Graph Sensor Data with Python and Matplotlib
Prepare Your Pi
To begin, you will need to flash an image of the Raspbian operating system (OS) onto an SD card (if you have not done so already). You have a couple of options:
- In the Python Programming Tutorial, follow the Install the OS section, making sure to go with the Full Desktop Setup
OR
- Follow the steps in the How to Use Remote Desktop on the Raspberry Pi with VNC tutorial to enable VNC
Once you have installed the OS for your Raspberry Pi, follow the steps in Configure Your Pi. If given the choice, choose the steps that relate to the Full Desktop setup.
Alias Python and Pip
We will be using Python 3 in this tutorial. At the time of writing, Python 2 was still the default version with Raspbian, which means that we will need to tell Linux that the command python should execute Python version 3.
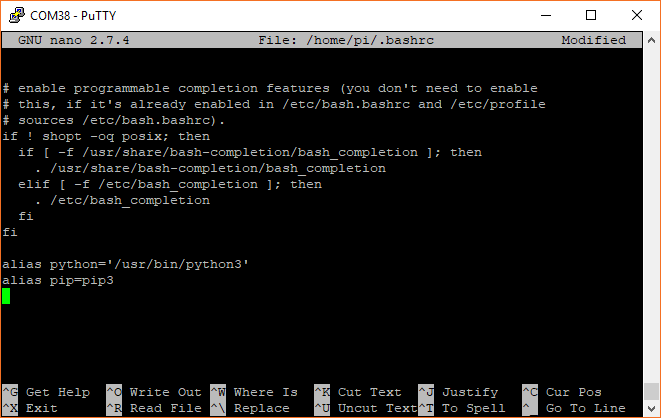
Open a terminal and enter the following command to edit the .bashrc file:
language:shell
nano ~/.bashrc
Scroll down to the bottom of the file, and add the following (if they are not already present):
language:shell
alias python='/usr/bin/python3'
alias pip=pip3
Exit out of nano with ctrl+x, press y, and press enter. Run the .bashrc script with:
language:shell
source ~/.bashrc
You can check the versions of Python and pip with:
language:shell
python --version
pip --version
Both should tell you the they are using a version of Python 3 (e.g. 3.5.3).
Enable I2C
By default, Raspbian disables the I2C port, which we'll need to talk to the TMP102.
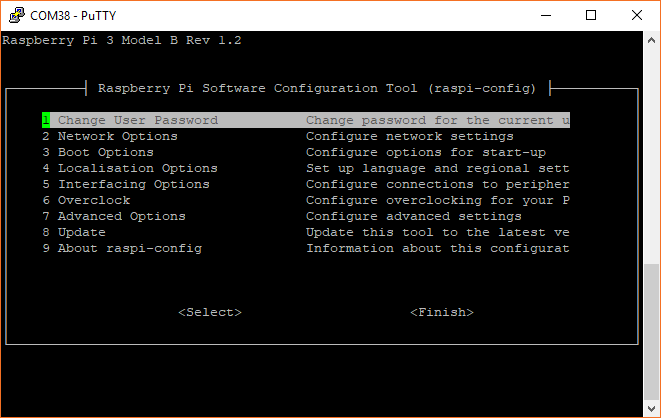
Bring up the Raspberry Pi configuration menu:
language:shell
sudo raspi-config
If asked to enter a password, type in the password you set for your Raspberry Pi. If you did not change it, the default password is raspberry.
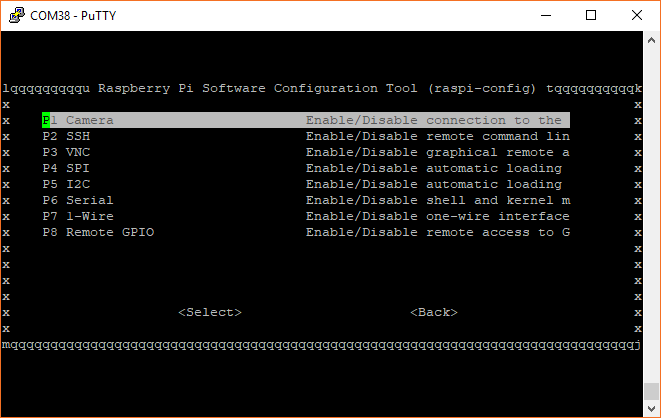
Select 5 Interfacing Options.
Select P5 I2C, select yes on the following screen, and press enter to enable the I2C port.
Back on the main screen, highlight Finish and press enter. A reboot is not necessary if you did not change any other options.
Install Dependencies
Like any good Linux project, we need to install a number of dependencies and libraries in order to get matplotlib to run properly. Make sure you have an Internet connection and in a terminal, enter the following commands. You may need to wait several minutes while the various packages are downloaded and installed.
language:shell
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libatlas3-base libffi-dev at-spi2-core python3-gi-cairo
pip install cairocffi
pip install matplotlib
You are now ready to build your circuit and make some graphs!