators, watches and simple displays. Adding an LCD to your project will make it super portable and allow you to integrate up to 32 characters (16 x 2) of information.
New Concepts
Contrast
Pin 3 on the LCD controls the contrast and brightness of the LCD. Using a simple voltage divider with a potentiometer, the contrast can be adjusted. As you rotate the knob on the potentiometer, you should notice that the screen will get brighter or darker and that the characters become more visible or less visible. The contrast of LCDs is highly dependent on factors such as temperature and the voltage used to power it. Thus, external contrast knobs are needed for displays that cannot automatically account for temperature and voltage changes.
Pixels
If you look closely at the characters on the LCD, you will notice that they are actually made up of lots of little squares. These little squares are called pixels. The size of displays is often represented in pixels. Pixels make up character space, which is the number of pixels in which a character can exist.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
The LCD has 16 pins, and it is polarized. The pins are numbered from left to right, 1 through 16. The LCD utilizes an extremely common parallel interface LCD driver chip from Hitachi called the HD44780. Thankfully, the Arduino community has developed a library to handle a great deal of the software-to-hardware interface. Below is a list of each of the pins on the LCD.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| LCD | A15-A30 (Pin 1 on A15) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E30 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E29 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 8 | E28 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | E27 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | E26 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | E25 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | E20 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E19 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | E18 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E16 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E15 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Potentiometer | A8 | A9 | A10 | |
| Jumper Wire | E9 | E17 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E8 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E10 | 5V Rail ( + ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_4A-LCDHelloWorld
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 4A-HelloWorld
The LCD will display the words "Hello World" and show how many seconds have passed since
the RedBoard was last reset.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> //the liquid crystal library contains commands for printing to the display
LiquidCrystal lcd(13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8); // tell the RedBoard what pins are connected to the display
void setup() {
lcd.begin(16, 2); //tell the lcd library that we are using a display that is 16 characters wide and 2 characters high
lcd.clear(); //clear the display
}
void loop() {
lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //set the cursor to the 0,0 position (top left corner)
lcd.print("Hello, world!"); //print hello, world! starting at that position
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //move the cursor to the first space of the bottom row
lcd.print(millis() / 1000); //print the number of seconds that have passed since the last reset
}
What You Should See
The LCD screen will show “Hello, world!” On the row below, a counter will count every second that passes.
Contrast Adjust
If you are not seeing any characters, are seeing barely visible characters, or see just white rectangles, then you need to adjust the contrast. Twist the potentiometer very slowly until you can clearly read the display. If you reach the end of the potentiometer's rotation, try twisting in the opposite direction.
Program Overview
- Import the LCD library.
- Make an LCD object called “lcd” that will be controlled using pins 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 and 13.
- “Begin” the LCD. This sets the dimensions of the LCD that you are working with (16 x 2). It needs to be called before any other commands from the LCD library are used.
- Clear the display.
- Set the cursor to the top left corner
lcd.setCursor(0,0);, then print “Hello, world!" - Move the cursor to the first space of the lower line
lcd.setCursor(0,1);, then print the number of seconds that have passed since the RedBoard was last reset.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
LCD Library:#include <LiquidCrystal.h> | Includes the liquid crystal library into your program. |
LCD Library Instance:LiquidCrystal LCD_name(RS_pin, enable_pin, d4, d5, d6, d7); | As with servos, you need to create an LCD object and give it a name (you can make more than one). The numbers in the brackets are pins on the RedBoard that connect to specific pins on the LCD. |
LCD Begin:lcd.begin(16, 2); | This line initializes the LCD object and tells the program the LCD's dimensions. In this case it is 16 characters by 2 characters. |
LCD Clear:lcd.clear(); | This method clears the pixels on the display. |
LCD Cursor:lcd.setCursor(0,0); | Move the cursor to a point on the 16x2 grid of characters. Text that you write to the LCD will start from the cursor. This line is starting back at position (0,0). |
LCD Print :lcd.print("Hello, world!"); | Prints a string of characters to the LCD starting at the cursor position. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the message | Try changing the code to display another message. |
| Show hours, minutes and seconds | Try adding some code so that the display shows the hours, minutes and seconds that have passed since the RedBoard was last reset. |
| Count button presses | By adding a button to the circuit, you can count the number of times the button was pressed or have the button change what the LCD is displaying. There could be many pages of information. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The screen is blank or flickering | Adjust the contrast by twisting the potentiometer. If it’s incorrectly adjusted, you won’t be able to read the text. Also, check the potentiometer, and make sure it's connected correctly. |
| Not working at all | Double check the circuit's wiring. There are a lot of wires in this circuit, and it's easy to mix up one or two. |
| Rectangles in first row | If you see 16 rectangles (like “█”) on the first row, it may be due to the jumper wires being loose on the breadboard. This is normal and can happen with other LCDs wired in parallel with a microcontroller. Make sure that the wires are fully inserted into the breadboard, then try pressing the reset button and adjusting the contrast using the potentiometer. |
| Still not working? | Jumper wires unfortunately can go "bad" from getting bent too much. The copper wire inside can break, leaving an open connection in your circuit. If you are certain that your circuit is wired correctly and that your code is error-free and uploaded but you are still encountering issues, try replacing one or more of the jumper wires for the component that is not working. |
Circuit 4B: Temperature Sensor
Want to create a DIY environmental monitor or weather station? You can use a small, low-cost sensor like the TMP36 to make devices that track and respond to temperature. In this activity you will also use the LCD screen to display sensor readings, a common use for LCDs in electronics projects.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
TMP36 Temperature Sensor
This temperature sensor has three legs. One connects to 5V, one to ground, and the voltage output from the third leg varies proportionally to changes in temperature. By doing some simple math with this voltage we can measure temperature in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
New Concepts
Algorithms
An algorithm is a process used in order to achieve a desired result. Often, the information needed to create an algorithm lives in the part's datasheet. This sketch uses a few formulas to turn a voltage value into a temperature value, making them all part of the larger temperature-retrieving algorithm. The first formula takes the voltage read on analog pin 0 and multiplies it to get a voltage value from 0V--5V:
language:c
voltage = analogRead(A0) * 0.004882813;
The number we are multiplying by comes from dividing 5V by the number of samples the analog pin can read (1024), so we get: 5 / 1024 = 0.004882813.
The second formula takes that 0--5V value and calculates degrees Centigrade:
language:c
degreesC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100.0;
The reason 0.5V is subtracted from the calculated voltage is because there is a 0.5V offset, mentioned on page 8 of the TMP36 datasheet. It's then multiplied by 100 to get a value that matches temperature.
The last formula takes the Centigrade temperature and converts it to a Fahrenheit temperature using the standard conversion formula:
language:c
degreesF = degreesC * (9.0/5.0) + 32.0;
Together, these three formulas make up the algorithm that converts voltage to degrees Fahrenheit.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
The temperature sensor is polarized and can only be inserted in one direction. See below for the pin outs of the temperature sensor. Pay very close attention to the markings on each side as you insert it into your circuit.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| LCD | A15-A30 (Pin 1 on A15) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E30 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E29 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 8 | E28 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | E27 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | E26 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | E25 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | E20 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E19 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | E18 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E16 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E15 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Potentiometer | A8 | A9 | A10 | |
| Jumper Wire | E9 | E17 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E8 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E10 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| TMP36 Temperature Sensor | A1 (GND) | A2 (Signal) | A3 (V+) | |
| Jumper Wire | E1 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Analog Pin 0 (A0) | E2 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E3 | 5V Rail ( + ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_4B-TemperatureSensor
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 4B - Temperature Sensor
The LCD will display readings from a temperature sensor in degrees Celsius and Fahrenheit.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> //the liquid crystal library contains commands for printing to the display
LiquidCrystal lcd(13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8); // tell the RedBoard what pins are connected to the display
float voltage = 0; //the voltage measured from the TMP36
float degreesC = 0; //the temperature in Celsius, calculated from the voltage
float degreesF = 0; //the temperature in Fahrenheit, calculated from the voltage
void setup() {
lcd.begin(16, 2); //tell the lcd library that we are using a display that is 16 characters wide and 2 characters high
lcd.clear(); //clear the display
}
void loop() {
voltage = analogRead(A0) * 0.004882813; //convert the analog reading, which varies from 0 to 1023, back to a voltage value from 0-5 volts
degreesC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100.0; //convert the voltage to a temperature in degrees Celsius
degreesF = degreesC * (9.0 / 5.0) + 32.0; //convert the voltage to a temperature in degrees Fahrenheit
lcd.clear(); //clear the LCD
lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //set the cursor to the top left position
lcd.print("Degrees C: "); //print a label for the data
lcd.print(degreesC); //print the degrees Celsius
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //set the cursor to the lower left position
lcd.print("Degrees F: "); //Print a label for the data
lcd.print(degreesF); //print the degrees Fahrenheit
delay(1000); //delay for 1 second between each reading (this makes the display less noisy)
}
What You Should See
The LCD will show the temperature in Celsius and Fahrenheit. The temperature readings will update every second. An easy way to see the temperature change is to press your finger to the sensor.
Program Overview
- Get the analog value from the TMP36 and convert it back to a voltage between 0 and 5V.
- Calculate the degrees Celsius from this voltage.
- Calculate the degrees Fahrenheit from this voltage.
- Clear the LCD.
- Print the Degrees C with a label on the first row.
- Print the Degrees F with a label on the second row.
- Wait for a second before taking the next reading.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Conversion Algorithms | Many of the sensors that you will use with your microcontroller work by changing a voltage in some predictable way in response to a property of the world (like temperature, light or magnetic fields).
Often, you will need to build an algorithm that converts these voltages to the desired value and units. The temperature sensor is a great example of this code. We use three equations to convert a voltage value into degrees in C and F.
voltage = analogRead(A0) * 0.004882813;
degreesC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100.0;
degreesF = degreesC * (9.0/5.0) + 32.0;
|
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Display the temperature in degrees Kelvin | Try adding an equation so that the temperature is displayed in degrees Kelvin (you will have to look up the formula for converting from degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit to Kelvin) |
| Display a bar graph | By changing the code you can display the temperature as a bar graph instead of a number. |
| Display values from another sensor | You can swap out the TMP36 for a potentiometer, photoresistor or other sensor and display the new set of values. |
| Add an RGB LED | Add an RGB LED that changes color based on the temperature. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Sensor is warm or hot to the touch | Make sure that you wired the temperature sensor correctly. The temperature sensor can get warm to the touch if it is wired incorrectly. Disconnect your microcontroller, rewire the circuit, and connect it back to your computer. |
| Temperature value is unchanging | Try pinching the sensor with your fingers to heat it up or pressing a bag of ice against it to cool it down. Also, make sure that the wires are connected properly to the temperature sensor. |
| Values not printing to screen | If you see text but no temperature values, there could be an error in your code. If you see no text at all, adjust the LCD contrast. |
Circuit 4C: DIY Who Am I? Game
"DIY Who Am I?" is based on the popular Hedbanz game or HeadsUp! app. It's a fun party game in which a player holds an LCD screen to his/her forehead so that the player can’t see the word(s) that appear on the screen. Other players have to give hints, act out charades or make noises that will make the player with the LCD guess the word(s).
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
New Components
4xAA Battery Holder
Included in your kit is a 4-cell AA battery holder. The 5-inch cable is terminated with a standard barrel jack connector. The connector mates with the barrel jack on the RedBoard, allowing you to easily make your project battery powered.
New Concepts
Button Debounce
When working with momentary buttons, it is usually necessary to add button debouncing to your code. This is because the code that is meant to execute when the button is pressed may execute faster than you can press and release the button (microcontrollers are fast!). The simplest way to debounce a button is to add a small delay to the end of your code. This sketch adds a 500 millisecond delay at the end of loop() to account for this. This simple addition will prevent a word from getting skipped when you press the button for the game.
For a more complex example of button debouncing, in the Arduino IDE click File > Examples > 02.Digital > Debounce.
Strings
Strings are used to print words and even sentences to an LCD or the Serial Monitor. Strings are actually just an array of characters with a null character at the end to let the program know where the end of the string is.
Arrays of Strings
In circuit 2A you used an array of characters to represent musical notes. In this program, you’ll want to make an array of strings. Strings use multiple characters to make words, so you’ll need to use a little trick to put them in an array. The trick is to use a pointer. When you declare your array, you’ll use an asterisk after the char data type, as follows:
language:c
const char* arrayOfStrings = {“Feynman” “Sagan”, “Tyson”, “Nye”};
Pointers
Pointers are an advanced programming topic. They can be difficult to understand the first time you're introduced to them. For now, think of pointers as a variable that "points" to the value contained in a certain address in memory. In this sketch, the char* variable points to arrayOfStrings address and returns the character values to create a list of strings.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Batteries are polarized. They have a positive end and a negative end. The battery holder has images indicating which end goes in which orientation for each cell.
Ensure all the batteries are inserted correctly before plugging the battery holder into the RedBoard.
Battery Holder Attachment
To attach the battery holder to the breadboard baseplate, first cut two strips of Dual Lock that are roughly 1 inch x 1 inch each, or 2.5cm x 2.5cm. Remove the adhesive backing and attach one piece to the back of the battery holder.
Adhere the second piece to the bottom of the breadboard baseplate (directly in the middle is recommended, as this will come into play in Project 5).
Last, press the battery holder to the baseplate so that the two pieces of Dual Lock snap together. Insert the batteries into the holder if you have not done so already. Remember that batteries are polarized and can only go in one way.
Remove the battery pack while building your circuit.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| LCD | A15-A30 (Pin 1 on A15) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E30 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E29 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 8 | E28 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | E27 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | E26 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | E25 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | E20 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E19 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | E18 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E16 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E15 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Potentiometer | A8 | A9 | A10 | |
| Jumper Wire | E9 | E17 | ||
| Jumper Wire | E8 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | E10 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Buzzer | G6 (Buzzer +) |
G8 (Buzzer -) |
||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 6 | J6 | ||
| Jumper Wire | J8 | GND Rail ( - ) |
||
| Push Button | D1/D3 | G1/G3 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 2 | J1 | ||
| Jumper Wire | J3 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_4C-DIYWhoAmI
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 4C - Heads Up Game
This is a DIY version of the popular Heads Up party game. To play, one person resets the RedBoard and holds the LCD
facing away from them so that they cannot see it (usually on their forehead). The display will show a short countdown
then display random words. The other player(s) who can see the screen must yell out clues until time runs out or the player
guesses what word is on the screen. If they guess correctly, they can press the button on the breadboard and another word
will be displayed.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> //the liquid crystal library contains commands for printing to the display
LiquidCrystal lcd(13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8); // tell the RedBoard what pins are connected to the display
int buttonPin = 2; //pin that the button is connected to
int buzzerPin = 6; //pin for driving the buzzer
int buttonPressTime = 0; //variable to show how much time the player has left to guess the word (and press the button)
long timeLimit = 15000; //time limit for the player to guess each word
long startTime = 0; //used to measure time that has passed for each word
int roundNumber = 0; //keeps track of the roundNumber so that it can be displayed at the end of the game
const int arraySize = 25;
const char* words[arraySize] = {"moose", "beaver", "bear", "goose", "dog", "cat", "squirrel", "bird", "elephant", "horse",
"bull", "giraffe", "seal", "bat", "skunk", "turtle", "whale", "rhino", "lion", "monkey",
"frog", "alligator", "kangaroo", "hippo", "rabbit"
};
// the start value in the sequence array must have a value that could never be an index of an array
// or at least a value outside the range of 0 to the size of the words array - 1; in this case, it can't be between 0 to 24
int sequence[] = { -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1}; //start with an array full of -1's
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP); //set the button pin as an input
lcd.begin(16, 2); //tell the LCD library the size of the screen
generateRandomOrder(); //generate an array of random numbers from 0 to 24 that will determine which order the words are shown in
showStartSequence(); //print the start sequence text
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { //for each of the 25 words in the sequence
lcd.clear(); //clear off the array
roundNumber = i + 1; //the array starts at 0, but the roundNumber will start counting from 1
lcd.print(roundNumber); //print the roundNumber (this is the current round number)
lcd.print(": "); //spacer between the number and the word
lcd.print(words[sequence[i]]); //print a random word from the word array
startTime = millis(); //record the time that this round started
while (digitalRead(buttonPin) == HIGH) { //do this until the button is pressed...
int roundedTime = round((timeLimit - (millis() - startTime)) / 1000); //calculate the time left in the round (dividing by 1000 converts the number to seconds
lcd.setCursor(14, 1); //set the cursor in the lower right corner of the screen
lcd.print(" ");
lcd.setCursor(14, 1); //set the cursor in the lower right corner of the screen
lcd.print(roundedTime); //print the time left in the time limit
delay(15);
if (millis() - startTime > timeLimit) { //if the time limit is up before the button is pressed
gameOver(); //end the game
}
if (digitalRead(buttonPin) == LOW) {
tone(buzzerPin, 272, 10); //emit a short beep when the button is pressed
}
} //exit this loop when the button is pressed
delay(500); //delay for a moment before going onto the next round, so that the button press doesn't get registered twice
}
//if you finish all 25 words
winner(); //show the you win message
}
//--------------FUNCTIONS------------------------------
//DISPLAYS A COUNTDOWN TO START THE GAME
void showStartSequence() {
lcd.clear(); //clear the screen
lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //move the cursor to the top left corner
lcd.print("Category:"); //print "Category:"
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //move the cursor to the bottom left corner
lcd.print("Animals"); //print "Animals:"
delay(2000); //Wait 2 seconds
lcd.clear(); //clear the screen
lcd.print("Get ready!"); //print "Get ready!"
delay(1000); //wait 1 second
lcd.clear(); //clear the screen
lcd.print("3"); //print "3"
delay(1000); //wait 1 second
lcd.clear(); //clear the screen
lcd.print("2"); //print "3"
delay(1000); //wait 1 second
lcd.clear(); //clear the screen
lcd.print("1"); //print "3"
delay(1000); //wait 1 second
}
//GENERATES A RANDOM ORDER FOR THE WORDS TO BE DISPLAYED
void generateRandomOrder() {
randomSeed(analogRead(0)); //reset the random seed (Arduino needs this to generate truly random numbers
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { //do this until all 25 positions are filled
int currentNumber = 0; //variable to hold the current number
boolean match = false; //does the currentNumber match any of the previous numbers?
//generate random numbers until you've generated one that doesn't match any of the other numbers in the array
do {
currentNumber = random(0, arraySize); //generate a random number from 0 to 24
match = false; //we haven't checked for matches yet, so start by assuming that it doesn't match
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) { //for all 25 numbers in the array
if (currentNumber == sequence[i]) { //does the currentNumber match any of the numbers?
match = true; //if so, set the match variable to true
}
}
} while (match == true); //if the match variable is true, generate another random number and try again
sequence[i] = currentNumber; //if the match variable is false (the new number is unique) then add it to the sequence
}
}
//GAME OVER
void gameOver() {
lcd.clear(); //clear the screen
lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //move the cursor the top left corner
lcd.print("Game Over"); //print "Game Over"
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //move to the bottom row
lcd.print("Score: "); //print a label for the score
lcd.print(roundNumber); //print the score (the round number is the same as the score)
//play the losing fog horn
tone(buzzerPin, 130, 250); //E6
delay(275);
tone(buzzerPin, 73, 250); //G6
delay(275);
tone(buzzerPin, 65, 150); //E7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 98, 500); //C7
delay(500);
while (true) {} //get stuck in this loop forever
}
//WINNER
void winner() {
lcd.clear(); //clear the screen
lcd.setCursor(7, 0); //move the cursor to the top center of the screen
lcd.print("YOU"); //print "You"
lcd.setCursor(7, 1); //move the cursor to the bottom center of the screen
lcd.print("WIN!"); //print "WIN!"
//play the 1Up noise
tone(buzzerPin, 1318, 150); //E6
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 1567, 150); //G6
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 2637, 150); //E7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 2093, 150); //C7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 2349, 150); //D7
delay(175);
tone(buzzerPin, 3135, 500); //G7
delay(500);
while (true) {} //get stuck in this loop forever
}
What You Should See
The game will begin with a prompt telling you the category of words. Then it will run through a short countdown. When the first round starts, the word to be guessed will be displayed in the top left, and a countdown will be displayed in the bottom right of the LCD screen. Each time the button is pressed (before the timer expires) a new word will be displayed. If you win or lose, a short song will play and text will be displayed.
Program Overview
- Generate a random order for the words to be displayed.
- Show the starting countdown on the LCD.
- Start a loop that will run 25 times (there are 25 words total). For each round: a. Print the round number and the word to be guessed. b. Display a countdown timer in the lower right-hand corner of the screen that counts down the time limit for each round. c. If the time limit runs out, play the losing song, print "Game Over" and show the player's final score. d. If the player presses the button before the time limit is up, advance to the next word.
- If the player gets through all 25 words, play the winning song and print “YOU WIN!”
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Array of Strings:const char* array_name [array_length] = | Makes an array of strings. The strings are stored as constants, so they can’t be changed once the program starts. |
Rounding function:round(value_to_round); | This math function rounds a number up or down to the nearest whole number. |
Random Function:random(min, max); | The random function takes a set of numbers and generates a pseudo-random number from that set. |
Button Debounce:delay(500); | This 500 millisecond delay at the end of the loop adds button debounce so that erroneous button presses are not detected by the RedBoard. |
| User Functions | Description |
generateRandomOrder(); | Makes an array that is a random ordering of the numbers from 1-25. This is used to display words for the game in a random order. |
showStartSequence(); | Shows the category of words on the LCD, then displays a countdown before the game starts. |
gameOver(); | Plays a sound and shows the text “Game Over” along with the player’s final score. |
winner(); | Shows the text “YOU WIN!” and plays a winning sound. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the time limit | Changing the time limit variable will change the difficulty of the game. |
| Change the words in the word list | Try changing the categories and words. The number of words in your words array must match the value of the variable “arraySize”. |
| Change the winning and losing songs | By changing the tones in the winner() and gameover() functions you can change which song plays at the end of the game. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The screen is blank or flickering | Adjust the contrast by twisting the potentiometer. If it’s incorrectly adjusted, you won’t be able to read the text. Also, check the potentiometer to make sure it's connected correctly. |
| No sound is coming from the buzzer | Check the wiring from the buzzer. Make sure you are using the correct pin as defined in your code. You may add a potentiometer volume knob if you desire. |
| The button doesn't work or words are getting skipped before they are guessed | If the button isn't working, check your wiring. If words are being skipped when the button is pressed, increase the debounce delay found at the end of the loop. It should be 500 milliseconds by default. Increasing this number by tiny increments will help with this problem. |
Project 5: Robot
Ah, robots. One of the most iconic and exciting electronics applications. In this project you will learn all about DC motors and motor drivers by building your own robot! You'll learn how to control a tethered robot first by sending it commands over serial. Then you will unleash your robot by removing the tether and making it autonomous.
New Components Introduced in This Project
Each of the components listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- TB6612FNG Motor Driver
- Switch
- DC Gearmotor
- Wheel
New Concepts Introduced in This Project
Each of the concepts listed below will be described in more detail as you progress through each circuit.
- Input Voltage
- Integrated Circuits
- H-Bridge Motor Driver
- ASCII Characters
- Converting Strings
- Autonomous Vehicles
You Will Learn
- How to control two motors using a motor driver
- How to send serial commands to create a remote-controlled robot
- How to build a robot that uses sensors to react to its environment
Circuit 5A: Motor Basics
In this circuit you will learn the basic concepts behind motor control. Motors require a lot of current, so you can’t drive them directly from a digital pin on the RedBoard. Instead, you’ll use what is known as a motor controller or motor driver board to power and spin the motor accordingly.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
Additional Materials
- Scissors (NOT INCLUDED)
New Components
Switch
A switch is a component that controls the open-ness or closed-ness of an electric circuit. Just like the momentary buttons used in earlier circuits, a switch can only exist in one of two states: open or closed. However, a switch is different in that it will stay in the position it was last in until it is switched again.
DC Gearmotors
The motors in your Inventor’s Kit have two main parts: a small DC motor that spins quickly and a plastic gearbox that gears down that output from the hobby motor so that it is slower but stronger, allowing it to move your robot. The motors have a clever design so that you can attach things that you want to spin fast (like a small fan or flag) to the hobby motor, and things that you want to be strong (like a wheel) to the plastic axle sticking out the side of the motor. The included wheels just so happen to fit on the plastic axles.


Inside the hobby motor are coils of wire that generate magnetic fields when electricity flows through them. When power is supplied to these electromagnets, they spin the drive shaft of the motor.
TB6612FNG Motor Driver
If you switch the direction of current through a motor by swapping the positive and negative leads, the motor will spin in the opposite direction. Motor controllers contain a set of switches (called an H-bridge) that let you easily control the direction of one or more motors. The TB6612FNG Motor Driver takes commands for each motor over three wires (two wires control direction, and one controls speed), then uses these signals to control the current through two wires attached to your motor.
New Concepts
Voltage In (VIN)
This circuit utilizes the VIN pin found with the other power pins. The VIN pin outputs a voltage that varies based on whatever voltage the RedBoard is powered with. If the RedBoard is powered through the USB port, then the voltage on VIN will be about 4.6--5V. However, if you power the RedBoard through the barrel jack (highlighted in the picture below), the VIN pin will reflect that voltage. For example, if you were to power the barrel jack with 9V, the voltage out on VIN would also be 9V.
Integrated Circuits (ICs) and Breakout Boards
An Integrated Circuit (IC) is a collection of electronic components --- resistors, transistors, capacitors, etc. --- all stuffed into a tiny chip and connected together to achieve a common goal. They come in all sorts of flavors, shapes and sizes. The chip that powers the RedBoard, the ATMega328, is an IC. The chip on the motor driver, the TB6612FNG, is another IC, one designed to control motors, referred to as an H-bridge.
Integrated circuits are often too small to work with by hand. To make working with ICs easier and to make them breadboard-compatible, they are often added to a breakout board, which is a printed circuit board that connects all the IC's tiny legs to larger ones that fit in a breadboard. The motor driver board in your kit is an example of a breakout board.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Most ICs have polarity and usually have a polarity marking in one of the corners. The motor driver is no exception. Be sure to insert the motor driver as indicated in the circuit diagrams. The motor driver pins are shown in the image below.
Each pin and its function is covered in the table below.
| Pin Label | Function | Power/Input/Output | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| VM | Motor Voltage | Power | This is where you provide power for the motors (2.2V to 13.5V) |
| VCC | Logic Voltage | Power | This is the voltage to power the chip and talk to the microcontroller (2.7V to 5.5V) |
| GND | Ground | Power | Common Ground for both motor voltage and logic voltage (all GND pins are connected) |
| STBY | Standby | Input | Allows the H-bridges to work when high (has a pulldown resistor so it must actively be pulled high) |
| AIN1/BIN1 | Input 1 for channels A/B | Input | One of the two inputs that determines the direction |
| AIN2/BIN2 | Input 2 for channels A/B | Input | One of the two inputs that determines the direction |
| PWMA/PWMB | PWM input for channels A/B | Input | PWM input that controls the speed |
| A01/B01 | Output 1 for channels A/B | Output | One of the two outputs to connect the motor |
| A02/B02 | Output 2 for channels A/B | Output | One of the two outputs to connect the motor |
When you're finished with Project 5, removing the motor driver from the breadboard can be difficult due to its numerous legs. To make this easier, use the included screwdriver as a lever to gently pry it out. Be careful not to bend the legs as you remove it.
The motors are also polarized. However, motors are unique in that they will still work when the two connections are reversed. They will just spin in the opposite direction when hooked up backward. To keep things simple, always think of the red wire as positive ( + ) and the black wire as negative ( - ).
Last, the switch is not polarized. It works the same no matter its orientation.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | 5V Rail ( + ) | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND Rail ( - ) | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | VIN | A1 | ||
| Motor Driver | C1-C8 (VM on C1) | G1-G8 (PWMA on G1) | ||
| Jumper Wire | A2 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | A3 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 8 | J5 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | J6 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | J7 | ||
| Jumper Wire | J4 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | J1 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | J2 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | J3 | ||
| Motor | A4 (Red +) | A5 (Black -) | ||
| Switch | F25 | F26 | F27 | |
| Jumper Wire | I26 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 7 | I27 |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_5A-MotorBasics.
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 5A - Motor Basics
Learn how to control one motor with the motor driver.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
//PIN VARIABLES
//the motor will be controlled by the motor A pins on the motor driver
const int AIN1 = 13; //control pin 1 on the motor driver for the right motor
const int AIN2 = 12; //control pin 2 on the motor driver for the right motor
const int PWMA = 11; //speed control pin on the motor driver for the right motor
int switchPin = 7; //switch to turn the robot on and off
//VARIABLES
int motorSpeed = 0; //starting speed for the motor
void setup() {
pinMode(switchPin, INPUT_PULLUP); //set this as a pullup to sense whether the switch is flipped
//set the motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(AIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMA, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); //begin serial communication with the computer
Serial.println("Enter motor speed (0-255)... "); //Prompt to get input in the serial monitor.
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) { //if the user has entered something in the serial monitor
motorSpeed = Serial.parseInt(); //set the motor speed equal to the number in the serial message
Serial.print("Motor Speed: "); //print the speed that the motor is set to run at
Serial.println(motorSpeed);
}
if (digitalRead(7) == LOW) { //if the switch is on...
spinMotor(motorSpeed);
} else { //if the switch is off...
spinMotor(0); //turn the motor off
}
}
/********************************************************************************/
void spinMotor(int motorSpeed) //function for driving the right motor
{
if (motorSpeed > 0) //if the motor should drive forward (positive speed)
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH); //set pin 1 to high
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
else if (motorSpeed < 0) //if the motor should drive backward (negative speed)
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH); //set pin 2 to high
}
else //if the motor should stop
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
analogWrite(PWMA, abs(motorSpeed)); //now that the motor direction is set, drive it at the entered speed
}
What You Should See
When you flip the switch, the motor will turn on and spin at the speed set by the motor speed variable (default is 0). By opening the serial monitor and sending numbers, you can change the speed of the motor. Any number from about 130 to 255 or -130 to -255 will work, though changes in the speed will be hard to notice. Send the number 0 to stop the motor. Adding a piece of tape to the motor shaft makes it easier to see it spinning.
Program Overview
- Check to see if a command has been sent through the Serial Monitor. If a command has been sent, then set the motor speed to the number that was sent over the Serial Monitor.
- Check to see if the switch is ON or OFF. a. If the switch is ON, drive the motor at the motor speed. b. If the switch is OFF, stop the motor.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Parsing Integers:Serial.parseInt(); | parseInt() receives integer numbers from the serial monitor. It returns the value of the number that it receives, so you can use it like a variable. |
Serial Available:Serial.available(); | Serial.available() checks how many bytes of data are being sent to the RedBoard. If it is greater than 0, then a message has been sent. It can be used in an if statement to run code only when a command has been received. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Make the switch change directions | Change the code so that the position of the switch changes the direction of the motor instead of turning it on and off. |
| Replace the switch with a button | Try wiring a button into the circuit instead of the sliding switch. Now the motor only turns on when you push the button. |
| Replace the switch with a sensor | Try changing the code so that the motor is activated by another sensor, like the photoresistor. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Motor not spinning | Check the wiring to the motor driver. There are a lot of connections, and it’s easy to mix one of them up with another. If it is still not working, you can test the B channel by moving you motor. (Black wire to A6, Red wire to A7). You’ll need to change the code as well. |
| Motor spins but then stops | In the Serial Monitor, make sure you have No line ending selected in the drop down menu next to the Baud Rate drop down menu. |
| Switch not working | Make sure that you are hooked up to the middle pin and one side pin on the switch. |
| Still not working? | Jumper wires unfortunately can go "bad" from getting bent too much. The copper wire inside can break, leaving an open connection in your circuit. If you are certain that your circuit is wired correctly and that your code is error-free and uploaded but you are still encountering issues, try replacing one or more of the jumper wires for the component that is not working. |
Circuit 5B: Remote-Controlled Robot
It’s remote control time! In this circuit, you’ll use a motor driver to control the speed and direction of two motors. You will also learn how to read multiple pieces of information from one serial command so that you can use the Serial Monitor to tell the robot what direction to move in and how far to move.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
Additional Materials
- Scissors (NOT INCLUDED)
New Concepts
ASCII Characters
ASCII is a standard formalized in the 1960s that assigns numbers to characters. This is a method of character encoding. When typing on a computer keyboard, each character you type has a number associated with it. This is what allows computers to know whether you are typing a lowercase "a," an uppercase "A" or a random character such as ampersand (&). In this experiment, you will be sending characters to the Serial Monitor to move your remote control robot. When you send a character, the microcontroller is actually interpreting that as a specific number. There are tons of ASCII tables available online. These tables make it easier to know which character is represented by which number.
Converting Strings to Integers
String variables hold words like “dog” or “Robert Smith” that are made up of multiple characters. Arduino has a set of special built-in methods for string variables that you can call by putting a period after the variable name, as follows:
string_variable_name. toInt();
The .toInt() method converts the string to a number, and there are a dozen other methods that can do things like tell you the length of a word or change all of the characters in a string to uppercase or lowercase.
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Before you build this circuit, you'll need to make a few modifications to the breadboard baseplate to make it more robot-like!
Assembling the Robot
Using scissors, cut two strips of Dual Lock that are 1.25 inches (3.175cm) long and 1 inch (2.5cm) wide. Remove the adhesive backing, and attach the two pieces to the very corners of the baseplate on the side located under the breadboard.
Cut two more strips that are 1.25 inches (3.175cm) long and 3/4 inch (1.9cm) wide. Remove the adhesive backing, and attach the strips to the two motors. Be sure that your motors are mirror images of each other when you attach the Dual Lock.
Press the motors to the baseplate, connecting the two Dual Lock surfaces. Try to get the motors as straight as possible so your robot will drive straight.
The bottom of your baseplate should look like the image below. Remember that the two motors should be mirror images of each other.
Attach the wheels by sliding them onto the plastic shafts on the gearmotor. The shaft is flat on one side, as is the wheel coupler. Align the two, and then press to fit the wheel onto the shaft.
Last, clip the binder clip onto the back end of the robot. This will act as a caster as the robot drives around.
Once you're finished, it's time to build the circuit. You may choose to remove the motors or leave them on while you build the circuit.
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the circuit diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | 5V Rail ( + ) | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | GND Rail ( - ) | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | VIN | A1 | ||
| Motor Driver | C1-C8 (VM on C1) | G1-G8 (PWMA on G1) | ||
| Jumper Wire | A2 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | A3 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 8 | J5 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | J6 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | J7 | ||
| Jumper Wire | J4 | 5V Rail ( + ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | J1 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | J2 | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | J3 | ||
| Motor 1 (Right) | A4 (Red +) | A5 (Black -) | ||
| Motor 2 (Left) | A6 (Black -) | A7 (Red +) | ||
| Switch | F25 | F26 | F27 | |
| Jumper Wire | I26 | GND Rail ( - ) | ||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 7 | I27 |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_5B-RemoteControlRobot
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 5B - Remote Control Robot
Control a two wheeled robot by sending direction commands through the serial monitor.
This sketch was adapted from one of the activities in the SparkFun Guide to Arduino.
Check out the rest of the book at
https://www.sparkfun.com/products/14326
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
//the right motor will be controlled by the motor A pins on the motor driver
const int AIN1 = 13; //control pin 1 on the motor driver for the right motor
const int AIN2 = 12; //control pin 2 on the motor driver for the right motor
const int PWMA = 11; //speed control pin on the motor driver for the right motor
//the left motor will be controlled by the motor B pins on the motor driver
const int PWMB = 10; //speed control pin on the motor driver for the left motor
const int BIN2 = 9; //control pin 2 on the motor driver for the left motor
const int BIN1 = 8; //control pin 1 on the motor driver for the left motor
int switchPin = 7; //switch to turn the robot on and off
const int driveTime = 20; //this is the number of milliseconds that it takes the robot to drive 1 inch
//it is set so that if you tell the robot to drive forward 25 units, the robot drives about 25 inches
const int turnTime = 8; //this is the number of milliseconds that it takes to turn the robot 1 degree
//it is set so that if you tell the robot to turn right 90 units, the robot turns about 90 degrees
//Note: these numbers will vary a little bit based on how you mount your motors, the friction of the
//surface that your driving on, and fluctuations in the power to the motors.
//You can change the driveTime and turnTime to make them more accurate
String botDirection; //the direction that the robot will drive in (this change which direction the two motors spin in)
String distance; //the distance to travel in each direction
/********************************************************************************/
void setup()
{
pinMode(switchPin, INPUT_PULLUP); //set this as a pullup to sense whether the switch is flipped
//set the motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(AIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMB, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); //begin serial communication with the computer
//prompt the user to enter a command
Serial.println("Enter a direction followed by a distance.");
Serial.println("f = forward, b = backward, r = turn right, l = turn left");
Serial.println("Example command: f 50");
}
/********************************************************************************/
void loop()
{
if (digitalRead(7) == LOW)
{ //if the switch is in the ON position
if (Serial.available() > 0) //if the user has sent a command to the RedBoard
{
botDirection = Serial.readStringUntil(' '); //read the characters in the command until you reach the first space
distance = Serial.readStringUntil(' '); //read the characters in the command until you reach the second space
//print the command that was just received in the serial monitor
Serial.print(botDirection);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(distance.toInt());
if (botDirection == "f") //if the entered direction is forward
{
rightMotor(200); //drive the right wheel forward
leftMotor(200); //drive the left wheel forward
delay(driveTime * distance.toInt()); //drive the motors long enough travel the entered distance
rightMotor(0); //turn the right motor off
leftMotor(0); //turn the left motor off
}
else if (botDirection == "b") //if the entered direction is backward
{
rightMotor(-200); //drive the right wheel forward
leftMotor(-200); //drive the left wheel forward
delay(driveTime * distance.toInt()); //drive the motors long enough travel the entered distance
rightMotor(0); //turn the right motor off
leftMotor(0); //turn the left motor off
}
else if (botDirection == "r") //if the entered direction is right
{
rightMotor(-200); //drive the right wheel forward
leftMotor(255); //drive the left wheel forward
delay(turnTime * distance.toInt()); //drive the motors long enough turn the entered distance
rightMotor(0); //turn the right motor off
leftMotor(0); //turn the left motor off
}
else if (botDirection == "l") //if the entered direction is left
{
rightMotor(255); //drive the right wheel forward
leftMotor(-200); //drive the left wheel forward
delay(turnTime * distance.toInt()); //drive the motors long enough turn the entered distance
rightMotor(0); //turn the right motor off
leftMotor(0); //turn the left motor off
}
}
}
else
{
rightMotor(0); //turn the right motor off
leftMotor(0); //turn the left motor off
}
}
/********************************************************************************/
void rightMotor(int motorSpeed) //function for driving the right motor
{
if (motorSpeed > 0) //if the motor should drive forward (positive speed)
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH); //set pin 1 to high
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
else if (motorSpeed < 0) //if the motor should drive backward (negative speed)
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH); //set pin 2 to high
}
else //if the motor should stop
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
analogWrite(PWMA, abs(motorSpeed)); //now that the motor direction is set, drive it at the entered speed
}
/********************************************************************************/
void leftMotor(int motorSpeed) //function for driving the left motor
{
if (motorSpeed > 0) //if the motor should drive forward (positive speed)
{
digitalWrite(BIN1, HIGH); //set pin 1 to high
digitalWrite(BIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
else if (motorSpeed < 0) //if the motor should drive backward (negative speed)
{
digitalWrite(BIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(BIN2, HIGH); //set pin 2 to high
}
else //if the motor should stop
{
digitalWrite(BIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(BIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
analogWrite(PWMB, abs(motorSpeed)); //now that the motor direction is set, drive it at the entered speed
}
What You Should See
Open the Serial Monitor. It should prompt you to enter a command that contains a direction and distance. When you type a direction and distance into the serial monitor the robot will move or turn.
Program Overview
- Prompt the user to enter a command and list the shortcuts for the directions.
- Wait for a serial command.
- Read the first part of the serial command and set that as the direction. Then read the second part of the command and set it as the distance: a. If the direction is “f”, drive both motors forward for the distance. b. If the direction is “b”, drive both motors backward for the distance. c. If the direction is “r”, drive the right motor backward and the left motor forward. d. If the direction is “l”, drive the left motor backward and the right motor forward.
Code to Note
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Parsing Strings:Serial.readStringUntil(‘ ‘); | Reads a serial message until the first space and saves it as a string. |
String to Int:string_name.toInt(); | If a number is stored in a string variable, this will convert it to an integer, which can be used in math equations. |
| User Functions | Description |
rightMotor(motor_distance); | Drive the right motor long enough to travel the specified distance. |
leftMotor(motor_distance); | Drive the left motor long enough to travel the specified distance. |
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Replace the switch with a button | Try wiring a button into the circuit instead of the sliding switch. Now the motor only turns on when you push the button! |
| Replace the switch with a sensor | Try changing the code so that the motor is activated by another sensor, like the photoresistor. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Motor not spinning | Check the wiring to the motor driver. There are a lot of connections, and it’s easy to mix one of them up with another. If only one motor is working, check the wires coming from the non-working motor. Make sure they have not come loose from the motor. |
| Switch not working | Make sure that you are hooked up to the middle pin and one side pin on the switch. |
| Still not working? | Jumper wires unfortunately can go "bad" from getting bent too much. The copper wire inside can break, leaving an open connection in your circuit. If you are certain that your circuit is wired correctly and that your code is error-free and uploaded but you are still encountering issues, try replacing one or more of the jumper wires for the component that is not working. |
Circuit 5C: Autonomous Robot
Free the robots! In this circuit, you’ll unplug your robot and program it to navigate the world on its own. When the robot senses an object using the distance sensor, it will back up and change course.
Parts Needed
Grab the following quantities of each part listed to build this circuit:
Additional Materials
- Scissors (NOT INCLUDED)
- 4x AA Batteries (NOT INCLUDED)
New Concepts
Autonomous Vehicles
The robot that you will build uses a simple sensor to avoid obstacles. This kind of system is used in Mars rovers, autonomous cars and the bots built for all kinds of robotics competitions. Understanding this example code will set you on the path to building bigger and better autonomous vehicles!
Hardware Hookup
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Keep in mind that the ultrasonic distance sensor needs a clear path to avoid unwanted interruptions in your robot's movements. Keep the distance sensor clear of any wires from your circuit.
Battery Holder Attachment
It's time to make this robot mobile by adding the battery pack.
If you did not attach the battery pack in Project 4, cut two pieces of Dual Lock that are about 1 inch x 1 inch (2.5cm x 2.5cm) each. Remove the adhesive backing and attach one piece to the back of the battery holder.
Adhere the second piece to the bottom of the baseplate, directly in the middle.
Press the battery holder to the baseplate so that the two pieces of Dual Lock snap together. Insert the batteries into the holder if you have not done so already. Remember that batteries are polarized and can only go in one way.
Clip the binder clip back on, and you are ready to roll!
You can choose to remove the motors and battery pack while you build the circuit or leave them on. The choice is yours.
Circuit Diagram
Hookup Table
| Component | RedBoard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard | Breadboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jumper Wire | 5V | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | GND | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | 5V Rail ( + ) | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | GND Rail ( - ) | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | VIN | A1 | |||
| Motor Driver | C1-C8 (VM on C1) |
G1-G8 (PWMA on G1) |
|||
| Jumper Wire | A2 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | A3 | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 8 | J5 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 9 | J6 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 10 | J7 | |||
| Jumper Wire | J4 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 11 | J1 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 12 | J2 | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 13 | J3 | |||
| Motor 1 (Right) | A4 (Red +) | A5 (Black -) | |||
| Motor 2 (Left) | A6 (Black -) | A7 (Red +) | |||
| Switch | F25 | F26 | F27 | ||
| Jumper Wire | I26 | GND Rail ( - ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 7 | I27 | |||
| Distance Sensor | A14 (Vcc) | A15 (Trig) | A16 (Echo) | A17 (GND) | |
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 6 | E15 (Trig) | |||
| Jumper Wire | Digital Pin 5 | E16 (Echo) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E14 | 5V Rail ( + ) | |||
| Jumper Wire | E17 | GND Rail ( - ) |
Open the Sketch
To open the code, go to: File > Examples > SIK_Guide_Code-V_4 > SIK_Circuit_5C-AutonomousRobot
You can also copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:c
/*
SparkFun Inventor’s Kit
Circuit 5C - Autonomous Robot
This robot will drive around on its own and react to obstacles by backing up and turning to a new direction.
This sketch was adapted from one of the activities in the SparkFun Guide to Arduino.
Check out the rest of the book at
https://www.sparkfun.com/products/14326
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics, with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
View circuit diagram and instructions at: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/sparkfun-inventors-kit-experiment-guide---v40
Download drawings and code at: https://github.com/sparkfun/SIK-Guide-Code
*/
//the right motor will be controlled by the motor A pins on the motor driver
const int AIN1 = 13; //control pin 1 on the motor driver for the right motor
const int AIN2 = 12; //control pin 2 on the motor driver for the right motor
const int PWMA = 11; //speed control pin on the motor driver for the right motor
//the left motor will be controlled by the motor B pins on the motor driver
const int PWMB = 10; //speed control pin on the motor driver for the left motor
const int BIN2 = 9; //control pin 2 on the motor driver for the left motor
const int BIN1 = 8; //control pin 1 on the motor driver for the left motor
//distance variables
const int trigPin = 6;
const int echoPin = 5;
int switchPin = 7; //switch to turn the robot on and off
float distance = 0; //variable to store the distance measured by the distance sensor
//robot behaviour variables
int backupTime = 300; //amount of time that the robot will back up when it senses an object
int turnTime = 200; //amount that the robot will turn once it has backed up
/********************************************************************************/
void setup()
{
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); //this pin will send ultrasonic pulses out from the distance sensor
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); //this pin will sense when the pulses reflect back to the distance sensor
pinMode(switchPin, INPUT_PULLUP); //set this as a pullup to sense whether the switch is flipped
//set the motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(AIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMB, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); //begin serial communication with the computer
Serial.print("To infinity and beyond!"); //test the serial connection
}
/********************************************************************************/
void loop()
{
//DETECT THE DISTANCE READ BY THE DISTANCE SENSOR
distance = getDistance();
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" in"); // print the units
if (digitalRead(switchPin) == LOW) { //if the on switch is flipped
if (distance < 10) { //if an object is detected
//back up and turn
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("BACK!");
//stop for a moment
rightMotor(0);
leftMotor(0);
delay(200);
//back up
rightMotor(-255);
leftMotor(-255);
delay(backupTime);
//turn away from obstacle
rightMotor(255);
leftMotor(-255);
delay(turnTime);
} else { //if no obstacle is detected drive forward
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Moving...");
rightMotor(255);
leftMotor(255);
}
} else { //if the switch is off then stop
//stop the motors
rightMotor(0);
leftMotor(0);
}
delay(50); //wait 50 milliseconds between readings
}
/********************************************************************************/
void rightMotor(int motorSpeed) //function for driving the right motor
{
if (motorSpeed > 0) //if the motor should drive forward (positive speed)
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH); //set pin 1 to high
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
else if (motorSpeed < 0) //if the motor should drive backward (negative speed)
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH); //set pin 2 to high
}
else //if the motor should stop
{
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
analogWrite(PWMA, abs(motorSpeed)); //now that the motor direction is set, drive it at the entered speed
}
/********************************************************************************/
void leftMotor(int motorSpeed) //function for driving the left motor
{
if (motorSpeed > 0) //if the motor should drive forward (positive speed)
{
digitalWrite(BIN1, HIGH); //set pin 1 to high
digitalWrite(BIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
else if (motorSpeed < 0) //if the motor should drive backward (negative speed)
{
digitalWrite(BIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(BIN2, HIGH); //set pin 2 to high
}
else //if the motor should stop
{
digitalWrite(BIN1, LOW); //set pin 1 to low
digitalWrite(BIN2, LOW); //set pin 2 to low
}
analogWrite(PWMB, abs(motorSpeed)); //now that the motor direction is set, drive it at the entered speed
}
/********************************************************************************/
//RETURNS THE DISTANCE MEASURED BY THE HC-SR04 DISTANCE SENSOR
float getDistance()
{
float echoTime; //variable to store the time it takes for a ping to bounce off an object
float calculatedDistance; //variable to store the distance calculated from the echo time
//send out an ultrasonic pulse that's 10ms long
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
echoTime = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); //use the pulsein command to see how long it takes for the
//pulse to bounce back to the sensor
calculatedDistance = echoTime / 148.0; //calculate the distance of the object that reflected the pulse (half the bounce time multiplied by the speed of sound)
return calculatedDistance; //send back the distance that was calculated
}
What You Should See:
When the switch is turned off, the robot will sit still. When the switch is turned on, the robot will drive forward until it senses an object.
When it does, it will stop, back up and turn to the right before driving forward again.
Program Overview
- If the switch is turned on,
- Then start sensing the distance. a. If no obstacle is detected, then drive forward. b. If an obstacle is detected, stop, back up, and turn right. c. If no obstacle is detected, start driving forward again.
Code to Note
This code builds upon all the concepts you've learn in all the previous projects. There are no new functions or objects.
Coding Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Change the distance at which your robot reacts | Try changing the distance at which your robot stops and turns away from an obstacle. |
| Change the behavior of the robot when it senses an obstacle | Try changing the code so that your robot does something different when it senses an obstacle. |
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| The robot drives backward and/or turns in the wrong direction | Check the wiring of your motors and the way that they are mounted to the breadboard and Arduino holder. If one of your motors is flipped around, reposition it, or switch its black and red wires on the breadboard (this will reverse the direction that it turns). |
| The robot runs into obstacles | You can try gently bending the pins of the distance sensor so that it points farther up, away from the floor. The robot will get stuck if one wheel hits an object that it is driving past (the distance sensor won’t see the obstacle unless it’s in front of the robot). |
| The robot drives backward and turns when there are no obstacles | Make sure the wires are not in front of the distance sensor. Also make sure you are not in a room with large HVAC vents. As in Project 3, these vents can wreak havoc on the ultrasonic distance sensor. |
| The robot drives slow or not at all, though the RedBoard is powered | If your board is powered but the robot is slow, won't move at all, or is behaving sporadically, check the batteries. These behaviors are symptoms of low or dead batteries. |
| Still not working? | Jumper wires unfortunately can go "bad" from getting bent too much. The copper wire inside can break, leaving an open connection in your circuit. If you are certain that your circuit is wired correctly and that your code is error-free and uploaded but you are still encountering issues, try replacing one or more of the jumper wires for the component that is not working. |
Resources and Going Further
SparkFun Inventor's Kit Guidebook - V3.3
BOK-13971
SparkFun Inventor's Kit Add-On Pack - v4.0
KIT-14310The SparkFun Arduino Inventor's Guide
BOK-14326There are tons of sensors and shields you can hookup to an Arduino that will help take your projects to the next level. Here's some further reading that may help you along in learning more about the world of electronics. For more inspiration and ideas for working with your SIK, check out these tutorials:
SIK Keyboard Instrument
Sensor Kit Resource Hub
Measuring Internal Resistance of Batteries
Light-Seeking Robot
Clap On Lamp
Endless Runner Game
Or check out these blog posts for ideas:
For more info on Arduino, check out these tutorials:
- Arduino Resources and Curriculum
- Arduino Comparison Guide
- Arduino Shields
- Installing Arduino
- Installing an Arduino Library
- Arduino Data Types
For more hardware related tutorials, give these a read:
We also have additional kits available that cover different microcontrollers, development environments, and robotics.
Reference files are available here:
- Example code on GitHub
- Fritzing diagrams on GitHub
- PDF version of the Guide - 25.9 MB
- SIK Projects code on GitHub
Thanks for following along!