ARGOS ARTIC R2 Satellite Transceiver Shield Hookup Guide
Hardware Overview
In this section we'll cover what's included on the ARGOS ARTIC R2 Satellite Transceiver Shield.
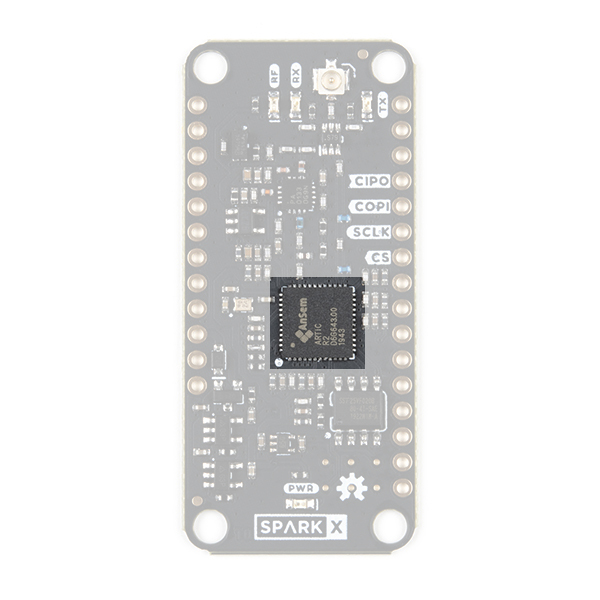
ARTIC R2
The heart of the ARGOS ARTIC R2 Satellite Transceiver Shield is, of course, the ARTIC R2 transceiver itself. This is a clever chip containing a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) which modulates transmit messages and demodulates received messages. The DSP can boot from on-board flash memory or from an external microcontroller via SPI. When transmitting, it produces a 1mW (0dBm) output signal which is fed to a separate power amplifier.
Our Arduino Library does all of the heavy lifting for you. By default, the library will tell the ARTIC R2 DSP to boot from the on-board flash memory. However, by changing one line of code, you can instead boot via SPI with your microcontroller providing the firmware for the DSP.
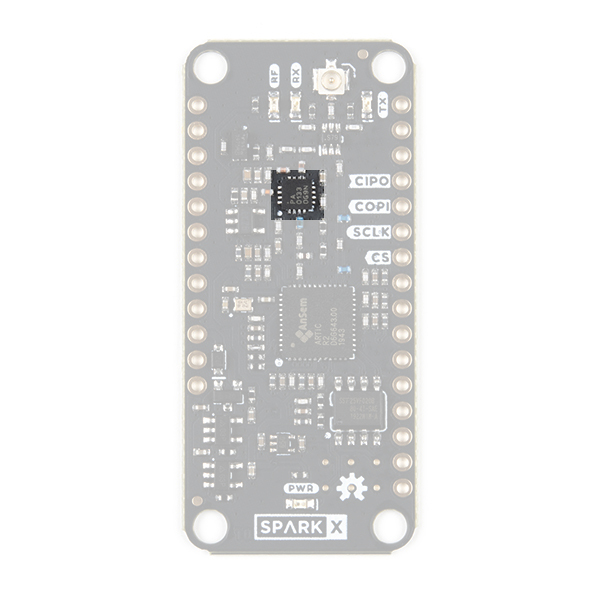
RF Amplifier
During transmit, the RFPA0133 power amplifier boosts the 0dBm (1mW) signal from the ARTIC R2.
Using full gain, the amplifier boosts the signal to approximately 25.8dBm (380mW). If you are using ARGOS 2 or 3 modulation and are transmitting from a 'noisy' environment, like a city, then you are probably going to need to use full power to ensure your messages get through. However, if you are using ARGOS 4 modulation and/or are transmitting from a 'quiet' environment, like the tundra or the ocean, then you will be able to transmit at reduced power.
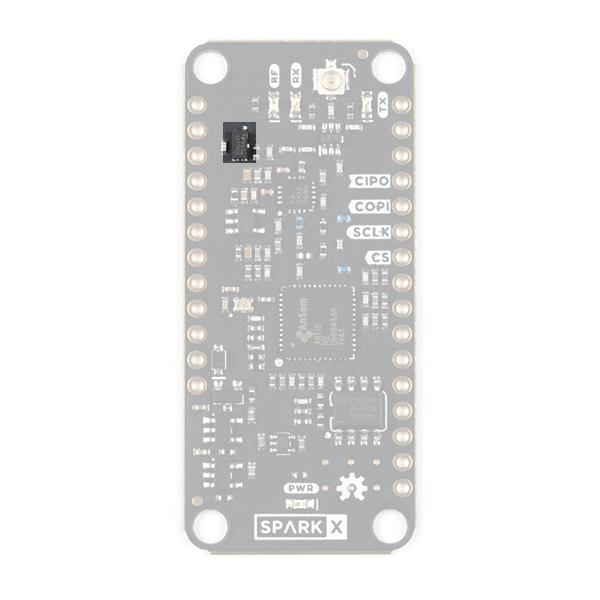
Gain Control
You can adjust the transmit gain through software and the on-board opto-isolated gain control circuit.
Our Arduino Library can reduce the gain for you. If you call:
language:c
myARTIC.attenuateTXgain(true);
from inside your code, the opto-isolator will pull the RFPA0133's G8 pin low, reducing the gain by approximately 5dB. This also has the advantage of reducing the transmit current by approximately 80mA.
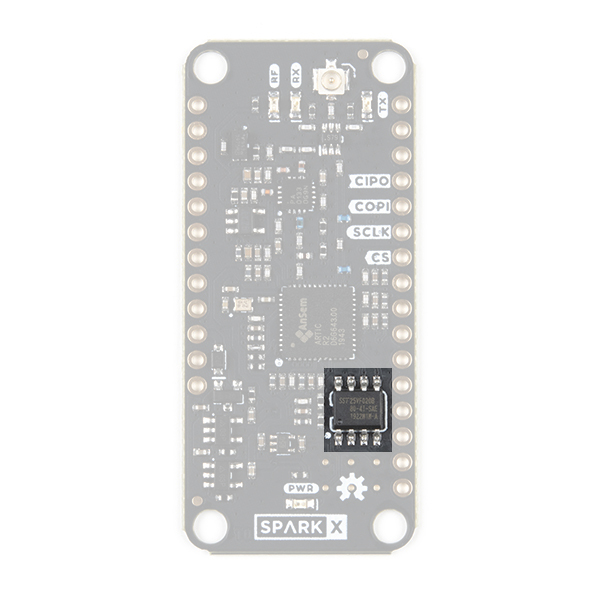
Flash Memory
By default, the DSP inside the ARTIC R2 will boot from the on-board flash memory. (But, as mentioned above, you also have the option of booting via SPI.)
During production testing at SparkFun, we program the flash memory with the ARTIC R2 firmware (ARTIC006) and a Platform ID allocated by CLS. You will need to register the Platform ID on your ARGOS account to activate it. The Arduino Library reads the Platform ID from memory and uses it in the transmissions.
Antenna
The antenna connection for the ARTIC R2 is u.FL.
Check out our tutorial if you haven't used u.FL before:
Three Quick Tips About Using U.FL
Power Circuit
The ARGOS ARTIC R2 Satellite Transceiver Shield can draw power from the standard Thing Plus / Feather VUSB and/or VBATT pins. The shield will preferentially draw 5V power from VUSB if connected, but can also be powered by a standard 3.6V LiPo battery via VBATT.
The power circuit comprises: an automatic switching circuit to select VUSB or VBATT; 3.3V, 3.0V and 1.8V regulators.
LEDs
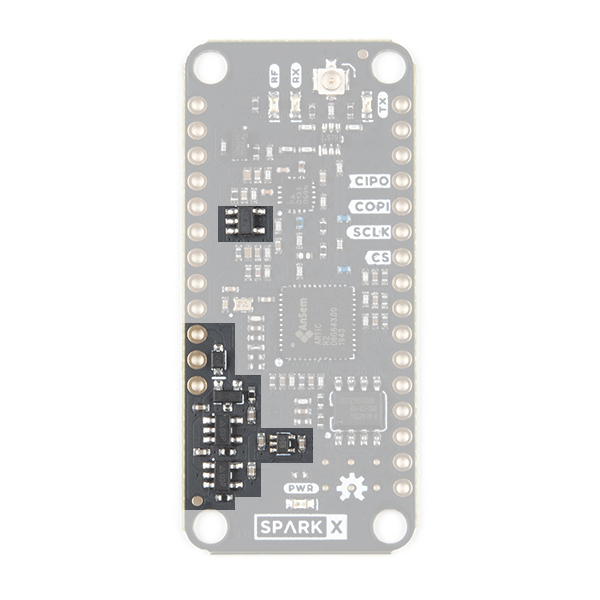
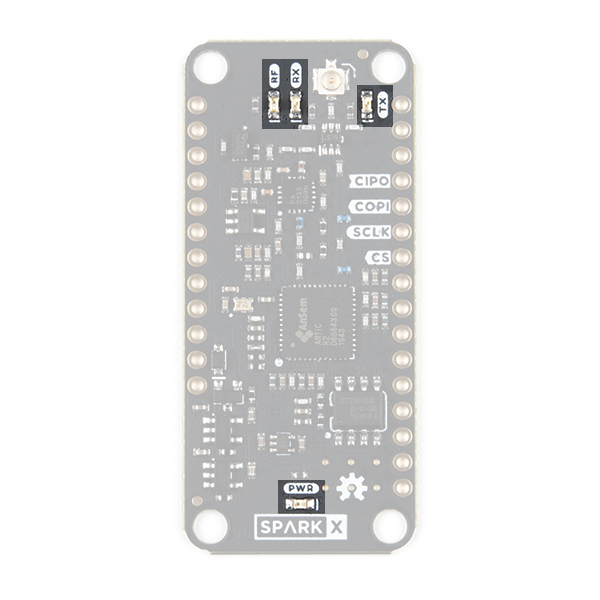
The ARGOS ARTIC R2 Satellite Transceiver Shield has four LEDs which indicate if the board is powered and if it is transmitting or receiving.
When lit, the LEDs indicate:
- RF: RF amplifier is powered on
- RX: ARTIC R2 is receiving
- TX: ARTIC R2 is transmitting
- PWR: ARTIC R2 shield power circuit is on
If you want to save power, you can disable the LEDs by cutting the jumper links on the back of the board:
If you haven't worked with jumpers before, please check out our tutorial.