RETIRED - Raspberry gPIo
This Tutorial is Retired!
This tutorial covers concepts or technologies that are no longer current. It's still here for you to read and enjoy, but may not be as useful as our newest tutorials.
View the updated tutorial: Raspberry gPIo
Hardware Setup
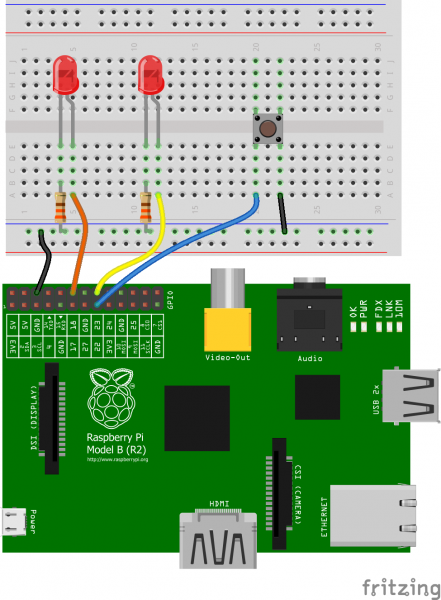
To get a head start you can assemble the circuit now. We'll use this setup for both the C and Python examples. We'll use two LEDs to test the output functionality (digital and PWM), and a button to test the input.
Our two LEDs are connected to the Pi's pins 18 and 23 -- those are the Broadcom chip-specific numbers. If you're basing your wiring off the P1 connector pin numbers, that'd be pins 12 and 16.
The button is connected to Broadcom pin 22, aka P1 pin 15.
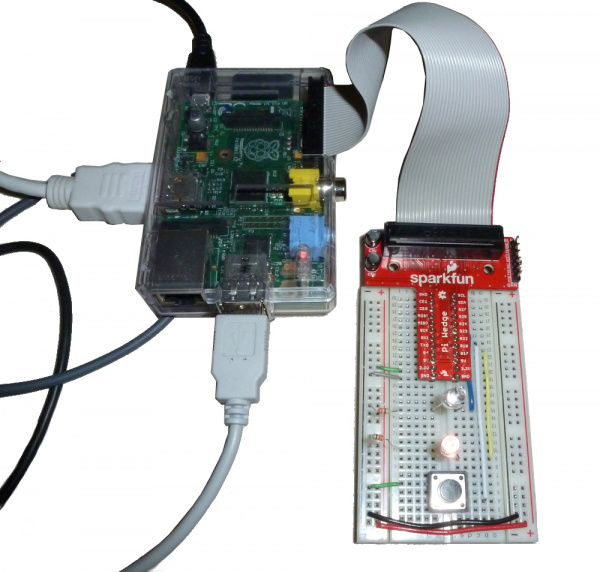
If you have Pi Wedge, the hookup should be pretty straight-forward. It'll look a little something like this when you're done:
If you don't have a Pi Wedge, male-to-female jumper wires help to make an easy transition from Pi to breadboard.