ESP32 Thing Plus (USB-C) Hookup Guide
Arduino Example: BLE
The ESP32 Arduino core also includes several Bluetooth examples that range from acting as a simple BLE device to functioning as a Bluetooth server. This example will demonstrate how users can send messages from their phone to ESP32 Thing Plus; and then display the message in the serial monitor. Users will need to install the BLE Scanner app (iPhone or Android) on their smart phone and enable the Bluetooth connection.
The example code is built into the Arduino IDE for the ESP32 Arduino core (users need to select and ESP32 board definition first). Once an ESP32 board has been selected, the built-in BLE examples will become available; select the BLE_write example from the Files > Examples > ESP32 BLE Arduino > BLE_write drop down menu. Compile and upload the example code. Make sure the correct port has been selected for the board.
language:c
/*
Based on Neil Kolban example for IDF: https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/blob/master/cpp_utils/tests/BLE%20Tests/SampleWrite.cpp
Ported to Arduino ESP32 by Evandro Copercini
*/
#include <BLEDevice.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLEServer.h>
// See the following for generating UUIDs:
// https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
#define SERVICE_UUID "4fafc201-1fb5-459e-8fcc-c5c9c331914b"
#define CHARACTERISTIC_UUID "beb5483e-36e1-4688-b7f5-ea07361b26a8"
class MyCallbacks: public BLECharacteristicCallbacks {
void onWrite(BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic) {
std::string value = pCharacteristic->getValue();
if (value.length() > 0) {
Serial.println("*********");
Serial.print("New value: ");
for (int i = 0; i < value.length(); i++)
Serial.print(value[i]);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("*********");
}
}
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
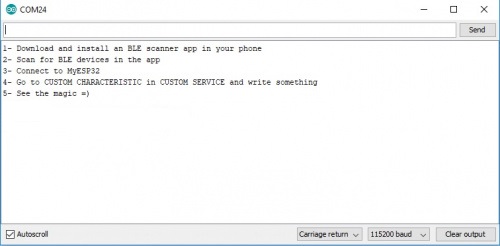
Serial.println("1- Download and install an BLE scanner app in your phone");
Serial.println("2- Scan for BLE devices in the app");
Serial.println("3- Connect to MyESP32");
Serial.println("4- Go to CUSTOM CHARACTERISTIC in CUSTOM SERVICE and write something");
Serial.println("5- See the magic =)");
BLEDevice::init("MyESP32");
BLEServer *pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
BLEService *pService = pServer->createService(SERVICE_UUID);
BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
CHARACTERISTIC_UUID,
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE
);
pCharacteristic->setCallbacks(new MyCallbacks());
pCharacteristic->setValue("Hello World");
pService->start();
BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = pServer->getAdvertising();
pAdvertising->start();
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
delay(2000);
}
Once the upload completes, open the serial monitor set the baud rate to 115200 bps.
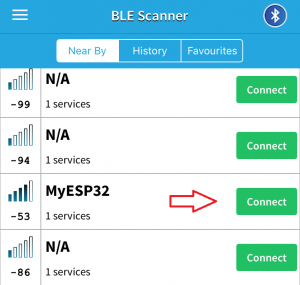
Then open the BLE Scanner app on a smart phone. User should see several BLE devices displayed; scroll through and connect to MyESP32.
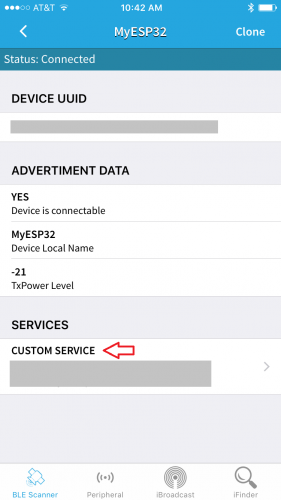
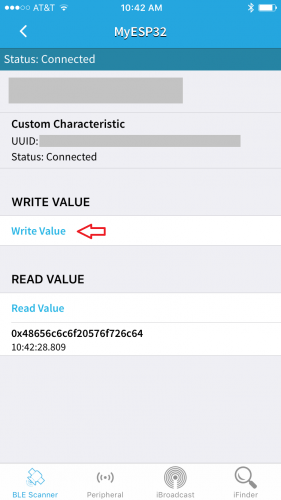
Once connected, users will be taken to the following page. Select CUSTOM SERVICE to set communication capability required for this example.
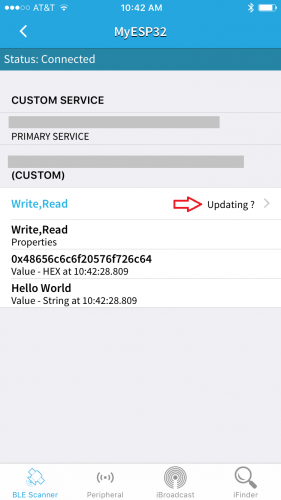
The next page, select the Write,Read option.
Finally, select the Write Value option to send a message to the board.
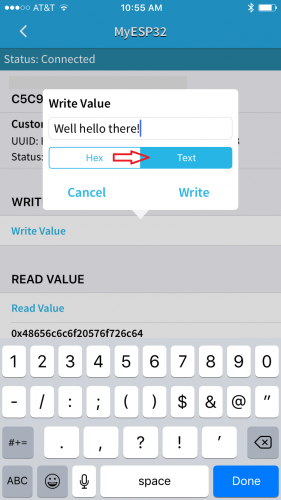
Make sure to select the Text option in the dialog box. Then, write a message in the text box and click the Write button.
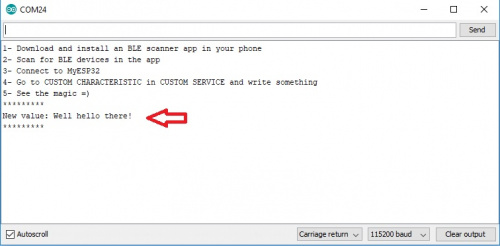
Now take look at the serial monitor, users should see New value: followed by the entry from the text box.
This is just a quick walk through of one of the provided examples. We recommend looking through the rest of the BLE examples and playing with the code. For more information on Bluetooth technology and how it works, check out our Bluetooth Basics Tutorial.