Contributors:
 bboyho
bboyho,
 Elias The Sparkiest
Elias The Sparkiest Introduction
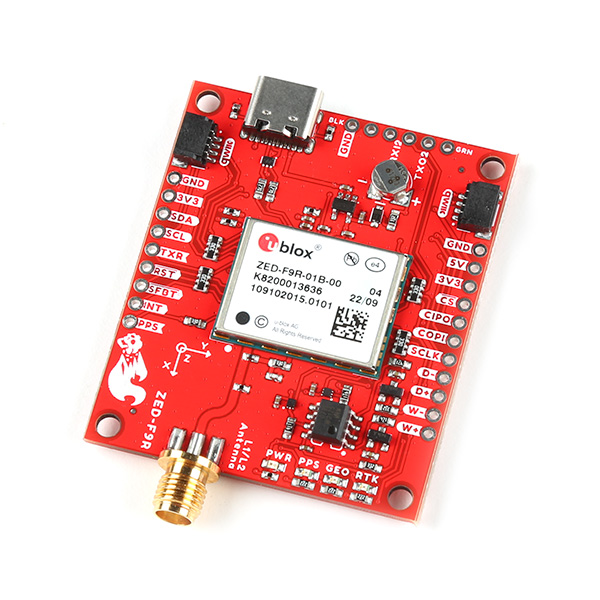
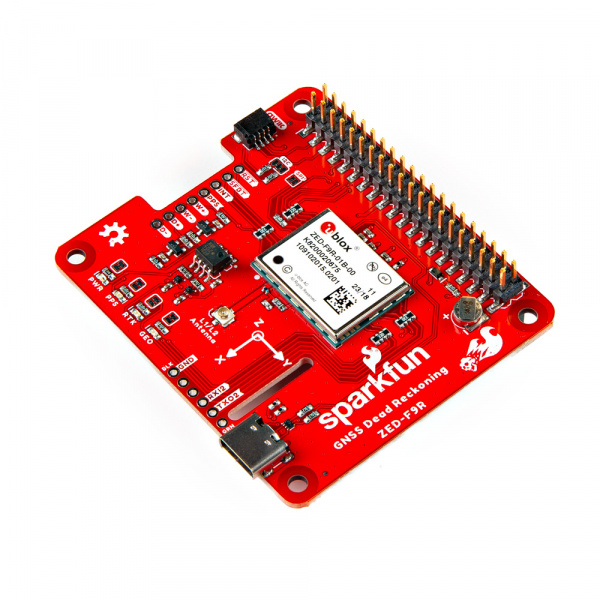
The SparkFun GPS ZED-F9R is the next iteration of u-blox's GPS offerings! This version takes advantage of dead reckoning for navigation. The u-blox ZED-F9R is a powerful GPS-RTK unit that uses a fusion of IMU, wheel ticks, a vehicle dynamics model, correction data, and GNSS measurements to provide highly accurate and continuous position for navigation in the difficult conditions. We will quickly get you set up using the Qwiic ecosystem through Arduino and Python so that you can start reading the output!
GPS-22693
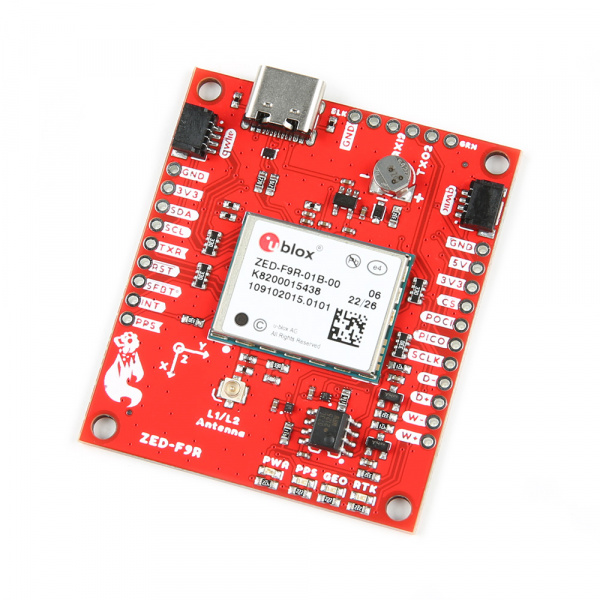
The SparkFun ZED-F9R GPS-RTK Breakout is a high precision, Automotive Dead Reckoning board with equally impressive configurat…
GPS-22660
The SparkFun ZED-F9R GPS-RTK Breakout is a high-precision Automotive Dead Reckoning board with equally impressive configurati…
GPS-21305
The SparkFun ZED-F9R GPS-RTK pHAT is a high-precision Automotive Dead Reckoning board with equally impressive configuration o…
Required Materials
To follow along with this tutorial, you will need the following materials. You may not need everything though depending on what you have. The wishlist on the left is for the ZED-F9R breakout board. The wishlist on the right includes parts for the ZED-F9R pHAT. Both include parts at a minimum to get the ZED-F9R up and running. Depending on your application, you may need additional parts for a correction source or connecting to you a vehicle to obtain heel tick/direction information. Add it to your cart, read through the guide, and adjust the cart as necessary.
Note: For those looking for the bare minimum without a microcontroller, check out the
GPS-RTK Dead Reckoning Kit. This includes the GNSS multi-band antenna, USB cable, ZED-F9R breakout board, and u.FL to SMA adapter. We also have the version with the SMA connector as well.
KIT-23452
The SparkFun GPS-RTK Dead Reckoning Kit provides you with what you need to start with GPS Real Time Kinematics and the u-blox…
KIT-23323
The SparkFun GPS-RTK Dead Reckoning Kit gives you just what you need to get started with GPS Real Time Kinematics and the u-b…
Retired
Microcontroller
Note: When this tutorial was originally written, a RedBoard Qwiic with ATmega328P was used. Since then, the Arduino Library has grown. Depending on the sketch (including the Arduino Library version) that you use, you may run the ATmega328P's limitations when compiling and uploading. We recommend using a more powerful microcontroller like the RedBoard IoT - ESP32 Development Board.
If you are using the breakout board and programming in Arduino, we recommend the IoT RedBoard ESP32 with the associated USB cable to start.
WRL-19177
The IoT RedBoard is an ESP32 WROOM-equipped development board that has everything you need in an Arduino Uno with extra perks…
PRT-14427
This is a 100mm long 4-conductor cable with 1mm JST termination. It’s designed to connect Qwiic enabled components together…
Retired
CAB-15427
These 2m cables have minor, yet genius modifications that allow both ends (the A & Micro-B) to be plugged into their ports re…
Single Board Computer
If you are using the pHAT and programming in Python, we recommend the desktop kit as it includes all the parts at a minimum to get started. Note that the Raspberry Pi 4 is power hungry so make sure that you have a sufficient power supply when using the GPS remotely. An alternative is using the Raspberry Pi Zero but it's not fast as the Raspberry Pi 4.
KIT-18735
The SparkFun Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W Basic Kit provides you with everything you need to get started with this successive Pi, al…
PRT-14803
The PiJuice is a fully uninterruptible power supply HAT that will always keep your Raspberry Pi powered.
Retired
KIT-16386
The SparkFun Raspberry Pi 4 Desktop Kit (4GB) includes everything you need to turn any monitor with an HDMI port into a deskt…
Retired
Antenna
We recommend using the multi-band magnetic mount antenna for the full RF reception and mounting it on top of a vehicle. The antenna uses an SMA connector, so make sure to get the u.FL to SMA cable if you decide to use those. Link for that is below in the antenna accessories. The length of the antenna cable was also useful in mounting it.
GPS-15192
The ANN-MB-00 GNSS multi-band antenna is extremely unique from other GNSS/GPS antennas in that it is designed to receive both…
GPS-17108
The AA.200 antenna is an active multiband GNSS magnetic mount antenna that exhibits excellent gain and good radiation pattern…
Retired
Note: If you want to try different chip antennas, you can try the
GNSS Antenna Evalutation Board listed below and make sure to get the u.FL to u.FL connector in the accessories. However, these antennas will not provide the full RF reception for the ZED-F9R. Additionally, if you are using a GNSS Antennas from the Evaluation Board, you will need to disconnect the inductor on the GPS breakout since they are passive antennas.
GPS-14986
This exceptional GPS/GNSS antenna is designed for both GPS and GLONASS reception.
GPS-14987
This tri-band GNSS antenna is ideal for GPS L1, GLONASS L1, and Beidou B2 reception.
GPS-15247
The SparkFun GNSS Chip Antenna Evaluation Board makes it easy to test out various sized GPS antennas and geometries.
Retired
GPS Antenna Accessories
Depending on your antenna, you will need an adapter to connect to the GPS-RTK's u.FL connector. If you need more than the metal from the top of a vehicle or are mounting it on a robot that does not have the necessary ground plane, you can use the GPS antenna ground plate to improve your GPS antenna's performance.
WRL-09145
This is a 4" connector cable that interfaces U.FL RF connectors to regular SMA connectors. This cable is commonly used to con…
GPS-17519
Using this simple steel plate effectively improves simple patch antenna performance to near professional level antenna setups…
Other Qwiic Cable Accessories
There are different Qwiic cable lengths available. Depending on your application, you can adjust it to your project's specifications.
KIT-15081
To make it even easier to get started, we've assembled this Qwiic Cable Kit with a variety of Qwiic cables from 50mm to 500mm…
PRT-17258
This polarized I2C cable insulation is made from silicon making it more flexible than our original Qwiic cable particularly i…
PRT-14427
This is a 100mm long 4-conductor cable with 1mm JST termination. It’s designed to connect Qwiic enabled components together…
Retired
PRT-14426
This is a 50mm long 4-conductor cable with 1mm JST termination. It’s designed to connect Qwiic enabled components together …
Retired
Heads up! If you are using the
RedBoard without a Qwiic connector, we recommend getting the Qwiic Shield for Arduino.
DEV-14352
The SparkFun Qwiic Shield is an easy-to-assemble board that provides a simple way to incorporate the Qwiic Connect System wit…
Suggested Reading
If you aren't familiar with the Qwiic system, we recommend reading here for an overview.
We would also recommend taking a look at the following tutorials if you aren't familiar with them.
GPS Basics
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is an engineering marvel that we all have access to for a relatively low cost and no subscription fee. With the correct hardware and minimal effort, you can determine your position and time almost anywhere on the globe.
I2C
An introduction to I2C, one of the main embedded communications protocols in use today.
How to Work with Jumper Pads and PCB Traces
Handling PCB jumper pads and traces is an essential skill. Learn how to cut a PCB trace, add a solder jumper between pads to reroute connections, and repair a trace with the green wire method if a trace is damaged.