Weather Station Wirelessly Connected to Wunderground
This Tutorial is Retired!
This tutorial covers concepts or technologies that are no longer current. It's still here for you to read and enjoy, but may not be as useful as our newest tutorials.
Firmware
You will need to associate your Imp to your Wifi network. This has been documented a few times. I used my cell phone and their free android app. It took a few tries, but I was eventually able to get the Imp to link up to my home network.
Note: This example assumes you are using the latest version of the Arduino IDE on your desktop. If this is your first time using Arduino, please review our tutorial on installing the Arduino IDE. If you have not previously installed an Arduino library, please check out our installation guide.
Below, you will find example code, but, for the latest version of everything, see the Wimp GitHub Repo.
language:c
/*
Weather Station using the Electric Imp
By: Nathan Seidle
SparkFun Electronics
Date: October 4th, 2013
License: This code is public domain but you buy me a beer if you use this and we meet someday (Beerware license).
Much of this is based on Mike Grusin's USB Weather Board code.
This code reads all the various sensors (wind speed, direction, rain gauge, humidty, pressure, light, batt_lvl)
and sends it to the imp, which then forwards that data to an Imp Agent on the cloud that does some processing then
bounces the weather data to Wunderground.
The Imp Shield has Card Detect tied to pin A0. We use A0 for wind direction. You will need to cut the trace on the Imp shield.
Current:
130 for 2 seconds while transmitting
~30mA during sleep
Todo:
Reset after 45 days to avoid millis roll over problems
What was the wind direction and speed gust for the last 10 minutes?
Is the 3.3V pin tied on the weather shield or elsewhere?
*/
#include <avr/wdt.h> //We need watch dog for this program
#include <Wire.h> //I2C needed for sensors
#include "MPL3115A2.h" //Pressure sensor
#include "HTU21D.h" //Humidity sensor
//#define ENABLE_LIGHTNING
//SoftwareSerial imp(8, 9); // RX, TX into Imp pin 7
MPL3115A2 myPressure; //Create an instance of the pressure sensor
HTU21D myHumidity; //Create an instance of the humidity sensor
//Hardware pin definitions
//-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
// digital I/O pins
const byte WSPEED = 3;
const byte RAIN = 2;
const byte STAT1 = 7;
#ifdef ENABLE_LIGHTNING
const byte LIGHTNING_IRQ = 4; //Not really an interrupt pin, we will catch it in software
const byte slaveSelectPin = 10; //SS for AS3935
#endif
// analog I/O pins
const byte WDIR = A0;
const byte LIGHT = A1;
const byte BATT = A2;
const byte REFERENCE_3V3 = A3;
//-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
#ifdef ENABLE_LIGHTNING
#include "AS3935.h" //Lighting dtector
#include <SPI.h> //Needed for lighting sensor
byte SPItransfer(byte sendByte);
AS3935 AS3935(SPItransfer, slaveSelectPin, LIGHTNING_IRQ);
#endif
//Global Variables
//-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
long lastSecond; //The millis counter to see when a second rolls by
unsigned int minutesSinceLastReset; //Used to reset variables after 24 hours. Imp should tell us when it's midnight, this is backup.
byte seconds; //When it hits 60, increase the current minute
byte seconds_2m; //Keeps track of the "wind speed/dir avg" over last 2 minutes array of data
byte minutes; //Keeps track of where we are in various arrays of data
byte minutes_10m; //Keeps track of where we are in wind gust/dir over last 10 minutes array of data
long lastWindCheck = 0;
volatile long lastWindIRQ = 0;
volatile byte windClicks = 0;
#ifdef ENABLE_LIGHTNING
byte lightning_distance = 0;
#endif
//We need to keep track of the following variables:
//Wind speed/dir each update (no storage)
//Wind gust/dir over the day (no storage)
//Wind speed/dir, avg over 2 minutes (store 1 per second)
//Wind gust/dir over last 10 minutes (store 1 per minute)
//Rain over the past hour (store 1 per minute)
//Total rain over date (store one per day)
byte windspdavg[120]; //120 bytes to keep track of 2 minute average
#define WIND_DIR_AVG_SIZE 120
int winddiravg[WIND_DIR_AVG_SIZE]; //120 ints to keep track of 2 minute average
float windgust_10m[10]; //10 floats to keep track of largest gust in the last 10 minutes
int windgustdirection_10m[10]; //10 ints to keep track of 10 minute max
volatile float rainHour[60]; //60 floating numbers to keep track of 60 minutes of rain
//These are all the weather values that wunderground expects:
int winddir; // [0-360 instantaneous wind direction]
float windspeedmph; // [mph instantaneous wind speed]
float windgustmph; // [mph current wind gust, using software specific time period]
int windgustdir; // [0-360 using software specific time period]
float windspdmph_avg2m; // [mph 2 minute average wind speed mph]
int winddir_avg2m; // [0-360 2 minute average wind direction]
float windgustmph_10m; // [mph past 10 minutes wind gust mph ]
int windgustdir_10m; // [0-360 past 10 minutes wind gust direction]
float humidity; // [%]
float tempf; // [temperature F]
float rainin; // [rain inches over the past hour)] -- the accumulated rainfall in the past 60 min
volatile float dailyrainin; // [rain inches so far today in local time]
//float baromin = 30.03;// [barom in] - It's hard to calculate baromin locally, do this in the agent
float pressure;
//float dewptf; // [dewpoint F] - It's hard to calculate dewpoint locally, do this in the agent
//These are not wunderground values, they are just for us
float batt_lvl = 11.8;
float light_lvl = 0.72;
// volatiles are subject to modification by IRQs
volatile unsigned long raintime, rainlast, raininterval, rain;
//-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
//Interrupt routines (these are called by the hardware interrupts, not by the main code)
//-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=
void rainIRQ()
// Count rain gauge bucket tips as they occur
// Activated by the magnet and reed switch in the rain gauge, attached to input D2
{
raintime = millis(); // grab current time
raininterval = raintime - rainlast; // calculate interval between this and last event
if (raininterval > 10) // ignore switch-bounce glitches less than 10mS after initial edge
{
dailyrainin += 0.011; //Each dump is 0.011" of water
rainHour[minutes] += 0.011; //Increase this minute's amount of rain
rainlast = raintime; // set up for next event
}
}
void wspeedIRQ()
// Activated by the magnet in the anemometer (2 ticks per rotation), attached to input D3
{
if (millis() - lastWindIRQ > 10) // Ignore switch-bounce glitches less than 10ms (142MPH max reading) after the reed switch closes
{
lastWindIRQ = millis(); //Grab the current time
windClicks++; //There is 1.492MPH for each click per second.
}
}
void setup()
{
wdt_reset(); //Pet the dog
wdt_disable(); //We don't want the watchdog during init
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(WSPEED, INPUT_PULLUP); // input from wind meters windspeed sensor
pinMode(RAIN, INPUT_PULLUP); // input from wind meters rain gauge sensor
pinMode(WDIR, INPUT);
pinMode(LIGHT, INPUT);
pinMode(BATT, INPUT);
pinMode(REFERENCE_3V3, INPUT);
pinMode(STAT1, OUTPUT);
midnightReset(); //Reset rain totals
//Configure the pressure sensor
myPressure.begin(); // Get sensor online
myPressure.setModeBarometer(); // Measure pressure in Pascals from 20 to 110 kPa
myPressure.setOversampleRate(128); // Set Oversample to the recommended 128
myPressure.enableEventFlags(); // Enable all three pressure and temp event flags
myPressure.setModeActive(); // Go to active mode and start measuring!
//Configure the humidity sensor
myHumidity.begin();
#ifdef ENABLE_LIGHTNING
startLightning(); //Init the lighting sensor
#endif
seconds = 0;
lastSecond = millis();
// attach external interrupt pins to IRQ functions
attachInterrupt(0, rainIRQ, FALLING);
attachInterrupt(1, wspeedIRQ, FALLING);
// turn on interrupts
interrupts();
Serial.println("Wimp Weather Station online!");
reportWeather();
// wdt_enable(WDTO_1S); //Unleash the beast
}
void loop()
{
wdt_reset(); //Pet the dog
//Keep track of which minute it is
if(millis() - lastSecond >= 1000)
{
lastSecond += 1000;
//Take a speed and direction reading every second for 2 minute average
if(++seconds_2m > 119) seconds_2m = 0;
//Calc the wind speed and direction every second for 120 second to get 2 minute average
windspeedmph = get_wind_speed();
winddir = get_wind_direction();
windspdavg[seconds_2m] = (int)windspeedmph;
winddiravg[seconds_2m] = winddir;
//if(seconds_2m % 10 == 0) displayArrays();
//Check to see if this is a gust for the minute
if(windspeedmph > windgust_10m[minutes_10m])
{
windgust_10m[minutes_10m] = windspeedmph;
windgustdirection_10m[minutes_10m] = winddir;
}
//Check to see if this is a gust for the day
//Resets at midnight each night
if(windspeedmph > windgustmph)
{
windgustmph = windspeedmph;
windgustdir = winddir;
}
//Blink stat LED briefly to show we are alive
digitalWrite(STAT1, HIGH);
//reportWeather(); //Print the current readings. Takes 172ms.
delay(25);
digitalWrite(STAT1, LOW);
//If we roll over 60 seconds then update the arrays for rain and windgust
if(++seconds > 59)
{
seconds = 0;
if(++minutes > 59) minutes = 0;
if(++minutes_10m > 9) minutes_10m = 0;
rainHour[minutes] = 0; //Zero out this minute's rainfall amount
windgust_10m[minutes_10m] = 0; //Zero out this minute's gust
minutesSinceLastReset++; //It's been another minute since last night's midnight reset
}
}
//Check to see if there's been lighting
#ifdef ENABLE_LIGHTNING
if(digitalRead(LIGHTNING_IRQ) == HIGH)
{
//We've got something!
lightning_distance = readLightning();
}
#endif
//Wait for the imp to ping us with the ! character
if(Serial.available())
{
byte incoming = Serial.read();
if(incoming == '!')
{
reportWeather(); //Send all the current readings out the imp and to its agent for posting to wunderground. Takes 196ms
//Serial.print("Pinged!");
#ifdef ENABLE_LIGHTNING
//Give imp time to transmit then read any erroneous lightning strike
delay(1000); //Give the Imp time to transmit
readLightning(); //Clear any readings and forget it
#endif
}
else if(incoming == '@') //Special character from Imp indicating midnight local time
{
midnightReset(); //Reset a bunch of variables like rain and daily total rain
//Serial.print("Midnight reset");
}
else if(incoming == '#') //Special character from Imp indicating a hardware reset
{
//Serial.print("Watchdog reset");
delay(5000); //This will cause the system to reset because we don't pet the dog
}
}
//If we go for more than 24 hours without a midnight reset then force a reset
//24 hours * 60 mins/hr = 1,440 minutes + 10 extra minutes. We hope that Imp is doing it.
if(minutesSinceLastReset > (1440 + 10))
{
midnightReset(); //Reset a bunch of variables like rain and daily total rain
//Serial.print("Emergency midnight reset");
}
delay(100); //Update every 100ms. No need to go any faster.
}
//Prints the various arrays for debugging
void displayArrays()
{
//Windgusts in this hour
Serial.println();
Serial.print(minutes);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(seconds);
Serial.print("Windgust last 10 minutes:");
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)
{
if(i % 10 == 0) Serial.println();
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(windgust_10m[i]);
}
//Wind speed avg for past 2 minutes
/*Serial.println();
Serial.print("Wind 2 min avg:");
for(int i = 0 ; i < 120 ; i++)
{
if(i % 30 == 0) Serial.println();
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(windspdavg[i]);
}*/
//Rain for last hour
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Rain hour:");
for(int i = 0 ; i < 60 ; i++)
{
if(i % 30 == 0) Serial.println();
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(rainHour[i]);
}
}
//When the imp tells us it's midnight, reset the total amount of rain and gusts
void midnightReset()
{
dailyrainin = 0; //Reset daily amount of rain
windgustmph = 0; //Zero out the windgust for the day
windgustdir = 0; //Zero out the gust direction for the day
minutes = 0; //Reset minute tracker
seconds = 0;
lastSecond = millis(); //Reset variable used to track minutes
minutesSinceLastReset = 0; //Zero out the backup midnight reset variable
}
//Calculates each of the variables that wunderground is expecting
void calcWeather()
{
//current winddir, current windspeed, windgustmph, and windgustdir are calculated every 100ms throughout the day
//Calc windspdmph_avg2m
float temp = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 120 ; i++)
temp += windspdavg[i];
temp /= 120.0;
windspdmph_avg2m = temp;
//Calc winddir_avg2m, Wind Direction
//You can't just take the average. Google "mean of circular quantities" for more info
//We will use the Mitsuta method because it doesn't require trig functions
//And because it sounds cool.
//Based on: http://abelian.org/vlf/bearings.html
//Based on: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1813483/averaging-angles-again
long sum = winddiravg[0];
int D = winddiravg[0];
for(int i = 1 ; i < WIND_DIR_AVG_SIZE ; i++)
{
int delta = winddiravg[i] - D;
if(delta < -180)
D += delta + 360;
else if(delta > 180)
D += delta - 360;
else
D += delta;
sum += D;
}
winddir_avg2m = sum / WIND_DIR_AVG_SIZE;
if(winddir_avg2m >= 360) winddir_avg2m -= 360;
if(winddir_avg2m < 0) winddir_avg2m += 360;
//Calc windgustmph_10m
//Calc windgustdir_10m
//Find the largest windgust in the last 10 minutes
windgustmph_10m = 0;
windgustdir_10m = 0;
//Step through the 10 minutes
for(int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++)
{
if(windgust_10m[i] > windgustmph_10m)
{
windgustmph_10m = windgust_10m[i];
windgustdir_10m = windgustdirection_10m[i];
}
}
//Calc humidity
humidity = myHumidity.readHumidity();
//float temp_h = myHumidity.readTemperature();
//Serial.print(" TempH:");
//Serial.print(temp_h, 2);
//Calc tempf from pressure sensor
tempf = myPressure.readTempF();
//Serial.print(" TempP:");
//Serial.print(tempf, 2);
//Total rainfall for the day is calculated within the interrupt
//Calculate amount of rainfall for the last 60 minutes
rainin = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 60 ; i++)
rainin += rainHour[i];
//Calc pressure
pressure = myPressure.readPressure();
//Calc dewptf
//Calc light level
light_lvl = get_light_level();
//Calc battery level
batt_lvl = get_battery_level();
//Lightning is checked in the main loop
}
//Returns the voltage of the light sensor based on the 3.3V rail
//This allows us to ignore what VCC might be (an Arduino plugged into USB has VCC of 4.5 to 5.2V)
float get_light_level()
{
float operatingVoltage = averageAnalogRead(REFERENCE_3V3);
float lightSensor = averageAnalogRead(LIGHT);
operatingVoltage = 3.3 / operatingVoltage; //The reference voltage is 3.3V
lightSensor *= operatingVoltage;
return(lightSensor);
}
//Returns the voltage of the raw pin based on the 3.3V rail
//The battery can ranges from 4.2V down to around 3.3V
//This function allows us to ignore what VCC might be (an Arduino plugged into USB has VCC of 4.5 to 5.2V)
//The weather shield has a pin called RAW (VIN) fed through through two 5% resistors and connected to A2 (BATT):
//3.9K on the high side (R1), and 1K on the low side (R2)
float get_battery_level()
{
float operatingVoltage = averageAnalogRead(REFERENCE_3V3);
float rawVoltage = averageAnalogRead(BATT);
operatingVoltage = 3.30 / operatingVoltage; //The reference voltage is 3.3V
rawVoltage *= operatingVoltage; //Convert the 0 to 1023 int to actual voltage on BATT pin
rawVoltage *= 4.90; //(3.9k+1k)/1k - multiply BATT voltage by the voltage divider to get actual system voltage
return(rawVoltage);
}
//Returns the instataneous wind speed
float get_wind_speed()
{
float deltaTime = millis() - lastWindCheck; //750ms
deltaTime /= 1000.0; //Covert to seconds
float windSpeed = (float)windClicks / deltaTime; //3 / 0.750s = 4
windClicks = 0; //Reset and start watching for new wind
lastWindCheck = millis();
windSpeed *= 1.492; //4 * 1.492 = 5.968MPH
/* Serial.println();
Serial.print("Windspeed:");
Serial.println(windSpeed);*/
return(windSpeed);
}
int get_wind_direction()
// read the wind direction sensor, return heading in degrees
{
unsigned int adc;
adc = averageAnalogRead(WDIR); // get the current reading from the sensor
// The following table is ADC readings for the wind direction sensor output, sorted from low to high.
// Each threshold is the midpoint between adjacent headings. The output is degrees for that ADC reading.
// Note that these are not in compass degree order! See Weather Meters datasheet for more information.
if (adc < 380) return (113);
if (adc < 393) return (68);
if (adc < 414) return (90);
if (adc < 456) return (158);
if (adc < 508) return (135);
if (adc < 551) return (203);
if (adc < 615) return (180);
if (adc < 680) return (23);
if (adc < 746) return (45);
if (adc < 801) return (248);
if (adc < 833) return (225);
if (adc < 878) return (338);
if (adc < 913) return (0);
if (adc < 940) return (293);
if (adc < 967) return (315);
if (adc < 990) return (270);
return (-1); // error, disconnected?
}
//Reports the weather string to the Imp
void reportWeather()
{
calcWeather(); //Go calc all the various sensors
Serial.print("$,winddir=");
Serial.print(winddir);
Serial.print(",windspeedmph=");
Serial.print(windspeedmph, 1);
Serial.print(",windgustmph=");
Serial.print(windgustmph, 1);
Serial.print(",windgustdir=");
Serial.print(windgustdir);
Serial.print(",windspdmph_avg2m=");
Serial.print(windspdmph_avg2m, 1);
Serial.print(",winddir_avg2m=");
Serial.print(winddir_avg2m);
Serial.print(",windgustmph_10m=");
Serial.print(windgustmph_10m, 1);
Serial.print(",windgustdir_10m=");
Serial.print(windgustdir_10m);
Serial.print(",humidity=");
Serial.print(humidity, 1);
Serial.print(",tempf=");
Serial.print(tempf, 1);
Serial.print(",rainin=");
Serial.print(rainin, 2);
Serial.print(",dailyrainin=");
Serial.print(dailyrainin, 2);
Serial.print(","); //Don't print pressure= because the agent will be doing calcs on the number
Serial.print(pressure, 2);
Serial.print(",batt_lvl=");
Serial.print(batt_lvl, 2);
Serial.print(",light_lvl=");
Serial.print(light_lvl, 2);
#ifdef LIGHTNING_ENABLED
Serial.print(",lightning_distance=");
Serial.print(lightning_distance);
#endif
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println("#,");
//Test string
//Serial.println("$,winddir=270,windspeedmph=0.0,windgustmph=0.0,windgustdir=0,windspdmph_avg2m=0.0,winddir_avg2m=12,windgustmph_10m=0.0,windgustdir_10m=0,humidity=998.0,tempf=-1766.2,rainin=0.00,dailyrainin=0.00,-999.00,batt_lvl=16.11,light_lvl=3.32,#,");
}
//Takes an average of readings on a given pin
//Returns the average
int averageAnalogRead(int pinToRead)
{
byte numberOfReadings = 8;
unsigned int runningValue = 0;
for(int x = 0 ; x < numberOfReadings ; x++)
runningValue += analogRead(pinToRead);
runningValue /= numberOfReadings;
return(runningValue);
}
//The following is for the AS3935 lightning sensor
#ifdef ENABLE_LIGHTNING
byte readLightning(void)
{
byte distance = 0;
//Check to see if we have lightning!
if(digitalRead(LIGHTNING_IRQ) == HIGH)
{
// first step is to find out what caused interrupt
// as soon as we read interrupt cause register, irq pin goes low
int irqSource = AS3935.interruptSource();
// returned value is bitmap field, bit 0 - noise level too high, bit 2 - disturber detected, and finally bit 3 - lightning!
if (irqSource & 0b0001)
{
//Serial.println("Noise level too high, try adjusting noise floor");
}
if (irqSource & 0b0100)
{
//Serial.println("Disturber detected");
distance = 64;
}
if (irqSource & 0b1000)
{
// need to find how far that lightning stroke, function returns approximate distance in kilometers,
// where value 1 represents storm in detector's near victinity, and 63 - very distant, out of range stroke
// everything in between is just distance in kilometers
distance = AS3935.lightningDistanceKm();
//Serial.print("Lightning: ");
//Serial.print(lightning_distance, DEC);
//Serial.println(" km");
//The AS3935 remembers the nearest strike distance. For example 15km away then 10, then overhead all following
//distances (10, 20, 30) will instead output as 'Storm overhead, watch out!'. Resetting the chip erases this.
lightning_init();
}
}
return(distance);
}
void startLightning(void)
{
pinMode(slaveSelectPin, OUTPUT); // set the slaveSelectPin as an output:
pinMode(LIGHTNING_IRQ, INPUT_PULLUP); //Set IRQ pin as input
SPI.begin(); //Start SPI
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE1); // NB! chip uses SPI MODE1
SPI.setClockDivider(SPI_CLOCK_DIV16); //Uno 16MHz / 16 = 1MHz
SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST); // and chip is MSB first
lightning_init(); //Setup the values for the sensor
Serial.println("Lightning sensor online");
}
void lightning_init()
{
AS3935.reset(); // reset all internal register values to defaults
// if lightning detector can not tune tank circuit to required tolerance,
// calibration function will return false
if(!AS3935.calibrate())
{
Serial.println("Tuning out of range, check your wiring, your sensor and make sure physics laws have not changed!");
}
AS3935.setOutdoors(); //The weather station is outdoors
AS3935.enableDisturbers(); //We want to know if a man-made event happens
AS3935.setNoiseFloor(3); //See table 16 of the AS3935 datasheet. 4-6 works. This was found through experimentation.
//printAS3935Registers();
}
/*void printAS3935Registers()
{
int noiseFloor = AS3935.getNoiseFloor();
int spikeRejection = AS3935.getSpikeRejection();
int watchdogThreshold = AS3935.getWatchdogThreshold();
Serial.print("Noise floor is: ");
Serial.println(noiseFloor, DEC);
Serial.print("Spike rejection is: ");
Serial.println(spikeRejection, DEC);
Serial.print("Watchdog threshold is: ");
Serial.println(watchdogThreshold, DEC);
}*/
byte SPItransfer(byte sendByte)
{
return SPI.transfer(sendByte);
}
#endif
Load the code onto your RedBoard (or Arduino of choice). Open a terminal window at 9600bps. You should see new weather data upon power up and every time you send the ! character.
Next, grab the two code blocks (agent and device shown above) for the Imp. The Electric Imp has two types of code: the device code runs on the actual SD card, the agent runs out on the cloud. The Imp itself is pretty powerful, but the cloud has far more resources. Thus, we do the low-level string manipulation on the device but leave the heavy lifting to the agent.
You'll need to replace STATION_ID and STATION_PASSWORD with your own ID and password.
Note: Because we are passing an http post, you can't have symbols in your password. You may need to change your Wunderground password to only have alphenumerics.
Setting Proper Altitude
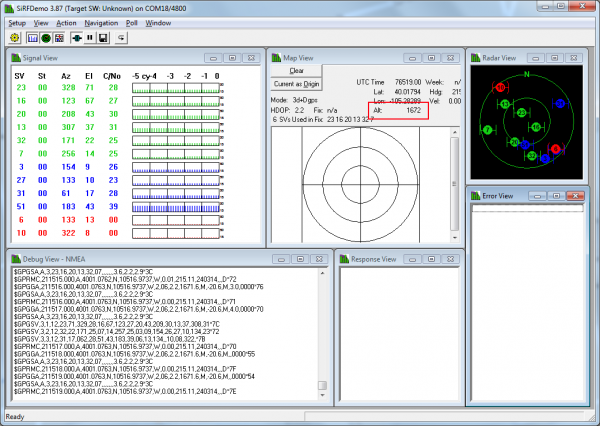
Weather stations across the world report a scaled pressure reading that takes into account the local altitude (this is often called the altimeter setting). In order to be as accurate as possible, we recommend you use a cell phone or a GPS module (my current favorite is the GP-635T) to obtain an altitude reading. Meters matter, so take a couple readings and average them together. Once you know your local altitude replace LOCAL_ALTITUDE_METERS in the agent.
You may also want to enter the altitude and location into Wunderground's site. This will give people in your community a better idea of what weather is happening at what location. Publicly posting your weather station's location has obvious privacy implications, so think about it before you make your station publicly viewable.
How It Works
The RedBoard monitors all the various sensors (humidity, temperature, rain gauge, etc) and does a little bit of processing on the data. It mashes up the individual data with identifiers and creates a comma delimited string. The Imp reads this concatenated string and looks for the correct header ($) and ender (#) characters. If an incomplete frame is received, it's ignored. The Imp then reports this string, verbatim, to the Agent out in the cloud.
The Agent receives this string and cracks it apart into its pieces. Because the RedBoard has pretty limited resources, we report raw Pascals to the Imp and let the Agent do the complex mmHg pressure and dew point calculations. Once all the pieces are calculated, we create another big string that is an http:// address. Posting this long link causes the weather data to be transmitted to Wunderground. After all that, we can check our weather station and see what the weather is like!