MicroMod ESP32 Processor Board Hookup Guide
Arduino Example: WiFi
The ESP32 Arduino core includes a handful of WiFi examples, which demonstrate everything from scanning for nearby networks to sending data to a client server. You can find the examples under the File > Examples > WiFi menu.
Here's another example using the WiFi library, which demonstrates how to connect to a nearby WiFi network and poll a remote domain (http://example.com/) as a client.
language:c
#include <WiFi.h>
// WiFi network name and password:
const char * networkName = "YOUR_NETWORK_HERE";
const char * networkPswd = "YOUR_PASSWORD_HERE";
// Internet domain to request from:
const char * hostDomain = "example.com";
const int hostPort = 80;
const int BUTTON_PIN = 0;
const int LED_PIN = LED_BUILTIN;
void setup()
{
// Initilize hardware:
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Connect to the WiFi network (see function below loop)
connectToWiFi(networkName, networkPswd);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // LED off
Serial.print("Press the Boot button to connect to ");
Serial.println(hostDomain);
}
void loop()
{
if (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW)
{ // Check if button has been pressed
while (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW)
; // Wait for button to be released
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // Turn on LED
requestURL(hostDomain, hostPort); // Connect to server
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn off LED
}
}
void connectToWiFi(const char * ssid, const char * pwd)
{
int ledState = 0;
printLine();
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi network: " + String(ssid));
WiFi.begin(ssid, pwd);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED)
{
// Blink LED while we're connecting:
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, ledState);
ledState = (ledState + 1) % 2; // Flip ledState
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("WiFi connected!");
Serial.print("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void requestURL(const char * host, uint8_t port)
{
printLine();
Serial.println("Connecting to domain: " + String(host));
// Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections
WiFiClient client;
if (!client.connect(host, port))
{
Serial.println("connection failed");
return;
}
Serial.println("Connected!");
printLine();
// This will send the request to the server
client.print((String)"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n" +
"Host: " + String(host) + "\r\n" +
"Connection: close\r\n\r\n");
unsigned long timeout = millis();
while (client.available() == 0)
{
if (millis() - timeout > 5000)
{
Serial.println(">>> Client Timeout !");
client.stop();
return;
}
}
// Read all the lines of the reply from server and print them to Serial
while (client.available())
{
String line = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.print(line);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("closing connection");
client.stop();
}
void printLine()
{
Serial.println();
for (int i=0; i<30; i++)
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println();
}
Make sure you fill in the networkName and networkPswd variables with the name (or SSID) and password of your WiFi network! Once you've done that and uploaded the code, open your serial monitor.
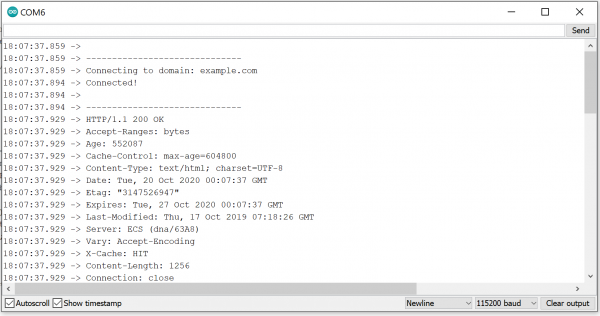
After your ESP32 connects to the WiFi network, it will wait for you to press the "Boot" button on your carrier board. Tapping that will cause the ESP32 to make an HTTP request to example.com. You should see a string of HTTP headers and HTML similar to the screenshot above.