Audio Codec Breakout - WM8960 Hookup Guide
Example 9: I2S Bluetooth
In this example, we will wirelessly connect a Bluetooth audio source and use the IoT RedBoard ESP32 as a Bluetooth audio sink. Once the audio codec is set as an I2S peripherial, the ESP32 will receive audio and play it back via I2S. Once the WM8960 receives the I2S audio, it will be sent to the DAC and then the headphone output.
Hardware Hookup
SparkFun Qwiic Wireless Speaker Kit
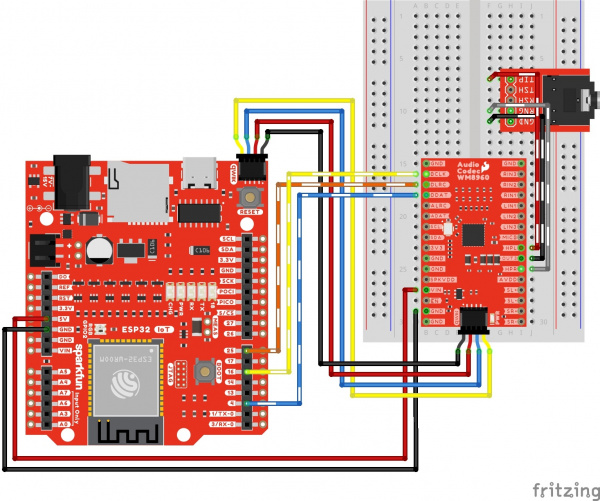
KIT-21773Connect power, I2C, I2S, and the headphone output as explained earlier. Your circuit should look similar to the circuit diagram below.
Connect a USB cable into your IoT RedBoard ESP32. Turn on the Bluetooth on your audio source (e.g. MP3 player, smartphone, or computer). Then connect your headphones to the output. For those that are sensitive to sounds, you may want to hear the example output before inserting the headphones into your ears.
Upload Code
From the menu, select the following: File > Examples > SparkFun WM8960 Arduino Library > Example_09_I2S_Bluetooth. If you have not already, select your Board (in this case the SparkFun ESP32 IoT RedBoard), and associated COM port. Then hit the upload button.
Open the Arduino Serial Monitor and set it to 1152000 baud to view the serial output. On your phone, pair and connect to the ESP32's Bluetooth. In this case, the name of the ESP32's Bluetooth is called "myCodec". Then hit the play button on your audio source. Make sure that the volume from the audio source is turned up. You should hear some music from the headphones.
Try adding a battery to the mix to untether the circuit from your computer. Do a little dance or flip and rock to the beat of the music! Of course, you'll want to be careful of the wires while moving around. For a more secure connection, you could take a solderable breadboard or an Arduino shield and manually wire the circuit together