RETIRED - Raspberry gPIo
This Tutorial is Retired!
This tutorial covers concepts or technologies that are no longer current. It's still here for you to read and enjoy, but may not be as useful as our newest tutorials.
View the updated tutorial: Raspberry gPIo
GPIO Pinout
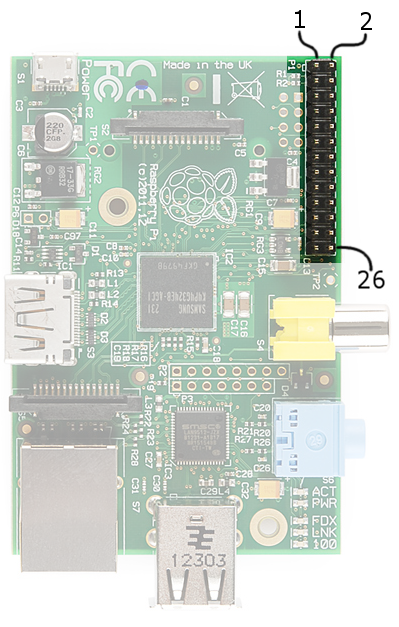
The majority of I/O pins on the Raspberry Pi exist on the 26-pin header labeled "P1". It's over in the corner of the board, adjacent to the composite video connector.
If you're coming to the Raspberry Pi as an Arduino user, you're probably used to referencing pins with a single, unique number. Programming the Pi's hardware works much the same, each pin has its own number...and then some.
There are (at least) two, different numbering schemes you may encounter when referencing Pi pin numbers: (1) Broadcom chip-specific pin numbers and (2) P1 physical pin numbers. You're usually free to use either number-system, but many programs require that you declare which scheme you're using at the very beginning of your program.
Here's a table showing all 26 pins on the P1 header, including any special function they may have, and their dual numbers:
| Broadcom Pin | Function | P1 Pin | P1 Pin | Function | Broadcom Pin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3V | 1 | 2 | 5V | |||
| 2 | SDA | 3 | 4 | 5V | ||
| 3 | SCL | 5 | 6 | GND | ||
| 4 | 7 | 8 | TX | 14 | ||
| GND | 9 | 10 | RX | 15 | ||
| 17 | 11 | 12 | PWM | 18 | ||
| 27 | 13 | 14 | GND | |||
| 22 | 15 | 16 | 23 | |||
| 3.3V | 17 | 18 | 24 | |||
| 10 | MOSI | 19 | 20 | GND | ||
| 9 | MISO | 21 | 22 | 25 | ||
| 11 | SCLK | 23 | 24 | CE0 | 8 | |
| GND | 25 | 26 | CE1 | 7 |
| Legend: | 5V | 3.3V | GND | I2C | SPI | PWM |
|---|
Note: The Broadcom pin numbers above relate to Rev2 of the Raspberry Pi only. If you have an older Rev1 Pi, check out this link for your Broadcom pin numbers.
As you can see, the Pi not only gives you access to 17 bi-directional I/O pins, but also Serial (UART), I2C, SPI, and even some PWM ("analog output").