Hazardous Gas Monitor
Calculate Gas Sensor PPM
Each of the gas sensors outputs an analog value from 0 to 4095. To convert this value into voltage, use the following equation:
Sensor Voltage = AnalogReading * 3.3V / 4095
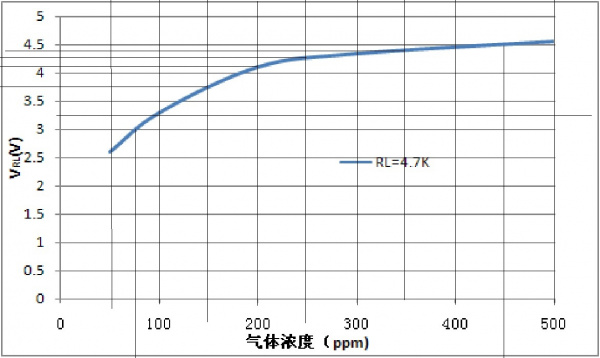
Once you have the sensor voltage, you can convert that into a parts per million ("PPM") reading using the sensitivity calibration curve on page 5 of the gas sensor datasheets. To do this, recreate the sensitivity curve by picking data points from the graph or using a graphical analysis software like Engauge Digitizer.
Plot PPM on the y-axis and V_RL on the x-axis, where V_RL is the sensor voltage. There is a lot of room for error with this method, but it will give us enough accuracy to identify dangerous levels of hazardous gases. Estimated error bars are around 20 PPM for the LPG and Methane sensors, and about 5 PPM for the CO sensor.
Next, find an approximate equation for the PPM vs. V_RL curve. I used an exponential fit (e.g. y = e^x) and got the following equations:
LPG sensor: PPM = 26.572*e^(1.2894*V_RL)
Methane sensor: PPM = 10.938*e(1.7742*V_RL)
CO sensor: PPM = 3.027*e^(1.0698*V_RL)