Non-Addressable RGB LED Strip Hookup Guide
Arduino Example Code
Note: This example assumes you are using the latest version of the Arduino IDE on your desktop. If this is your first time using Arduino, please review our tutorial on installing the Arduino IDE.
To follow along, check out the GitHub repository. There are five examples in the repo. Two of which are simple examples to turn on a certain color based on the type of LED that you are using. We'll go over the other three examples.
The three examples from this GitHub Repo that we will go over are listed below. Click on one of the links below to jump to the example!
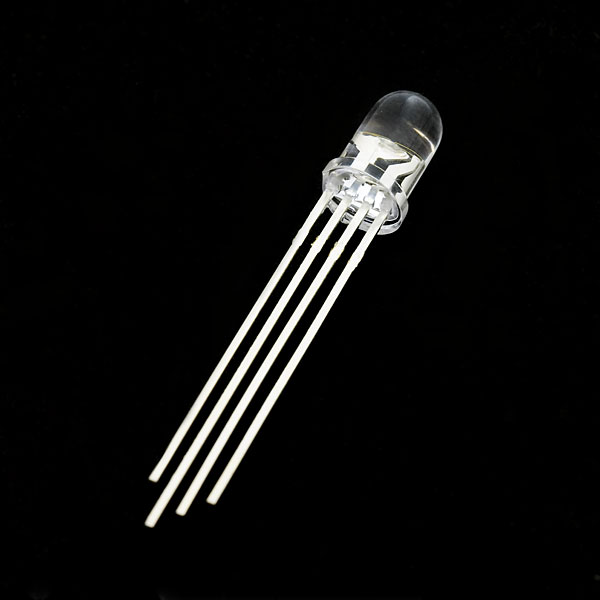 |
 |
 |
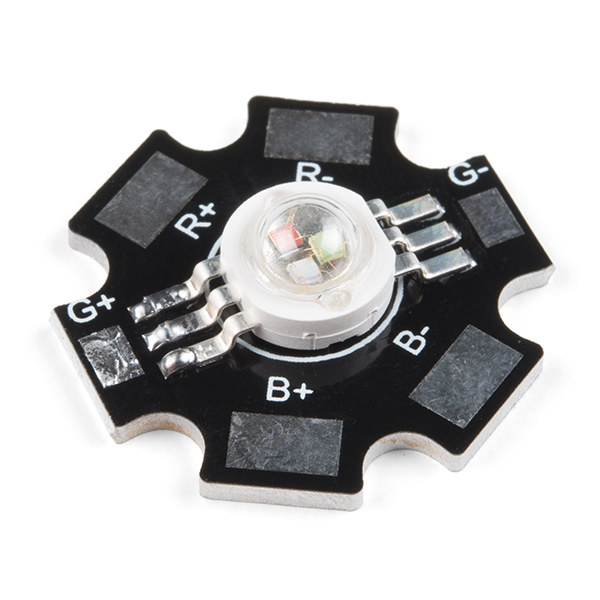 |
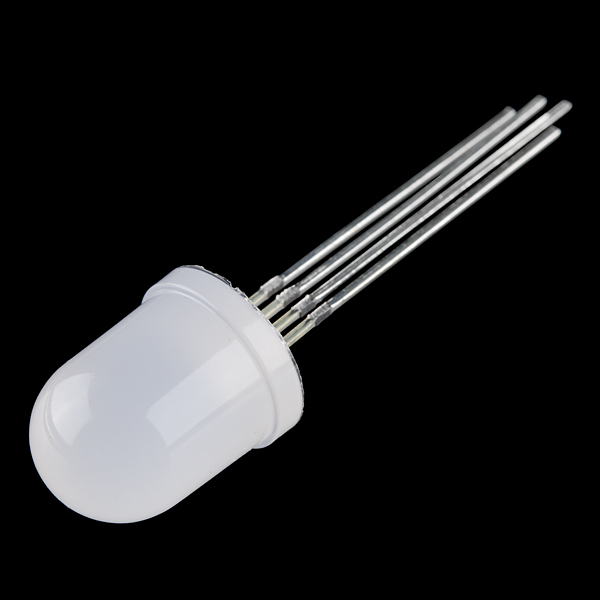
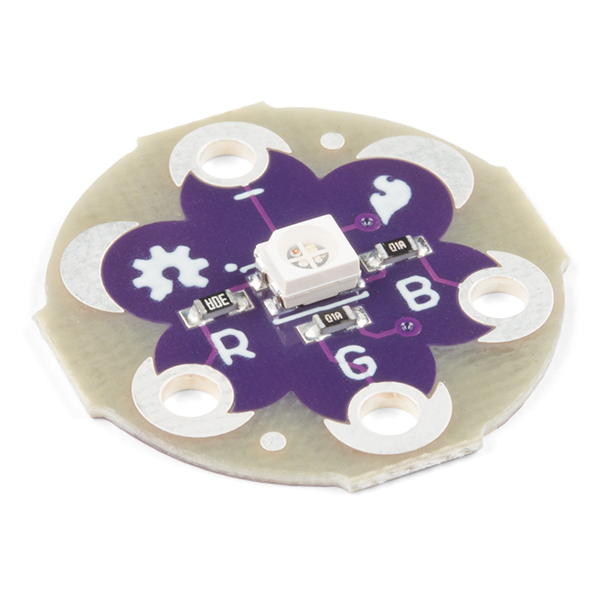
| Clear Common Anode RGB LED- 5mm | Diffused Common Cathode RGB LED- 10mm | SMD Common Cathode RGB LED on a Sewable PCB | High Power RGB LED on a PCB |
Example 1: Custom Color Cycling
This code will cycle through 12 colors and white. This is useful to test to see if you wired the colors correctly or want to show a color. There are options to adjust the brightness, type of LED, and rate at which the colors cycle.
If you have not already, unzip the GitHub repo and open the example code called Example1_RGB-CycleLED.ino. The path of the example code will probably look similar to: ... \ Non-Addresssable_RGB_LED_Strip_Code \ Firmware \ Arduino \ Example1_RGB-CycleLED. You can also copy the code below and paste it into the Arduino IDE. Select the board (in this case the Arduino/Genuino Uno) and COM port that the board enumerated to. Then hit the upload button to upload to your Arduino.
language:c
/******************************************************************************
Example1_RGB-CycleLED.ino
Non-Addressable RGB LED Custom Color Cycle
WRITTEN BY: Ho Yun "Bobby" Chan @ SparkFun Electronics
DATE: November 4, 2019
GITHUB REPO: https://github.com/sparkfun/Non-Addresssable_RGB_LED_Strip_Code
DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT SPECIFICS:
Firmware developed using Arduino IDE v1.8.9
============================== DESCRIPTION ==============================
Expand your color options using analogWrite() and a non-addressable RGB LED.
This code will cycle through 12 colors and white. There are options to adjust
the brightness, type of LED, and rate at which the colors cycle.
This example code works with an individual common anode and common cathode
RGB LED. If you have a transistor or constant current LED driver, you can
also use it to control an RGB LED strip or a higher power RGB LED.
We'll assume that you are using a common anode LEDs in the strip. For more
information checkout our tutorial: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/731
Notes: There are twelve rainbow colors (primary, secondary, tertiary).
Unlike digitalWrite(), which can be only HIGH (on) or LOW (off),
analogWrite() lets you smoothly change the brightness from 0 (off) to 255 (fully on).
When analogWrite() is used with the RGB LED, you can create millions of colors!
For simplicity, we'll use 12 rainbow colors and white. We will be blinking
between each color.
In the analogWrite() functions:
0 is off
128 is halfway on (used for the tertiary colors)
255 is full brightness.
========== TUTORIAL ==========
Non-Addressable RGB LED Strip Hookup Guide
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/731
Transistors | Applictions I: Switches
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/transistors/all#applications-i-switches
==================== PRODUCTS THAT USE THIS CODE ====================
LED RGB Strip (1M Bare) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12021
LED RGB Strip (1M Sealed) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12023
LED RGB Strip (5B Bare) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12022
LED RGB Strip (5M Sealed) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12024
Triple Output High Power RGB LED - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/15200
PicoBuck LED Driver - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/13705
N-Channel MOSFET Power Control Kit - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12959
==================== HARDWARE CONNECTIONS ====================
The hardware connection depends on your hardware and setup. Below is one possible
arrangement.
RGB Common Anode LED Strip => BJT/MOSFET => Arduino PWM Pin
R pin => transistor => 5
G pin => transistor => 6
B pin => transistor => 9
- pin -
LICENSE: This code is released under the MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
******************************************************************************/
//Debug mode, comment one of these lines out using a syntax
//for a single line comment ("//"):
//#define DEBUG 0 //0 = LEDs only
#define DEBUG 1 //1 = LEDs w/ serial output
// Define our LED pins to a PWM Pin
#define redPin 5
#define greenPin 6
#define bluePin 9
// Create integer variables for our LED color value
int redValue = 0;
int greenValue = 0;
int blueValue = 0;
//Create brightness variable
//Ranging from 0.0-1.0:
// 0.0 is off
// 0.5 is 50%
// 1.0 is fully on
float brightnessLED = 0.1;
//Create variables for type of LED and if it is used with a transistor
boolean commonAnode = false;
boolean commonCathode = true; //i.e.) When pin is HIGH, LED will also go HIGH without a transistor/PicoBuck
// Note:
// Common Anode is `commonAnode`
// Common Cathode LED is `commonCathode`
// Common Anode RGB LED Strip with transistor is `!commonAnode`
// RGB High Power LED with PicoBuck is also `!commonAnode`
boolean rgbType = !commonAnode;
int blinkRate = 1000; //in milliseconds
void setup() {
// Make all of our LED pins outputs:
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
allOFF(); //initialize LEDs with it turned off
rgbCalc();//calculate for RGB type
rgbShow(); //make sure to show it happening
#if DEBUG
Serial.begin(9600); //initialize Serial Monitor
//while (!Serial); // Comment out to wait for serial port to connect to Serial Monitor. Option for native USB.
Serial.println("Custom Color Cycling w/ an RGB LED. This example will cycle through 13 colors.");
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println("Note: Make sure to adjust the code for a common cathode or common anode.");
Serial.println(" ");
#endif
}//end setup()
void loop()
{
//used to visually check when Arduino is initialized
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("RED");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
redON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("ORANGE");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
orangeON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("YELLOW");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
yellowON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("CHARTRUESE");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
chartrueseON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("GREEN");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
greenON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("SPRING GREEN");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
springGreenON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("CYAN");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
cyanON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("AZURE");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
azureON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("BLUE");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
blueON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("VIOLET");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
violetON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("MAGENTA");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
magentaON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("ROSE");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
roseON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("WHITE");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
whiteON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("OFF");
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(blinkRate);
}//end loop
// ==================== CUSTOM FUNCTIONS DEFINED BELOW ====================
void allOFF() {
// Black (all LEDs off)
// RGB LEDs:
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
}
void redON() {
// Red
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
}
void orangeON() {
// Orange
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 128;
blueValue = 0;
}
void yellowON() {
// Yellow
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
}
void chartrueseON() {
// Chartruese
redValue = 128;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
}
void greenON() {
// Green
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
}
void springGreenON() {
// Spring Green
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 128;
}
void cyanON() {
// Cyan
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 255;
}
void azureON() {
// Azure
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 128;
blueValue = 255;
}
void blueON() {
// Blue
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
}
void violetON() {
// Violet
redValue = 128;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
}
void magentaON() {
// Magenta
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
}
void roseON() {
// Rose
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 128;
}
void whiteON() {
// White (all LEDs on)
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 255;
}
void rgbCalc() {
//use this to correctly light up LED depending on the setup
if (rgbType == commonAnode) {
/* If using a common anode LED, a pin
should turn ON the LED when the pin is LOW.*/
redValue = 255 - redValue;
greenValue = 255 - greenValue;
blueValue = 255 - blueValue;
}
else {
/* If using a common cathode LED, an analog pin
should turn on the LED when the pin is HIGH. The
logic is flipped when using a Common Anode RGB LED
strip, NPN BJT/N-Channel MOSFET, and microcontroller
Leave RGB values as is, we're good!*/
}
redValue = int(redValue * brightnessLED);
greenValue = int(greenValue * brightnessLED);
blueValue = int(blueValue * brightnessLED);
}
void rgbShow() {
//once value is calculated, show the LED color
analogWrite(redPin, redValue);
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
}
Once the code has been uploaded, the RGB LED will cycle through each of the 12 colors, white, and then turn off. Each color has its own function. When the function is called, the custom color will have a certain analog value for red, green, and blue. Before displaying the color, the values are calculated depending on the type of LED being used (either a common cathode or common anode). By default, we are assuming that the strip uses common anode LEDs but we are using a transistor to control them so rgbType is set to !commonAnode. The color is further calculated based on the intensity of the LED. After calculating the LED color lights up whenever the function rgbShow() is called.
Open the Arduino Serial Monitor set to 9600 baud to see the output as the color changes. Try adjusting the brightness or blink rate. If you are not seeing the correct color associated with the output, make sure to check your connections and ensure that the correct type of RGB LED is selected.
Example 2: Fading
This code will fade through 12 colors and white. There are options to adjust the brightness, type of LED, and rate at which the colors fade.
If you have not already, unzip the GitHub repo and open the example code called Example2_RGB-FadeLED.ino. The path of the example code will probably look similar to: ...Non-Addresssable_RGB_LED_Strip_Code\Firmware\Arduino\Example2_RGB-FadeLED.ino. You can also copy the code below and paste it into the Arduino IDE. Select the board (in this case the Arduino/Genuino Uno) and COM port that the board enumerated to. Then hit the upload button to upload to your Arduino.
language:c
/******************************************************************************
Example2_RGB-FadeLED.ino
Non-Addressable RGB LED Custom Color Fade
WRITTEN BY: Ho Yun "Bobby" Chan @ SparkFun Electronics
DATE: November 4, 2019
GITHUB REPO: https://github.com/sparkfun/Non-Addresssable_RGB_LED_Strip_Code
DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT SPECIFICS:
Firmware developed using Arduino IDE v1.8.9
============================== DESCRIPTION ==============================
Expand your color options using analogWrite() and a non-addressable RGB LED.
This code will fade through 12 colors and white. There are options to adjust
the brightness, type of LED, and rate at which the colors fade.
This example code works with an individual common anode and common cathode
RGB LED. If you have a transistor or constant current LED driver, you can
also use it to control an RGB LED strip or a higher power RGB LED.
We'll assume that you are using a common anode LEDs in the strip. For more
information checkout our tutorial: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/731
Notes: There are twelve rainbow colors (primary, secondary, tertiary).
Unlike digitalWrite(), which can be only HIGH (on) or LOW (off),
analogWrite() lets you smoothly change the brightness from 0 (off) to 255 (fully on).
When analogWrite() is used with the RGB LED, you can create millions of colors!
For simplicity, we'll use 12 rainbow colors and white. We will be fading
between each color.
In the analogWrite() functions:
0 is off
128 is halfway on (used for the tertiary colors)
255 is full brightness.
========== TUTORIAL ==========
Non-Addressable RGB LED Strip Hookup Guide
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/731
Transistors | Applictions I: Switches
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/transistors/all#applications-i-switches
==================== PRODUCTS THAT USE THIS CODE ====================
LED RGB Strip (1M Bare) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12021
LED RGB Strip (1M Sealed) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12023
LED RGB Strip (5B Bare) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12022
LED RGB Strip (5M Sealed) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12024
Triple Output High Power RGB LED - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/15200
PicoBuck LED Driver - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/13705
N-Channel MOSFET Power Control Kit - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12959
==================== HARDWARE CONNECTIONS ====================
The hardware connection depends on your hardware and setup. Below is one possible
arrangement.
RGB Common Anode LED Strip => BJT/MOSFET => Arduino PWM Pin
R pin => transistor => 5
G pin => transistor => 6
B pin => transistor => 9
- pin -
LICENSE: This code is released under the MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
******************************************************************************/
//Debug mode, comment one of these lines out using a syntax
//for a single line comment ("//"):
//#define DEBUG 0 //0 = LEDs only
#define DEBUG 1 //1 = LEDs w/ serial output
// Define our LED pins to a PWM Pin
#define redPin 5
#define greenPin 6
#define bluePin 9
// Create integer variables for our LED color value
int redValue = 0;
int greenValue = 0;
int blueValue = 0;
//Create brightness variable
//Ranging from 0.0-1.0:
// 0.0 is off
// 0.5 is 50%
// 1.0 is fully on
float brightnessLED = 0.1;
//Create variables for type of LED and if it is used with a transistor
boolean commonAnode = false;
boolean commonCathode = true;//i.e.) When pin is HIGH, LED will also go HIGH without a transistor/PicoBuck
// Note:
// Common Anode is `commonAnode`
// Common Cathode LED is `commonCathode`
// Common Anode RGB LED Strip with transistor is `!commonAnode`
// RGB High Power LED with PicoBuck is also `!commonAnode`
boolean rgbType = !commonAnode;
int colorMode = 1; //color mode to control LED color
//Variables for fading LED
int prevFadeVal = 0;
int currentFadeVal = 0;
boolean increasing = true;
int fadeVal = 5; //value to step when increasing/decreasing, recommended to be 1 or 5, larger numbers will have problems lighting up
int fadeMAX = 255; //maximum fade value
int fadeMIN = 0; //minimum fade value
int fadeDelay = 30;//delay between each step
void setup() {
// Make all of our LED pins outputs
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
allOFF(); //make sure to initialize LEDs with it turned off
rgbCalc();//calculate for RGB type
rgbShow(); //make sure to show it happening
#if DEBUG
Serial.begin(9600); //initialize Serial Monitor
//while (!Serial); // Comment out to wait for serial port to connect to Serial Monitor. Option for native USB.
Serial.println("Custom Color Fading w/ an RGB LED.");
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println("Note: Make sure to adjust the code for a common cathode or common anode.");
Serial.println(" ");
#endif
}//end setup()
void loop()
{
switch (colorMode) {
case 1://FADE RED
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE RED ==========
case 2://FADE ORANGE
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
if (redValue > 0 && greenValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
redValue = 0;
}
// takes x amount of steps if you do not set it to zero for certain brightness (i.e. takes 8 more steps to turn off for 0.1)
//Serial.print("Red Value =");
//Serial.println( int((currentFadeVal) * brightnessLED));
//Serial.print("Green Value =");
//Serial.println( int((currentFadeVal * 0.498) * brightnessLED));
break;
//========== END FADE ORANGE ==========
case 3://FADE YELLOW
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE YELLOW ==========
case 4://FADE CHARTRUESE
redValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
if (greenValue > 0 && redValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
greenValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE CHARTRUESE ==========
case 5://FADE GREEN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE GREEN ==========
case 6://FADE SPRING GREEN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
rgbCalc();
if (greenValue > 0 && blueValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
greenValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE SPRING GREEN ==========
case 7://FADE CYAN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE CYAN ==========
case 8://FADE AZURE
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
if (blueValue > 0 && greenValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
blueValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE AZURE ==========
case 9://FADE BLUE
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE BLUE ==========
case 10://FADE VIOLET
redValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
if (blueValue > 0 && redValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
blueValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE VIOLET ==========
case 11://FADE MAGENTA
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE MAGENTA ==========
case 12://FADE ROSE
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498;
rgbCalc();
if (redValue > 0 && blueValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
redValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE ROSE ==========
case 13://FADE WHITE
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE WHITE ==========
default:
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
break;
}
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("Color Fading = ");
if (colorMode == 1) {
Serial.print("RED");
}
else if (colorMode == 2) {
Serial.print("ORANGE");
}
else if (colorMode == 3) {
Serial.print("YELLOW");
}
else if (colorMode == 4) {
Serial.print("CHARTRUESE");
}
else if (colorMode == 5) {
Serial.print("GREEN");
}
else if (colorMode == 6) {
Serial.print("SPRING GREEN");
}
else if (colorMode == 7) {
Serial.print("CYAN");
}
else if (colorMode == 8) {
Serial.print("AZURE");
}
else if (colorMode == 9) {
Serial.print("BLUE");
}
else if (colorMode == 10) {
Serial.print("VIOLET");
}
else if (colorMode == 11) {
Serial.print("MAGENTA");
}
else if (colorMode == 12) {
Serial.print("ROSE");
}
else if (colorMode == 13) {
Serial.print("WHITE");
}
else {
Serial.print("OFF");
}
Serial.print(" | Brightness % = ");
Serial.print(brightnessLED * 100);
Serial.print("%");
Serial.print(" | Fade Val Before Calc= ");
Serial.println(currentFadeVal);
#endif
rgbShow();
delay(fadeDelay);
if (increasing == true) {
//increasing
currentFadeVal += fadeVal;
}
else {
//decreasing
currentFadeVal -= fadeVal;
}
if (currentFadeVal > fadeMAX) {
increasing = false;
prevFadeVal -= fadeVal;//undo addition
currentFadeVal = prevFadeVal;
}
else if (currentFadeVal < fadeMIN) {
increasing = true;
prevFadeVal += fadeVal;//undo subtraction
currentFadeVal = prevFadeVal;
colorMode += 1;//next color
if (colorMode > 13) {
colorMode = 0;
}
}
prevFadeVal = currentFadeVal;
}//END LOOP
// ==================== CUSTOM FUNCTIONS DEFINED BELOW ====================
void allOFF() {
// Black (all LEDs off)
// RGB LEDs:
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
}
void redON() {
// Red
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
}
void orangeON() {
// Orange
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 128;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
}
void yellowON() {
// Yellow
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
}
void chartrueseON() {
// Chartruese
redValue = 128;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
}
void greenON() {
// Green
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
}
void springGreenON() {
// Spring Green
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 128;
rgbCalc();
}
void cyanON() {
// Cyan
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 255;
rgbCalc();
}
void azureON() {
// Azure
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 128;
blueValue = 255;
rgbCalc();
}
void blueON() {
// Blue
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
rgbCalc();
}
void violetON() {
// Violet
redValue = 128;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
rgbCalc();
}
void magentaON() {
// Magenta
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
rgbCalc();
}
void roseON() {
// Rose
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 128;
rgbCalc();
}
void whiteON() {
// White (all LEDs on)
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 255;
rgbCalc();
}
void rgbCalc() {
//use this to correctly light up LED depending on the setup
if (rgbType == commonAnode) {
/* If using a common anode LED, a pin
should turn ON the LED when the pin is LOW.*/
redValue = 255 - redValue;
greenValue = 255 - greenValue;
blueValue = 255 - blueValue;
}
else {
/* If using a common cathode LED, an analog pin
should turn on the LED when the pin is HIGH. The
logic is flipped when using a Common Anode RGB LED
strip, NPN BJT/N-Channel MOSFET, and microcontroller
Leave RGB values as is, we're good!*/
}
redValue = int(redValue * brightnessLED);
greenValue = int(greenValue * brightnessLED);
blueValue = int(blueValue * brightnessLED);
}
void rgbShow() {
//once value is calculated, show the LED color
analogWrite(redPin, redValue);
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
}
Once the code has been uploaded, you should see the colors fading in and out. Open the serial monitor at 9600 to see what color is fading and its respective fade value. Due to the calculations and serial output, the fading can appear to be slow. You may want to adjust the baud rate to a higher value like 115200, adjust the fade delay, or turn off the debugging by defining DEBUG as 0. Additionally, the LEDs may turn off if the fade value and brightness is too small. This is due to the minimum voltage required to turn on the LEDs. You should see something similar to the GIF below. The GIF repeats a small sample of the colors fading. You will see all of the colors cycling in your setup.
Example 3: Full Demo
// in front of this line of code.
//brightnessLED = analogRead(knobPin) / 1023.0; //potentiometer for Brightnessloop().
This code will turn on a color, blink, fade, or cycle through 12 colors depending on the button input. The color cycle used in this demo will fade between each of the 12 colors. There are options to adjust the brightness, type of LED, and rate at which the colors cycle. The RedBoard will only change the color and pattern after pressing the button again.
If you have not already, unzip the GitHub repo and open the example code called Example3_RGB-FullDemoLED.ino. The path of the example code will probably look similar to: ...Non-Addresssable_RGB_LED_Strip_Code\Firmware\Arduino\Example3_RGB-FullDemoLED. You can also copy the code below and paste it into the Arduino IDE. Select the board (in this case the Arduino/Genuino Uno) and COM port that the board enumerated to. Then hit the upload button to upload to your Arduino.
language:c
/******************************************************************************
Example3_RGB-FullDemoLED.ino
Non-Addressable RGB LED Full Demo
WRITTEN BY: Ho Yun "Bobby" Chan @ SparkFun Electronics
DATE: November 4, 2019
GITHUB REPO: https://github.com/sparkfun/Non-Addresssable_RGB_LED_Strip_Code
DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT SPECIFICS:
Firmware developed using Arduino IDE v1.8.9
============================== DESCRIPTION ==============================
Expand your color options using analogWrite() and a non-addressable RGB LED.
This code will either turn on a color, blink, fade, or cycle through 12
colors and white depending on the button input. There are options to adjust
the brightness, type of LED, and rate at which the colors blink/fade/cycle.
This example code works with an individual common anode and common cathode
RGB LED. If you have a transistor or constant current LED driver, you can
also use it to control an RGB LED strip or a higher power RGB LED.
We'll assume that you are using a common anode LEDs in the strip. For more
information checkout our tutorial: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/731
Notes: There are twelve rainbow colors (primary, secondary, tertiary).
Unlike digitalWrite(), which can be only HIGH (on) or LOW (off),
analogWrite() lets you smoothly change the brightness from 0 (off) to 255 (fully on).
When analogWrite() is used with the RGB LED, you can create millions of colors!
For simplicity, we'll use 12 rainbow colors and white.
In the analogWrite() functions:
0 is off
128 is halfway on (used for the tertiary colors)
255 is full brightness.
========== TUTORIAL ==========
Non-Addressable RGB LED Strip Hookup Guide
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/731
Transistors | Applictions I: Switches
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/transistors/all#applications-i-switches
==================== PRODUCTS THAT USE THIS CODE ====================
LED RGB Strip (1M Bare) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12021
LED RGB Strip (1M Sealed) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12023
LED RGB Strip (5B Bare) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12022
LED RGB Strip (5M Sealed) - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12024
Triple Output High Power RGB LED - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/15200
PicoBuck LED Driver - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/13705
N-Channel MOSFET Power Control Kit - https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12959
==================== HARDWARE CONNECTIONS ====================
The hardware connection depends on your hardware and setup. Below is one possible
arrangement.
RGB Common Anode LED Strip => BJT/MOSFET => Arduino PWM Pin
R pin => transistor => 5
G pin => transistor => 6
B pin => transistor => 9
- pin -
LICENSE: This code is released under the MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
******************************************************************************/
//Debug mode, comment one of these lines out using a syntax
//for a single line comment ("//"):
//#define DEBUG 0 //0 = LEDs only
#define DEBUG 1 //1 = LEDs w/ serial output
// Define our LED pins to a PWM Pin
#define redPin 5
#define greenPin 6
#define bluePin 9
// Create integer variables for our LED color value
int redValue = 0;
int greenValue = 0;
int blueValue = 0;
// Define our Potentiometer to a Analog Pin for Brightness
// This is needed if you use a Potentiometer
#define knobPin A0
//Create brightness variable
//Ranging from 0.0-1.0:
// 0.0 is off
// 0.5 is 50%
// 1.0 is fully on
float brightnessLED = 0.1;
//Create variables for type of LED and if it is used with a transistor
boolean commonAnode = false;
boolean commonCathode = true;//i.e.) When pin is HIGH, LED will also go HIGH without a transistor/PicoBuck
// Note:
// Common Anode LED is `commonAnode`
// Common Cathode LED is `commonCathode`
// Common Anode RGB LED Strip with transistor is `!commonAnode`
// RGB High Power LED with PicoBuck is also `!commonAnode`
boolean rgbType = !commonAnode;
//Variables to keep track of color and pattern
int colorMode = 0; //color mode to control LED color
int pattern = 0; //pattern to turn off, stay on, fade, blink
//Variables for fading LED
int prevFadeVal = 0;
int currentFadeVal = 0;
boolean increasing = true;
int fadeVal = 5; //value to step when increasing/decreasing, recommended to be 1 or 5, larger numbers will have problems lighting up
int fadeMAX = 255; //maximum fade value
int fadeMIN = 0; //minimum fade value
int fadeDelay = 30;//delay between each step
//Variables for blinking LED
int blinkVal = 0;
boolean blinkON = false;
int counter = 0; //use as a "delay"
int blinkRate = 750; //in milliseconds
//Variables to transition between RGB in a rainbow
int rainbowRedVal = 0;
int rainbowGreenVal = 0;
int rainbowBlueVal = 0;
int rainbowTransitionVal = 0;
int rainbowDelay = 5; //in milliseconds to transition between colors
//Note: You'll want to not make `rainbowDelay` too long as this will
// cause delays with button presses
//Button variables for color
const int button1Pin = 2;
boolean button1State = false;
boolean prevbutton1State = false;
boolean currentbutton1State = false;
//Button variables for pattern
const int button2Pin = 3;
boolean button2State = false;
boolean prevbutton2State = false;
boolean currentbutton2State = false;
void setup() {
// Make all of our LED pins outputs:
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
if (rgbType == commonAnode) {
//set values 255 to turn off OFF if common anode
rainbowRedVal = 255;
rainbowGreenVal = 255;
rainbowBlueVal = 255;
}
sequenceTest();//visually initialization
allOFF(); //make sure to initialize LEDs with it turned off
rgbCalc();//calculate for RGB type
rgbShow(); //make sure to show it happening
pinMode(button1Pin, INPUT_PULLUP); //use internal pullup resistor with button
pinMode(button2Pin, INPUT_PULLUP); //use internal pullup resistor with button
#if DEBUG
Serial.begin(9600); //initialize Serial Monitor
//while (!Serial); // Comment out to wait for serial port to connect to Serial Monitor. Option for native USB.
Serial.println("Custom Color Mixing Demo w/ an RGB LED. Toggling the buttons will adjust the color and pattern.");
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println("Note: Make sure to adjust the code for a common cathode or common anode.");
Serial.println("Default is set to no color and off!");
Serial.println(" ");
#endif
}//end setup()
void loop()
{
button1State = digitalRead(button1Pin);// button for Color Mode
button2State = digitalRead(button2Pin);// button for Pattern
//==================== CHECK POTENTIOMETER FOR BRIGHTNESS ====================
//Uncomment the line below if you are using a potentiometer or photoresistor (i.e. light sensor)
//brightnessLED = analogRead(knobPin) / 1023.0; //potentiometer for Brightness
/* Note: If you do not have a potentiometer or analog sensor attached,
the LEDs will flicker when the LED pulls a certain amount of power
due to the pin floating. Make sure to also GND the sensor close to your
Arduino to reduce the noise.
The LEDs can flicker at low values when using the fade mode. Make sure
to adjust the potentiometer to a certain brightness or fade values
for smooth fading.*/
/*
#if DEBUG
Serial.print(" Brightness Value % = ");
Serial.println(brightnessLED * 100);
#endif
*/
//==================== END CHECK POTENTIOMETER FOR BRIGHTNESS ====================
//==================== CHECK BUTTON FOR COLOR MODE ====================
//if button is pressed, it will be pulled low
if (button1State == LOW) {
currentbutton1State = true; // button has been pressed once
if (prevbutton1State != currentbutton1State) { //check to see if button is still being pressed
colorMode = colorMode + 1; //change color MODE after button has been pressed
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("Color Mode = ");
if (colorMode == 1) {
Serial.println("RED");
}
else if (colorMode == 2) {
Serial.println("ORANGE");
}
else if (colorMode == 3) {
Serial.println("YELLOW");
}
else if (colorMode == 4) {
Serial.println("CHARTRUESE");
}
else if (colorMode == 5) {
Serial.println("GREEN");
}
else if (colorMode == 6) {
Serial.println("SPRING GREEN");
}
else if (colorMode == 7) {
Serial.println("CYAN");
}
else if (colorMode == 8) {
Serial.println("AZURE");
}
else if (colorMode == 9) {
Serial.println("BLUE");
}
else if (colorMode == 10) {
Serial.println("VIOLET");
}
else if (colorMode == 11) {
Serial.println("MAGENTA");
}
else if (colorMode == 12) {
Serial.println("ROSE");
}
else if (colorMode == 13) {
Serial.println("WHITE");
}
else {
Serial.println("OFF");
}
#endif
//Cycle through colors when pressing buttons
if (colorMode < 0 || colorMode > 13) {
//reset ledMode
colorMode = 0;
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
}
}
else { //do nothing because finger is still on button
}
prevbutton1State = currentbutton1State;//update button1 state
}
//button has not been pressed, it will be high
else {
currentbutton1State = false;
prevbutton1State = currentbutton1State;//update button1 state
}
//==================== END CHECK BUTTON FOR COLOR MODE ====================
//==================== CHECK BUTTON FOR PATTERN ====================
if (button2State == LOW) {
currentbutton2State = true; //button has been pressed once
if (prevbutton2State != currentbutton2State) { //check to see if button is still being pressed
pattern = pattern + 1; //change LED pattern after button has been pressed
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("Pattern = ");
if (pattern == 1) {
Serial.println("ON");//print what pattern
}
else if (pattern == 2) {
Serial.println("FADE");//print what pattern
}
else if (pattern == 3) {
Serial.println("BLINK");//print what pattern
}
else if (pattern == 4) {
Serial.println("RAINBOW");//print what pattern
}
else {
Serial.println("OFF");//print what pattern
}
#endif
if (pattern < 0 || pattern > 4) {
//reset pattern
pattern = 0;
}
}
else { //do nothing because finger is still on button
}
prevbutton2State = currentbutton2State; //update button2 state
}
//button has not been pressed, it will be high
else {
currentbutton2State = false;
prevbutton2State = currentbutton2State; //update button2 state
}
switch (pattern) {
case 1:
patternON();
break;
case 2:
patternFade();
break;
case 3:
patternBlink();
break;
case 4:
patternRainbow();
break;
default:
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
break;
}
//==================== END CHECK BUTTON FOR PATTERN ====================
}//end loop
// ==================== CUSTOM FUNCTIONS DEFINED BELOW ====================
void allOFF() {
// Black (all LEDs off)
// RGB LEDs:
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
}
void redON() {
// Red
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
}
void orangeON() {
// Orange
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 128;
blueValue = 0;
}
void yellowON() {
// Yellow
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
}
void chartrueseON() {
// Chartruese
redValue = 128;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
}
void greenON() {
// Green
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 0;
}
void springGreenON() {
// Spring Green
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 128;
}
void cyanON() {
// Cyan
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 255;
}
void azureON() {
// Azure
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 128;
blueValue = 255;
}
void blueON() {
// Blue
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
}
void violetON() {
// Violet
redValue = 128;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
}
void magentaON() {
// Magenta
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 255;
}
void roseON() {
// Rose
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 128;
}
void whiteON() {
// White (all LEDs on)
redValue = 255;
greenValue = 255;
blueValue = 255;
}
//-------------------- sequenceTest() FUNCTION --------------------
void sequenceTest() {
//used to visually check when Arduino is initialized
redON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
orangeON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
yellowON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
chartrueseON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
greenON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
springGreenON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
cyanON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
azureON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
blueON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
violetON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
magentaON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
roseON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
whiteON();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
rgbShow();
delay(50);
}//-------------------- END sequenceTest() FUNCTION --------------------
void rgbCalc() {
//use this to correctly light up LED depending on the setup
if (rgbType == commonAnode) {
/* If using a common anode LED, a pin
should turn ON the LED when the pin is LOW.*/
redValue = 255 - redValue;
greenValue = 255 - greenValue;
blueValue = 255 - blueValue;
}
else {
/* If using a common cathode LED, an analog pin
should turn on the LED when the pin is HIGH. The
logic is flipped when using a Common Anode RGB LED
strip, NPN BJT/N-Channel MOSFET, and microcontroller
Leave RGB values as is, we're good!*/
}
redValue = int(redValue * brightnessLED);
greenValue = int(greenValue * brightnessLED);
blueValue = int(blueValue * brightnessLED);
}
void rgbShow() {
//once value is calculated, show the LED color
analogWrite(redPin, redValue);
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
}
//-------------------- patternON() FUNCTION --------------------
void patternON() {
// button is pressed, change LED color/sequence
switch (colorMode)
{
case 1:
redON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 2:
orangeON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 3:
yellowON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 4:
chartrueseON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 5:
greenON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 6:
springGreenON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 7:
cyanON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 8:
azureON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 9:
blueON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 10:
violetON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 11:
magentaON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 12:
roseON();
rgbCalc();
break;
case 13:
whiteON();
rgbCalc();
break;
default:
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
break;
}//end switch
rgbShow();
}//-------------------- end patternON() FUNCTION --------------------
//-------------------- patternFade() FUNCTION --------------------
void patternFade() {
switch (colorMode) {
case 1://FADE RED
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE RED ==========
case 2://FADE ORANGE
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
if (redValue > 0 && greenValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
redValue = 0;
}
// takes x amount of steps if you do not set it to zero for certain brightness (i.e. takes 8 more steps to turn off for 0.1)
//Serial.print("Red Value =");
//Serial.println( int((currentFadeVal) * brightnessLED));
//Serial.print("Green Value =");
//Serial.println( int((currentFadeVal * 0.498) * brightnessLED));
break;
//========== END FADE ORANGE ==========
case 3://FADE YELLOW
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE YELLOW ==========
case 4://FADE CHARTRUESE
redValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
if (greenValue > 0 && redValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
greenValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE CHARTRUESE ==========
case 5://FADE GREEN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE GREEN ==========
case 6://FADE SPRING GREEN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
rgbCalc();
if (greenValue > 0 && blueValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
greenValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE SPRING GREEN ==========
case 7://FADE CYAN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE CYAN ==========
case 8://FADE AZURE
redValue = 0;
greenValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498; // 128/255 = ~0.498039
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
if (blueValue > 0 && greenValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
blueValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE AZURE ==========
case 9://FADE BLUE
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE BLUE ==========
case 10://FADE VIOLET
redValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
if (blueValue > 0 && redValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
blueValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE VIOLET ==========
case 11://FADE MAGENTA
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE MAGENTA ==========
case 12://FADE ROSE
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = currentFadeVal * 0.498;
rgbCalc();
if (redValue > 0 && blueValue == 0) {
//tertiary component is 1/2, so when it calculates to decimal with fade value,
//it will be basically be off, make sure to turn off other color so that
//it does not just show the other color
redValue = 0;
}
break;
//========== END FADE ROSE ==========
case 13://FADE WHITE
redValue = currentFadeVal;
greenValue = currentFadeVal;
blueValue = currentFadeVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
//========== END FADE WHITE ==========
default:
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
break;
}
rgbShow();
delay(fadeDelay);
if (increasing == true) {
currentFadeVal += fadeVal;
}
else { //decreasing
currentFadeVal -= fadeVal;
}
if (currentFadeVal > fadeMAX) {
increasing = false;
prevFadeVal -= fadeVal;//undo addition
currentFadeVal = prevFadeVal;
}
else if (currentFadeVal < fadeMIN) {
increasing = true;
prevFadeVal += fadeVal;//unto subtraction
currentFadeVal = prevFadeVal;
}
prevFadeVal = currentFadeVal;
}//-------------------- END patternFade() FUNCTION --------------------
//-------------------- patternBlink() FUNCTION --------------------
void patternBlink() {
switch (colorMode) {
case 1://RED
redValue = blinkVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 2://ORANGE
redValue = blinkVal;
greenValue = blinkVal * 0.498;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 3://YELLOW
redValue = blinkVal;
greenValue = blinkVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 4://CHARTREUSE
redValue = blinkVal * 0.498;
greenValue = blinkVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 5://GREEN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = blinkVal;
blueValue = 0;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 6://SRING GREEN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = blinkVal;
blueValue = blinkVal * 0.498;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 7://CYAN
redValue = 0;
greenValue = blinkVal;
blueValue = blinkVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 8://AZURE
redValue = 0;
greenValue = blinkVal * 0.498;
blueValue = blinkVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 9://BLUE
redValue = 0;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = blinkVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 10://VIOLET
redValue = blinkVal * 0.498;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = blinkVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 11://MAGENTA
redValue = blinkVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = blinkVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 12://ROSE
redValue = blinkVal;
greenValue = 0;
blueValue = blinkVal * 0.498;
rgbCalc();
break;
case 13://WHITE
redValue = blinkVal;
greenValue = blinkVal;
blueValue = blinkVal;
rgbCalc();
break;
default:
allOFF();
rgbCalc();
break;
}
rgbShow();
if (counter == blinkRate) {
if (blinkON == true) {
blinkVal = 0;
blinkON = false;
}
else { //it was on, so turn off
blinkVal = 255;
blinkON = true;
}
counter = 0;
}
else {
counter = counter + 1;
}
}//-------------------- patternBlink() FUNCTION //--------------------
//-------------------- patternRainbow() FUNCTION --------------------
void patternRainbow() {
if (rgbType == commonCathode) {
if (rainbowTransitionVal == 0) {
//RED
rainbowRedVal += 5;
if (rainbowRedVal >= 255) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 1;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 1) {
//RED TO ORANGE TO YELLOW
rainbowGreenVal += 5;
if (rainbowGreenVal >= 255) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 2;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 2) {
//YELLOW to CHARTREUSE to GREEN
rainbowRedVal -= 5;
if (rainbowRedVal <= 0) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 3;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 3) {
//GREEN to SPRING GREEN to CYAN
rainbowBlueVal += 5;
if (rainbowBlueVal >= 255) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 4;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 4) {
//CYAN to AZURE to BLUE
rainbowGreenVal -= 5;
if (rainbowGreenVal <= 0) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 5;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 5) {
//BLUE to VIOLET to MAGENTA
rainbowRedVal += 5;
if (rainbowRedVal >= 255) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 6;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 6) {
//MAGENTA to ROSE to RED
rainbowBlueVal -= 5;
if (rainbowBlueVal <= 0) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 1;
}
}
}//end check for commonCathode
else {
if (rainbowTransitionVal == 0) {
//RED
rainbowRedVal -= 5;
if (rainbowRedVal <= 0) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 1;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 1) {
//RED TO ORANGE TO YELLOW
rainbowGreenVal -= 5;
if (rainbowGreenVal <= 0) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 2;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 2) {
//YELLOW to CHARTREUSE to GREEN
rainbowRedVal += 5;
if (rainbowRedVal >= 255) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 3;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 3) {
//GREEN to SPRING GREEN to CYAN
rainbowBlueVal -= 5;
if (rainbowBlueVal <= 0) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 4;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 4) {
//CYAN to AZURE to BLUE
rainbowGreenVal += 5;
if (rainbowGreenVal >= 255) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 5;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 5) {
//BLUE to VIOLET to MAGENTA
rainbowRedVal -= 5;
if (rainbowRedVal <= 0) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 6;
}
}
else if (rainbowTransitionVal == 6) {
//MAGENTA to ROSE to RED
rainbowBlueVal += 5;
if (rainbowBlueVal >= 255) {
rainbowTransitionVal = 1;
}
}
}//end check for commonAnode
redValue = int(rainbowRedVal * brightnessLED);
greenValue = int(rainbowGreenVal * brightnessLED);
blueValue = int(rainbowBlueVal * brightnessLED);
// Note: the rainbow function calculates the function here so
// we do not need to call the `rgbCalc()` function
rgbShow();
delay(rainbowDelay);
}//-------------------- END patternRainbow() FUNCTION --------------------
// ==================== END CUSTOM FUNCTIONS DEFINED ====================
Once the code has been uploaded, the demo will cycle through the defined colors. Pressing the buttons will cycle through the color or pattern. Opening the Arduino serial monitor at 9600 will show the current color mode or pattern after every button press.


