TB6612FNG Hookup Guide
Contributors:
 M-Short
M-Short
Board Overview
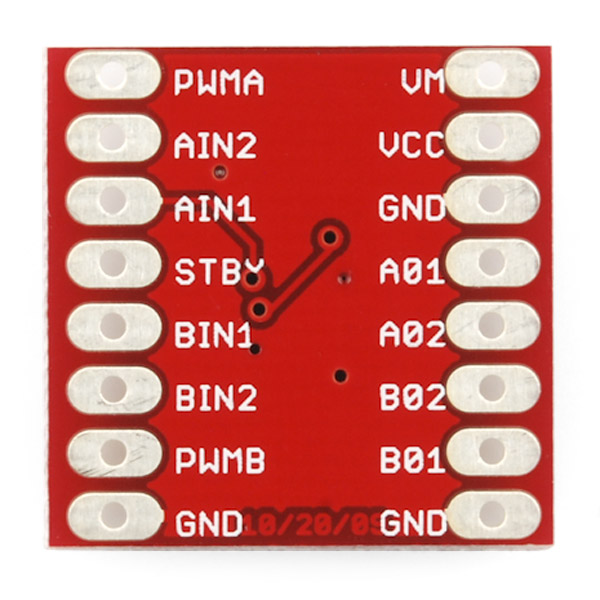
Let's discuss the pinout for the TB6612FNG breakout. We basically have three types of pins: power, input, and output, and they are all labeled on the back of the board.
Back of the board
Each pin and its function is covered in the table below.
| Pin Label | Function | Power/Input/Output | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| VM | Motor Voltage | Power | This is where you provide power for the motors (2.2V to 13.5V) |
| VCC | Logic Voltage | Power | This is the voltage to power the chip and talk to the microcontroller (2.7V to 5.5V) |
| GND | Ground | Power | Common Ground for both motor voltage and logic voltage (all GND pins are connected) |
| STBY | Standby | Input | Allows the H-bridges to work when high (has a pulldown resistor so it must actively pulled high) |
| AIN1/BIN1 | Input 1 for channels A/B | Input | One of the two inputs that determines the direction. |
| AIN2/BIN2 | Input 2 for channels A/B | Input | One of the two inputs that determines the direction. |
| PWMA/PWMB | PWM input for channels A/B | Input | PWM input that controls the speed |
| A01/B01 | Output 1 for channels A/B | Output | One of the two outputs to connect the motor |
| A02/B02 | Output 2 for channels A/B | Output | One of the two outputs to connect the motor |
Now, for a quick overview of how to control each of the channels. If you are using an Arduino, don't worry about this too much as the library takes care of all of this for you. If you are using a different control platform, pay attention. When the outputs are set to High/Low your motor will run. When they are set to Low/High the motor will run in the opposite direction. In both cases, the speed is controlled by the PWM input.
| In1 | In2 | PWM | Out1 | Out2 | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | H | H/L | L | L | Short brake |
| L | H | H | L | H | CCW |
| L | H | L | L | L | Short brake |
| H | L | H | H | L | CW |
| H | L | L | L | L | Short brake |
| L | L | H | OFF | OFF | Stop |
Don't forget STBY must be high for the motors to drive.