Dialog ULP WiFi DA16200 R3 Shield Hookup Guide
Contributors:
 Alex the Giant, Ell C
Alex the Giant, Ell C
Example 3: Connecting to WiFi
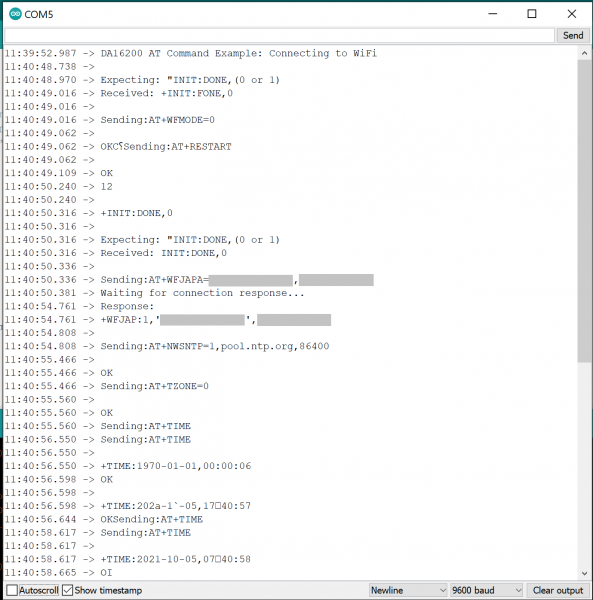
Let's check out the WiFi with a simple example to grab the time.
Copy and paste the code below into a fresh Arduino sketch. Find the lines that define the SOFTWARE_SERIAL_BAUD and uncomment the line that contains the appropriate baud rate.
language:c
/******************************************************************************
Example_03 WiFi Communcation
Connect WiFi using the provided network credentials
Talk to NTP server to set the current date/time
Update the time to the correct time zone
Print the current time approx. once every second
Development environment specifics:
IDE: Arduino 1.8.13
Hardware Platform: SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic (3.3V LOGIC!!!!)
Hardware Connections:
Connect the shield to a 3.3V logic Arduino R3 board
Make sure switch is in the "SW" position
ARDUINO --> WiFi Shield
8 --> RX1
9 --> TX1
4 --> RTC_PWR_KEY
3.3V --> 3.3V
GND --> GND
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
******************************************************************************/
#include<SoftwareSerial.h>
#define RX1 8
#define TX1 9
#define RTC_PWR_KEY 4
//#define SOFTWARE_SERIAL_BAUD 115200
//#define SOFTWARE_SERIAL_BAUD 9600
String wifiSSID = "SSID";
String wifiPass = "PASSWORD";
int timezoneOffset = 0; //The hours offset from UTC (Mountain time is -6 for daylight savings, and -7 for standard)
SoftwareSerial WiFiSerial(RX1,TX1); //Configure SoftwareSerial
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
WiFiSerial.begin(SOFTWARE_SERIAL_BAUD); //Set SoftwareSerial baud
//Enable DA16200 Module RTC power block
pinMode(RTC_PWR_KEY,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RTC_PWR_KEY,HIGH);
Serial.println("DA16200 AT Command Example: Connecting to WiFi\n");
//Listen for ready message ("+INIT:DONE")
byte count = 0;
String msg = "";
while(count<20)
{
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
msg += char(WiFiSerial.read());
}
if(msg.length() > 5) break;
count++;
delay(100);
}
msg = msg.substring(3,msg.length()); //Remove NULL,CR,LF characters from response
if(msg.length()>5)
{
Serial.println("Expecting: \"INIT:DONE,(0 or 1)");
Serial.println("Received: " + msg);
}
else
{
Serial.println("Failed to receive initialization message.\n" \
"Make sure you're using the correct baud rate.\n");
while(1);
}
//Configure module for STA mode
Serial.println("Sending:AT+WFMODE=0");
WiFiSerial.println("AT+WFMODE=0");
//Wait for "OK" response
while(1)
{
msg = "";
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
msg += char(WiFiSerial.read());
delay(1);
}
Serial.print(msg);
if(msg.length() > 1) break;
}
//Apply a software reset to finish changing the mode
Serial.println("Sending:AT+RESTART");
WiFiSerial.println("AT+RESTART");
//Wait for "OK" response
while(1)
{
msg = "";
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
msg += char(WiFiSerial.read());
delay(1);
}
Serial.print(msg);
if(msg.length() > 1) break;
}
//Listen for ready message ("+INIT:DONE") after the reset is finished
count = 0;
msg = "";
while(count<20)
{
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
msg += char(WiFiSerial.read());
}
if(msg.length() > 5) break;
count++;
delay(100);
}
Serial.println(count);
Serial.println(msg);
msg = msg.substring(3,msg.length()); //Remove NULL,CR,LF characters from response
if(msg.length()>5)
{
Serial.println("Expecting: \"INIT:DONE,(0 or 1)");
Serial.println("Received: " + msg);
}
else
{
Serial.println("Failed to receive initialization message.\n" \
"Continuing anyway...\n");
}
//Connect to WiFi using the provided credentials
Serial.println("Sending:AT+WFJAPA=" + wifiSSID + "," + wifiPass);
WiFiSerial.println("AT+WFJAPA=" + wifiSSID + "," + wifiPass);
Serial.println("Waiting for connection response...");
while(1)
{
msg = "";
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
msg += char(WiFiSerial.read());
delay(1);
}
if(msg.length() > 10)
{
Serial.print("Response:");
Serial.println(msg);
break;
}
}
msg = msg.substring(3,msg.length()); //Remove NULL,CR,LF characters from response
//If connection to AP is successful, response will be WFJAP:1,SSID,IP_ADDRESS, or WJAP:0 if failed
if(msg.startsWith("WFJAP:1"))
{
//Talk to NTP server to get the current time, along with how often to get time sync
Serial.println("Sending:AT+NWSNTP=1,pool.ntp.org,86400");
WiFiSerial.println("AT+NWSNTP=1,pool.ntp.org,86400");
//Wait for "OK" response
while(1)
{
String msg = "";
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
msg += char(WiFiSerial.read());
delay(1);
}
Serial.print(msg);
if(msg.length() > 1) break;
}
//Provides the correct UTC offset for the current time
Serial.println("Sending:AT+TZONE="+String(timezoneOffset*3600));
WiFiSerial.println("AT+TZONE="+String(timezoneOffset*3600));
//Wait for "OK" response
while(1)
{
String msg = "";
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
msg += char(WiFiSerial.read());
delay(1);
}
Serial.print(msg);
if(msg.length() > 1) break;
}
}
else
{
Serial.println("Connection unsucessful :(\n\n" \
"Make sure the WiFi credentials are correct, and the module is in the station mode");
while(1);
}
}
void loop() {
//Get the current time
Serial.println("Sending:AT+TIME");
WiFiSerial.println("AT+TIME");
while(WiFiSerial.available())
{
Serial.print(char(WiFiSerial.read()));
delay(1);
}
delay(1000);
}
Set your Board and Serial Port, and then upload the sketch to your Arduino. Then open the serial monitor. Make sure your baud rate is set to 9600. You'll begin to see output.