LSM9DS0 Hookup Guide
Advanced Arduino Example
The basic example is perfect if all you want to do is poll the LSM9DS0 a few times per second to get movement data, but what if you want to make use of the IMU's interrupt outputs? Using interrupts you can get read data in from the LSM9DS0 as soon as it's available. This example will show you how to get more out of your LSM9DS0 Breakout.
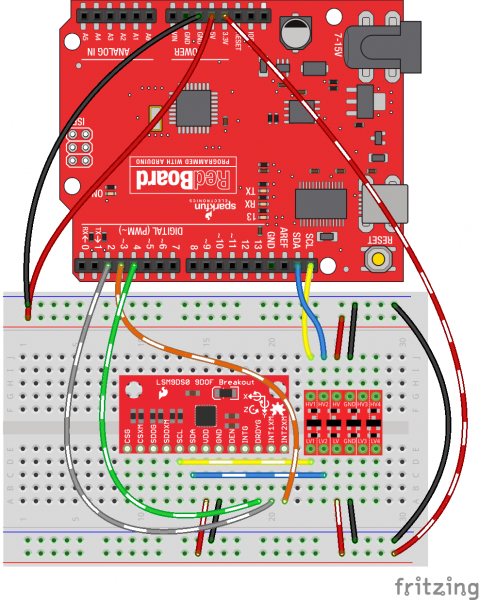
Circuit Diagram
In addition to the SDA and SCL pins, this example will make use of the DRDYG, INT1XM, and INT2XM pins. Here's the hookup diagram:
Again, you'll need to use a logic level converter between SDAs and SCLs. There is no need for level shifting on the three interrupt lines -- the 3.3V output from the LSM9DS0 will be enough to trigger a logic high on the Arduino (see Logic Levels).
Example Code: LSM9DS0_SerialMenus
Open up the LSM9DS0_SerialMenus example by going to File > Examples > SFE_LSM9DS0 > LSM9DS0_SerialMenus. Here's the code:
language:c
/*****************************************************************
LSM9DS0_SerialMenus.ino
SFE_LSM9DS0 Library Example Code: Interact With Serial Menus
Jim Lindblom @ SparkFun Electronics
Original Creation Date: February 14, 2014 (Happy Valentines Day!)
https://github.com/sparkfun/LSM9DS0_Breakout
This Arduino sketch is a demo of all things SEF_LSM9DS0 library.
Once you attach all hardware, and upload the sketch, open your
Serial monitor at 115200 BPS. Follow the menu prompts to either:
1) Stream readings from the accelerometer.
2) Stream readings from the gyroscope.
3) Stream readings from the magnetometer.
4) Set the scales of each sensor (e.g. +/-4g, 500DPS, 8Gs)
5) Switch to/from calculated or raw data (e.g. ADC ticks or
g's, DPS, and Gs)
6) Set the output data rate of each sensor.
Hardware setup: This library supports communicating with the
LSM9DS0 over either I2C or SPI. In addition to those wires, this
sketch demos how to use the interrupts. Here's what the I2C setup
looks like:
LSM9DS0 --------- Arduino
CSG ------------- NONE (Pulled HIGH [indicates I2C mode])
CSXM ------------ NONE (Pulled HIGH [indicates I2C mode])
SDOG ------------ NONE (Pulled HIGH [sets I2C address])
SDOXM ----------- NONE (Pulled HIGH [sets I2C address])
SCL ---------- SCL (A5 on older 'Duinos')
SDA ---------- SDA (A4 on older 'Duinos')
VDD ------------- 3.3V
GND ------------- GND
DEN ------------- NONE (Not used in this example)
INTG ------------ NONE (Not used in this example)
DRDYG ------------ 4 (Could be any digital pin)
INT1XM ----------- 3 (Could be any digital pin)
INT2XM ----------- 2 (Could be any digital pin)
The LSM9DS0 has a maximum voltage of 3.6V. Make sure you power it
off the 3.3V rail! And either use level shifters between SCL
and SDA or just use a 3.3V Arduino Pro.
Development environment specifics:
IDE: Arduino 1.0.5
Hardware Platform: Arduino Pro 3.3V/8MHz
LSM9DS0 Breakout Version: 1.0
This code is beerware; if you see me (or any other SparkFun
employee) at the local, and you've found our code helpful, please
buy us a round!
Distributed as-is; no warranty is given.
*****************************************************************/
// The SFE_LSM9DS0 requires both the SPI and Wire libraries.
// Unfortunately, you'll need to include both in the Arduino
// sketch, before including the SFE_LSM9DS0 library.
#include <SPI.h> // Included for SFE_LSM9DS0 library
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SFE_LSM9DS0.h>
///////////////////////
// Example I2C Setup //
///////////////////////
// SDO_XM and SDO_G are both grounded, therefore our addresses are:
#define LSM9DS0_XM 0x1D // Would be 0x1E if SDO_XM is LOW
#define LSM9DS0_G 0x6B // Would be 0x6A if SDO_G is LOW
// Create an instance of the LSM9DS0 library called `dof` the
// parameters for this constructor are:
// [SPI or I2C Mode declaration], [gyro I2C address], [xm I2C address]
LSM9DS0 dof(MODE_I2C, LSM9DS0_G, LSM9DS0_XM);
///////////////////////
// Example SPI Setup //
///////////////////////
//#define LSM9DS0_CSG 9 // CSG connected to Arduino pin 9
//#define LSM9DS0_CSXM 10 // CSXM connected to Arduino pin 10
//LSM9DS0 dof(MODE_SPI, LSM9DS0_CSG, LSM9DS0_CSXM);
///////////////////////////////
// Interrupt Pin Definitions //
///////////////////////////////
const byte INT1XM = 2; // INT1XM tells us when accel data is ready
const byte INT2XM = 3; // INT2XM tells us when mag data is ready
const byte DRDYG = 4; // DRDYG tells us when gyro data is ready
// A boolean to keep track of whether we're printing raw (ADC)
// or calculated (g's, DPS, Gs) sensor data:
boolean printRaw = true;
void setup()
{
// Set up interrupt pins as inputs:
pinMode(INT1XM, INPUT);
pinMode(INT2XM, INPUT);
pinMode(DRDYG, INPUT);
Serial.begin(115200); // Start serial at 115200 bps
// Use the begin() function to initialize the LSM9DS0 library.
// You can either call it with no parameters (the easy way):
uint16_t status = dof.begin();
// Or call it with declarations for sensor scales and data rates:
//uint16_t status = dof.begin(dof.G_SCALE_2000DPS, dof.A_SCALE_6G, dof.M_SCALE_2GS);
// begin() returns a 16-bit value which includes both the gyro and
// accelerometers WHO_AM_I response. You can check this to make sure
// communication was successful.
Serial.println(status, HEX);
}
void loop()
{
// Print the control menu:
printMenu();
// Then wait for any serial data to come in:
while (!Serial.available())
;
// Once serial data is received, call parseMenu to act on it:
parseMenu(Serial.read());
}
void printAccel()
{
// Only read from the accelerometer if the accel interrupts,
// which means that new data is ready.
if (digitalRead(INT1XM))
{
// Use the readAccel() function to get new data from the accel.
// After calling this function, new values will be stored in
// the ax, ay, and az variables.
dof.readAccel();
Serial.print("A: ");
if (printRaw)
{
Serial.print(dof.ax);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.ay);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.az);
}
else
{
Serial.print(dof.calcAccel(dof.ax));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcAccel(dof.ay));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.calcAccel(dof.az));
}
}
}
void printGyro()
{
// Only read from the gyro if the DRDY interrupts,
// which means that new data is ready.
if (digitalRead(DRDYG))
{
// Use the readGyro() function to get new data from the gyro.
// After calling this function, new values will be stored in
// the gx, gy, and gz variables.
dof.readGyro();
Serial.print("G: ");
if (printRaw)
{
Serial.print(dof.gx);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.gy);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.gz);
}
else
{
Serial.print(dof.calcGyro(dof.gx));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcGyro(dof.gy));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.calcGyro(dof.gz));
}
}
}
void printMag()
{
// Only read from the magnetometer if the INT2XM interrupts,
// which means that new data is ready.
if (digitalRead(INT2XM))
{
// Use the readMag() function to get new data from the mag.
// After calling this function, new values will be stored in
// the mx, my, and mz variables.
dof.readMag();
Serial.print("M: ");
if (printRaw)
{
Serial.print(dof.mx);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.my);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.mz);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(calcHeading(dof.mx, dof.my, dof.mz));
}
else
{
Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.mx), 4);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.my), 4);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.mz), 4);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(calcHeading(dof.mx, dof.my, dof.mz));
}
}
}
// Here's a simple example function to calculate heading based on
// magnetometer readings. This only works when the 9DOF is flat
// (x-axis normal to gravity).
float calcHeading(float hx, float hy, float hz)
{
if (hy > 0)
{
return 90 - atan(hx / hy) * 180 / PI;
}
else if (hy < 0)
{
return 270 - atan(hx / hy) * 180 / PI;
}
else // hy = 0
{
if (hx < 0) return 180;
else return 0;
}
}
// This function will print all data from all sensors at once.
// It'll wait until every sensor interrupt triggers before
// printing.
void streamAll()
{
if ((digitalRead(INT2XM)) && (digitalRead(INT1XM)) &&
(digitalRead(DRDYG)))
{
printAccel();
printGyro();
printMag();
}
}
void setScale()
{
char c;
Serial.println(F("Set accelerometer scale:"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 2G"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 4G"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 6G"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) +/- 8G"));
Serial.println(F("\t5) +/- 16G"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_2G);
break;
case '2':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_4G);
break;
case '3':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_6G);
break;
case '4':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_8G);
break;
case '5':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_16G);
break;
}
Serial.println(F("Set gyroscope scale:"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 245 DPS"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 500 DPS"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 2000 DPS"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_245DPS);
break;
case '2':
dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_500DPS);
break;
case '3':
dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_2000DPS);
break;
}
Serial.println(F("Set magnetometer scale:"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 2GS"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 4GS"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 8GS"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) +/- 12GS"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_2GS);
break;
case '2':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_4GS);
break;
case '3':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_8GS);
break;
case '4':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_12GS);
break;
}
}
void setRaw()
{
if (printRaw)
{
printRaw = false;
Serial.println(F("Printing calculated readings"));
}
else
{
printRaw = true;
Serial.println(F("Printing raw readings"));
}
}
void setODR()
{
char c;
Serial.println(F("Set Accelerometer ODR (Hz):"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) 3.125 \t 6) 100"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) 6.25 \t 7) 200"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) 12.5 \t 8) 400"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) 25 \t 9) 800"));
Serial.println(F("\t5) 50 \t A) 1600"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_3125);
break;
case '2':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_625);
break;
case '3':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_125);
break;
case '4':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_25);
break;
case '5':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_50);
break;
case '6':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_100);
break;
case '7':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_200);
break;
case '8':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_400);
break;
case '9':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_800);
break;
case 'A':
case 'a':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_1600);
break;
}
Serial.println(F("Set Gyro ODR/Cutoff (Hz):"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) 95/12.5 \t 8) 380/25"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) 95/25 \t 9) 380/50"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) 190/125 \t A) 380/100"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) 190/25 \t B) 760/30"));
Serial.println(F("\t5) 190/50 \t C) 760/35"));
Serial.println(F("\t6) 190/70 \t D) 760/50"));
Serial.println(F("\t7) 380/20 \t E) 760/100"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_95_BW_125);
break;
case '2':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_95_BW_25);
break;
case '3':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_125);
break;
case '4':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_25);
break;
case '5':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_50);
break;
case '6':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_70);
break;
case '7':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_20);
break;
case '8':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_25);
break;
case '9':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_50);
break;
case 'A':
case 'a':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_100);
break;
case 'B':
case 'b':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_30);
break;
case 'C':
case 'c':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_35);
break;
case 'D':
case 'd':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_50);
break;
case 'E':
case 'e':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_100);
break;
}
Serial.println(F("Set Magnetometer ODR (Hz):"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) 3.125 \t 4) 25"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) 6.25 \t 5) 50"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) 12.5 \t 6) 100"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_3125);
break;
case '2':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_625);
break;
case '3':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_125);
break;
case '4':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_25);
break;
case '5':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_50);
break;
case '6':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_100);
break;
}
}
void printMenu()
{
Serial.println();
Serial.println(F("////////////////////////////////////////////"));
Serial.println(F("// LSM9DS0 Super Awesome Amazing Fun Time //"));
Serial.println(F("////////////////////////////////////////////"));
Serial.println();
Serial.println(F("1) Stream Accelerometer"));
Serial.println(F("2) Stream Gyroscope"));
Serial.println(F("3) Stream Magnetometer"));
Serial.println(F("4) Stream output from all sensors"));
Serial.println(F("5) Set Sensor Scales"));
Serial.println(F("6) Switch To/From Raw/Calculated Readings"));
Serial.println(F("7) Set Output Data Rates"));
Serial.println();
}
void parseMenu(char c)
{
switch (c)
{
case '1':
while(!Serial.available())
printAccel();
break;
case '2':
while(!Serial.available())
printGyro();
break;
case '3':
while(!Serial.available())
printMag();
break;
case '4':
while(!Serial.available())
{
streamAll();
}
break;
case '5':
setScale();
break;
case '6':
setRaw();
break;
case '7':
setODR();
break;
}
}
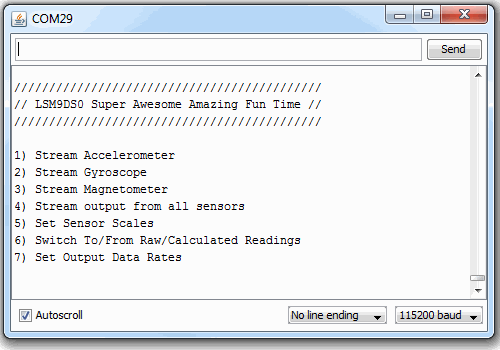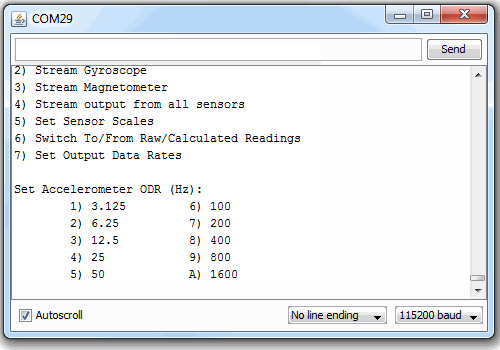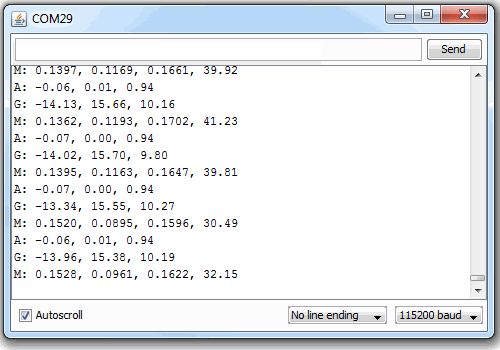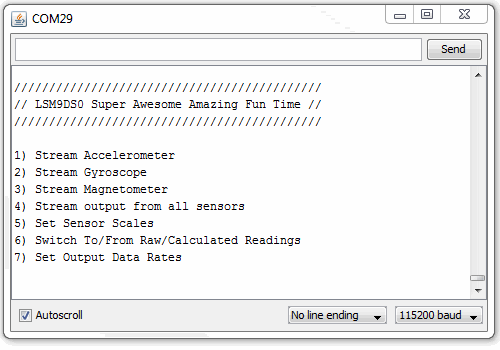
Upload the code, then open up your serial monitor with the baud rate set to 115200 bps. Then just follow the menu prompts to interact with the sensor. You can stream the accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer individually or together.
Send any key to stop the streaming and bring the menu back.
There are also menu items that allow you to set the range and data rates of the sensors. Make sure you give those a spin, and see how they affect the output of the sensor.