QuickLogic Thing Plus (EOS S3) Hookup Guide
Hardware Overview
The QuickLogic Thing Plus EOS S3 is a small form factor system ideal for enabling the next generation of low-power Machine Learning (ML) capable Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Unlike other development boards which are based on proprietary hardware and software tools, the QuickLogic Things Plus is based on 100% open source hardware, compatible with the Feather form factor, and is built around 100% open source software (including the Symbiflow FPGA Tools).
The QuickLogic is powered by QuickLogic’s EOS™ S3, the first eFPGA-enabled Arm Cortex©-M4F MCU to be fully supported with Zephyr RTOS and FreeRTOS.
Other functionality includes:
- QuickLogic EOS S3 MCU Platform
- ST micro LIS2DH12TR accelerometer
- Vesper VM3011 Adaptive ZeroPower Listening™ Digital Piezoelectric MEMS PDM Microphone
- SparkFun’s Qwiic connector to enable easy connection to large number of Qwiic modules
- 16Mbit of on-board flash memory
- User button and RGB LED
- Powered from USB or a single Li-Po battery
- Integrated battery charger
- USB data signals tied to programmable logic
- IO signals routed into general purpose pinheads
- Compatible with standard 0.1" breadboards
Benefits
- QuickLogic Thing Plus EOS S3 is small, Feather compatible, inexpensive, and is 100% supported by open source tools.
- With a Cortex M4F MCU and integrated eFPGA, the EOS S3 lets you innovate with 100% open source hardware and software.
Applications
- Tiny ML applications (such as with SensiML’s AI Software Platform and Google’s TensorFlow Lite)
- General purpose MCU applications
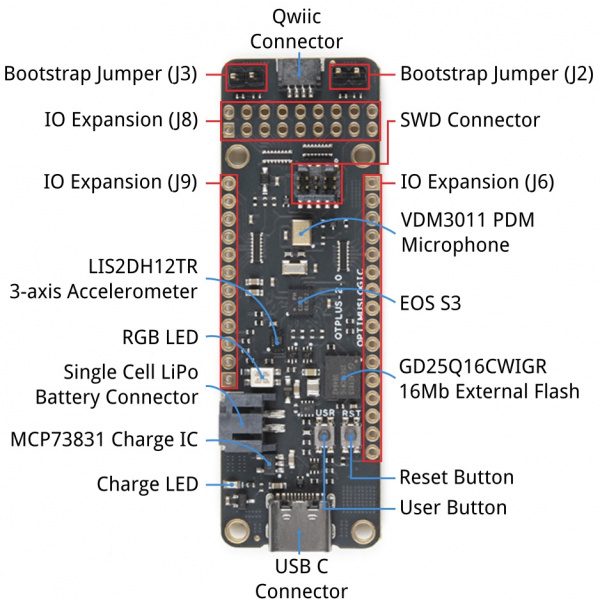
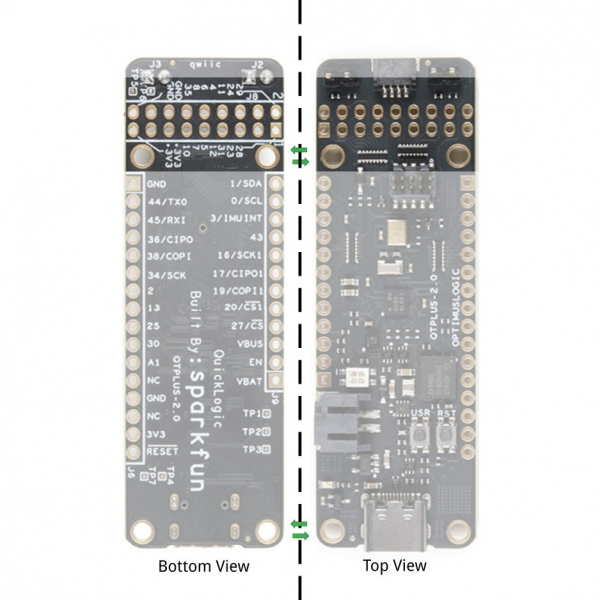
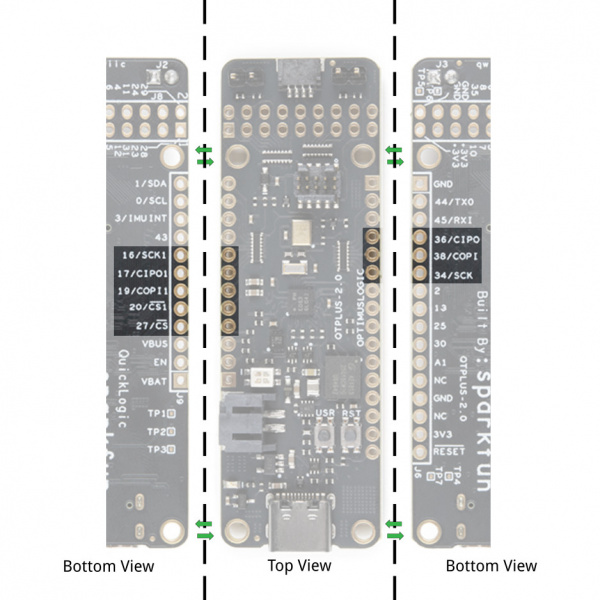
Board Layout
Below is a quick overview of the board layout and components.
- QuickLogic EOS S3 MCU Platform
- ST micro LIS2DH12TR accelerometer
- SparkFun’s Qwiic connector
- Vesper’s VM3011 MEMS PDM microphone
- 16Mbit of on-board flash memory
- User button and RGB LED
- Hardware Reset button
- Powered from USB or a single Li-Po battery
- Integrated battery charger
- USB data signals tied to programmable logic
- IO signals break-routed into general purpose pinheads
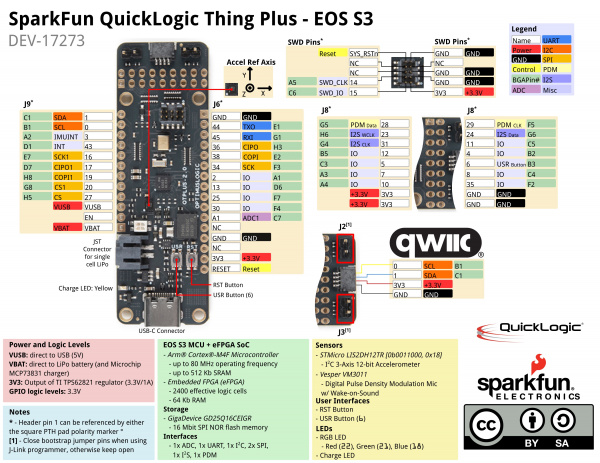
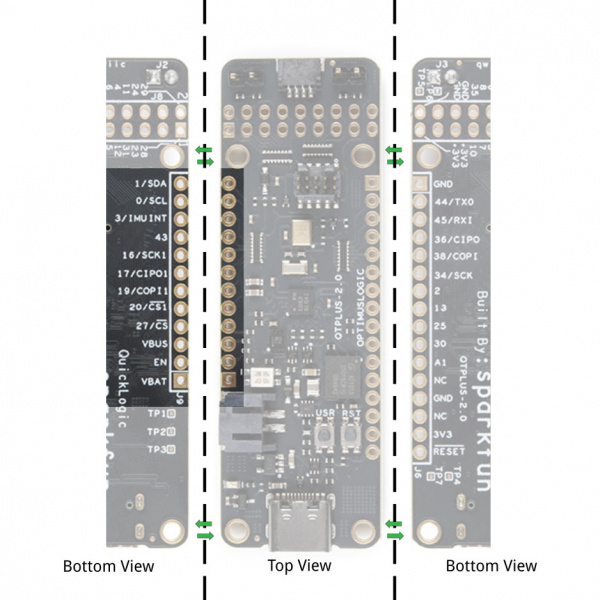
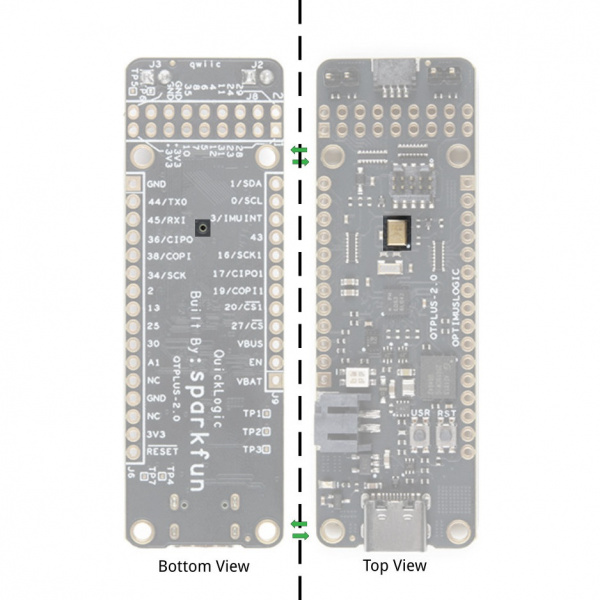
IO Expansion Connectors EOS S3 MCU IO Map to QuickLogic Thing Plus
Below is the graphical datasheet of the QuickLogic Thing Plus EOS S3 to reference the pins followed by a table listing the EOS S3 pins. Due to the size of the board and components, the silkscreen is printed on the back of the board. You can flip over the board reference the pin name and its respective function as well.
| EOS S3 MCU IO | QuickLogic Thing Plus Function | Additional Function | Expansion |
|---|---|---|---|
| IO_0 | I2C0 SCL | J9.11 | |
| IO_1 | I2C0 SDA | J9.12 | |
| IO_2 | IO | J6.7 | |
| IO_3 | Accelerometer LIS2DH12TR Interrupt | J9.10 | |
| IO_4 | IO | J8.8 | |
| IO_5 | IO | J8.9 | |
| IO_6 | User Button Input | J8.10 | |
| IO_7 | IO | J8.11 | |
| IO_8 | IO | J8.12 | |
| IO_10 | IO | J8.13 | |
| IO_11 | IO | J8.6 | |
| IO_12 | IO | J8.7 | |
| IO_13 | IO | J6.8 | |
| IO_14 | Serial Wire Debug CLK | J6.4 | |
| IO_15 | Serial Wire Debug DATA | J6.2 | |
| IO_16 | IO | SPI Peripheral CLK | J9.8 |
| IO_17 | IO | SPI Peripheral CIPO (input) | J9.7 |
| IO_18 | Blue LED | N/A | |
| IO_19 | IO | SPI Peripheral COPI | J9.6 |
| IO_20 | IO | SPI Peripheral CSn | J9.5 |
| IO_21 | Green LED | N/A | |
| IO_22 | Red LED | N/A | |
| IO_23 | IO | I2S Peripheral WCLK (Frame) | J8.3 |
| IO_24 | IO | I2S Peripheral DATA (dout) | J8.4 |
| IO_25 | IO | J6.9 | |
| IO_27 | IO | SPI Controller CS2 | J9.2 |
| IO_28 | PDM Data; to isolate, remove R28 | J8.1 | |
| IO_29 | PDM CKO | J8.2 | |
| IO_30 | IO | J6.10 | |
| IO_31 | IO | I2S Peripheral CLK (input) | J8.5 |
| IO_32 | IO | J9.3 | |
| IO_33 | IO | J9.4 | |
| IO_34 | SPI Controller CLK | J6.6 | |
| IO_36 | SPI Controller CIPO | J6.4 | |
| IO_38 | SPI Controller COPI (flash) | J6.5 | |
| IO_40 | IO | N/A | |
| IO_43 | IO | Interrupt Output to Host | J9.9 |
| IO_44 | IO | UART TX | J6.2 |
| IO_45 | IO | UART RX | J6.3 |
Connector J9
| J2 | EOS S3 MCU IO | BGA Pin# | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBAT | ||
| 2 | 3.3V Circuit Enable | ||
| 3 | VBUS | ||
| 4 | IO_27 | HS | IO; SPI Controller CSn2 |
| 5 | IO_20 | G8 | SPI Peripheral SSn input; EOS S3 boot-strap |
| 6 | IO_19 | H8 | SPi Peripheral COPI input; EOS S3 boot-strap |
| 7 | IO_17 | D7 | SPI Peripheral CIPO output |
| 8 | IO_16 | E7 | SPI Peripheral CLK input |
| 9 | IO_43 | D1 | EOS S3 Interrupt Output |
| 10 | IO_3 | A2 | Accel Interrupt input |
| 11 | IO_0 | B1 | I2C0 SCL |
| 12 | IO_1 | C1 | I2C0 SDA |
Connector J6
| J6 | EOS S3 MCU IO | BGA Pin# | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ground | ||
| 2 | IO_44 | E1 | S3 UART TX |
| 3 | IO_45 | G1 | S3 UART RX |
| 4 | IO_36 | H3 | SPI Controller CIPO input |
| 5 | IO_38 | E2 | SPI Controller COPI output |
| 6 | IO_34 | F3 | SPI Controller CLK output |
| 7 | IO_2 | A1 | IO |
| 8 | IO_13 | D6 | IO |
| 9 | IO_25 | F7 | IO |
| 10 | IO_30 | F4 | IO |
| 11 | ADC1 | C7 | ADC1 input |
| 12 | No Connect | ||
| 13 | Ground | ||
| 14 | No Connect | ||
| 15 | +3.3V | ||
| 16 | SYS_RSTn | F8 | EOS S3 HW reset input |
Connector J8
| J8 | EOS S3 MCU IO | BGA Pin# | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IO_28 | G5 | PDM microphone Data |
| 2 | IO_29 | F5 | PDM microphone CLK |
| 3 | IO_23 | H6 | I2S Peripheral WCLK Input |
| 4 | IO_24 | G6 | I2S Peripheral DATA output |
| 5 | IO_31 | G4 | I2S Peripheral CLK input |
| 6 | IO_11 | C5 | IO |
| 7 | IO_12 | B5 | IO |
| 8 | IO_4 | B2 | IO |
| 9 | IO_5 | C3 | IO |
| 10 | IO_6 | B3 | User button input |
| 11 | IO_7 | A3 | IO |
| 12 | IO_8 | C4 | IO |
| 13 | IO_10 | A4 | IO |
| 14 | IO_35 | F2 | IO |
| 15 | +3.3V | ||
| 16 | Ground | ||
| 17 | +3.3V | ||
| 18 | Ground |
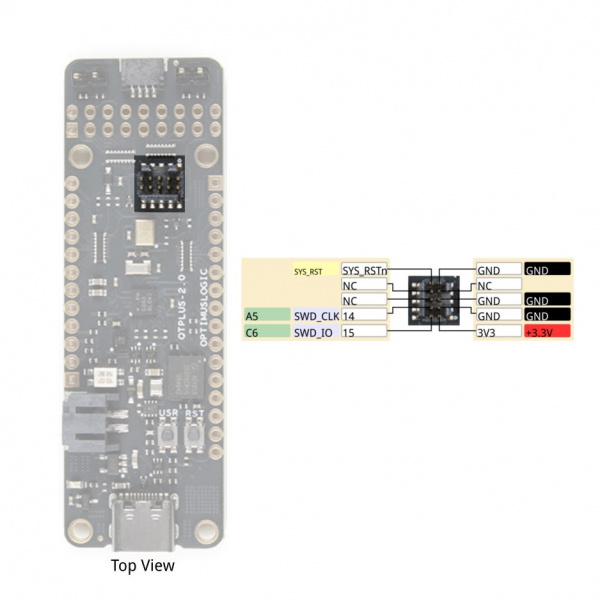
Development Connector
EOS S3 MCU SWD Connector
Below is the SWD connector used to program the board. Taken from the graphical datasheet are the pin labels on the right for reference.
| J7 | EOS S3 MCU IO | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | +3.3V | |
| 2 | IO_15 | SWD_IO |
| 3 | Ground | |
| 4 | IO_14 | SWD_CLK |
| 5 | Ground | |
| 6 | No Connect | |
| 7 | No Connect | |
| 8 | No Connect | |
| 9 | Ground | |
| 10 | SYS_RSTn | Hardware Reset |
Boot-strap IO_19 & IO_20
There are two pair of IO pins that are reserved for flashing the EOS S3 with a programmer. When booting a program from flash, you'll need to keep these pins open.
- Install both shunts to use SWD Debugger for development
- Remove both shunts for boot-from-flash
Power
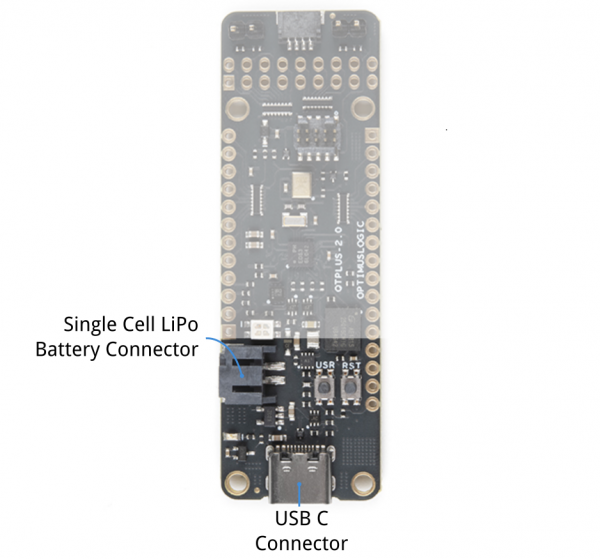
There are two ways to provide power to the QuickLogic Thing Plus: USB connector (J5) or Battery connector (J4). When both ports are connected at the same time, the USB power activates the battery charging circuit that provide charging current to the battery.
When using a rechargeable battery, the minimum input voltage will determine the maximum currents that the system needs to support. This is important when connecting additional peripherals to the QuickLogic Thing Plus that also requires connection to +3.3V for supplies.
The MCP73831 LiPo charger is set to ~212.76mA for the default charge rate. Before you plug a battery into the charger, you should be aware of your battery's capacity and the charge current supplied by the charger. To be safe, you should keep the charge current at or below 1C of your battery. That means you should connect a LiPo battery that has a capacity of ~212.75mAh or higher to charge safely. For more information on the charge LED's status, check out the LiPo USB Charger breakout board for the MCP73831.
RGB LED
Speaking of LEDs, the board includes a build in RGB LED. As listed earlier in the tutorial, the leds can be controlled using pin 22 (red),p in 21 (green), and pin 18 (blue). Note that the pins are not routed to the edge of the board.
User and Reset Buttons
The board includes a user button and hardware reset button. These are also connected to the edge of the board as well. The reset pin is also connected to the SWD pin when connecting to a programmer.
Connecting Additional Peripherals to the QuickLogic Thing Plus
QuickLogic Thing Plus supports direct connection to FeatherWing module (providing that the FeatherWing module has Stack Headers installed) via expansion connector J2 and J3. Refer to AdaFruit's web site for additional information on available FeatherWing modules.
Sensor with I2C Port
QuickLogic Thing Plus board supports connecting to sensor module with I2C peripheral interface via expansion connectors J2. You can also access the pins along the J9 header.
QuickLogic Thing Plus I2C supports I2C Standard mode (100KHz) and Fast mode (400KHz). There is one I2C bus available; additional I2C IP can be implemented in EOS S3 FPGA.
- I2C0 bus: J2 pin 12 (SDA) and J2 pin 11 (SCL); the signals (SCL and SDA) are connected to 4.7KΩ pull-up resistor. This bus is shared with onboard I2Csensor, LIS2DH12TR (b0011000x).
Steps to connect external I2C sensors to QuickLogic Thing Plus board:
- Ground connection
- Power connection (+3.3V supplies); check supply voltage level meeting connecting module requirement
- Connect SCL and SDA signals; check IO level (> +3.0V IO only)
- Keep connecting wires as short as possible
- Configure the I2Caddress to avoid LIS2DH12TR assigned address (b0011000x)
- Check SCL and SDA rise time (< 1000 ns for Standard mode and < 300 ns for Fast mode)
Note: You may need to use oscilloscope to validate the rise time for SCL and SDA to stay within rise time specification
LIS2DH12TR Accelerometer
The board includes the LIS2DH12TR triple axis accelerometer. Below is the reference axis of the IC based on the datasheet. This sensor connected to the I2C bus. The address for the accelerometer is set to 0b0011000 (0x18). The accelerometer INT1 pin is connected to pin 3.
Sensor with SPI Peripheral Port
QuickLogic Thing Plus board supports connecting to sensor module with SPI peripheral interface via expansion connectors J6 and J9: SPI CONTROLLER CLK (J6 pin 6), SPI CONTROLLER CIPO (J6 pin 4), SPI CONTROLLER COPI (J6 pin 5) and SPI CONTROLLER CS2 (J9 pin 4).
The maximum supported SPI clock frequency is 10MHz.
Steps to connect external SPI sensor to QuickLogic Thing Plus board:
- Ground connection
- Power connection (+3.3V supplies check supply voltage level meeting connecting module requirement
- Connect SPI CONTROLLER signals; check IO level (> +3.0V IO only)
- Keep connecting wires as short as possible
- Check signal quality using scope
PDM Microphones
Single PDM Microphone
The on-board PDM microphone (Vesper VM3011) is configured as left channel output (driving active data on falling edge of PDM CLK). Based on the design of the microphone, there is a drill hit through the board that allows an opening for the sound.
QuickLogic Thing Plus supports external PDM microphone connection via expansion connector J8: PDM CLK (J8 pin 2) and PDM DATA (J8 pin 1).
Steps to connect one external PDM microphone to QuickLogic Thing Plus board:
- Ground connection
- Power connection (+3.3V supplies check supply voltage level meeting connecting module requirement
- Remove R28 (100Ω resistor)
- Connect PDM CLK and PDM DATA signals; check IO level (> +3.0V IO only)
- Keep connecting wires as short as possible
- PDM microphone is configured as right channel microphone; the L/R signal or Channel signal is connected to VDD
- Check signal quality using scope
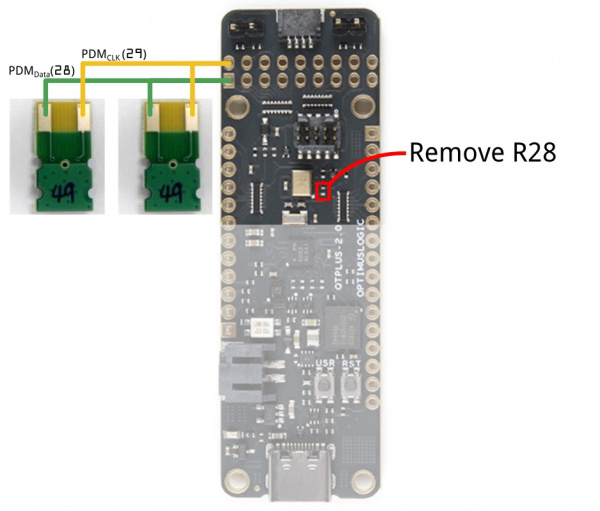
Double PDM Microphone
To support two external PDM microphones configuration, it is required to disable the connection of the on-board PDM microphone.
QuickLogic Thing Plus supports external PDM microphone connection via expansion connector J8: PDM CLK (J8 pin 2) and PDM DATA (J8 pin 1).
Steps to connect two external PDM microphones to QuickLogic Thing Plus board:
- Ground connection
- Power connection (+3.3V supplies check supply voltage level meeting connecting module requirement
- Remove R28 (100Ω resistor)
- Connect PDM CLK and PDM DATA signals; check IO level (> +3.0V IO only)
- Keep connecting wires as short as possible; avoid star connection scheme (see figure below)
- Configure one PDM microphone as left channel and one PDM microphone as right channel
- Check signal quality using scope
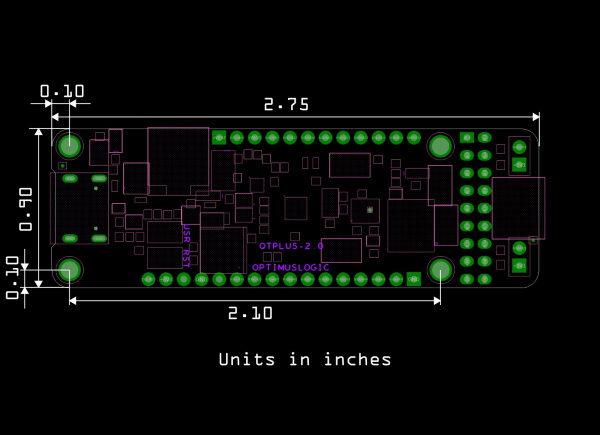
Board Dimensions
The board is 2.75"x2.10". While the board uses the Thing Plus footprint, length of the board is slightly longer than other Thing Plus designs.