Experiment Guide for the SparkFun Tinker Kit
This Tutorial is Retired!
This tutorial covers concepts or technologies that are no longer current. It's still here for you to read and enjoy, but may not be as useful as our newest tutorials.
View the updated tutorial: Activity Guide for SparkFun Tinker Kit
Experiment 5: Reading a Button Press
Introduction
Up until now, we’ve focused mostly on outputs. Now we’re going to go to the other end of the spectrum and play around with inputs. In Experiment 2, we used an analog input to read the potentiometer. In this experiment, we’ll be reading one of the most common and simple inputs – a push button – by using a digital input. We will use it to cycle through different colors on the RGB.
Parts Needed
You will need the following parts:
- 1x Breadboard
- 1x SparkFun RedBoard
- 1x RGB LED
- 3x 330Ω Resistor
- 8x Jumper Wires
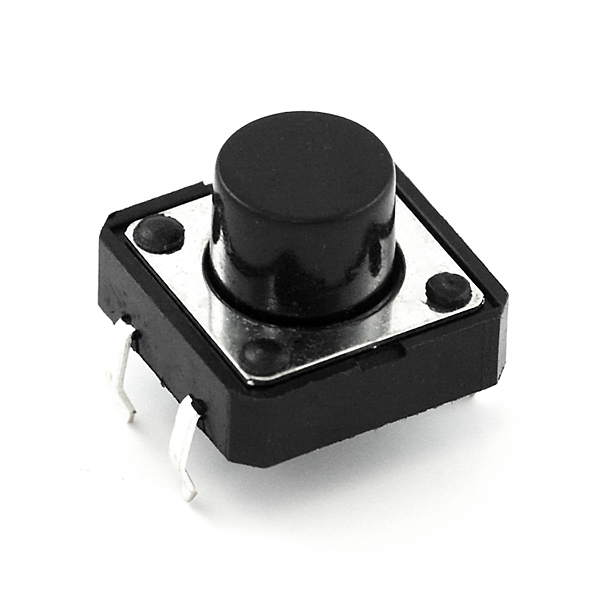
- 1x Push Button
- 1x 10K Resistors
Didn't Get the Tinker Kit?
If you are conducting this experiment and didn't get the Tinker Kit, we suggest using these parts:
Resistor 330 Ohm 1/6 Watt PTH - 20 pack
COM-11507Suggested Reading
Before continuing with this experiment, we recommend you be somewhat familiar with the concepts in these tutorials:
Introducing the Push Button
A momentary push button closes or completes the circuit only while it is being pressed. The button has four pins, which are broken out into two sets of two pins. When you press down on the button and get a nice "click," the button bridges the two sets of pins and allows current to flow through the circuit.
How do you know which pins are paired up? The buttons included in this kit will only fit across the breadboard ditch in one direction. Once you get the button pressed firmly into the breadboard (across the ditch), the pins are horizontally paired. The pins toward the top of the breadboard are connected, and the pins toward the button of the breadboard are connected.
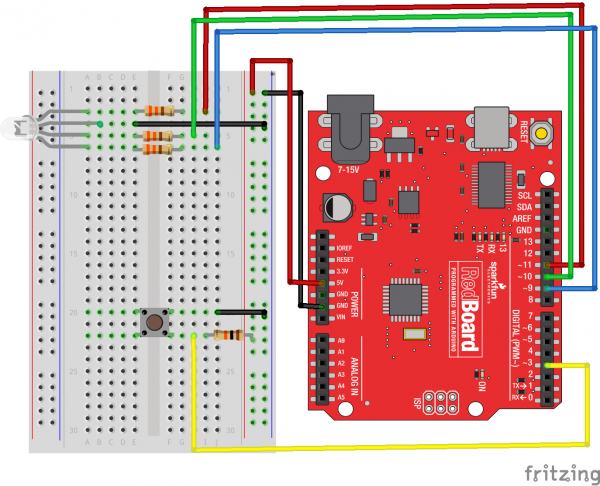
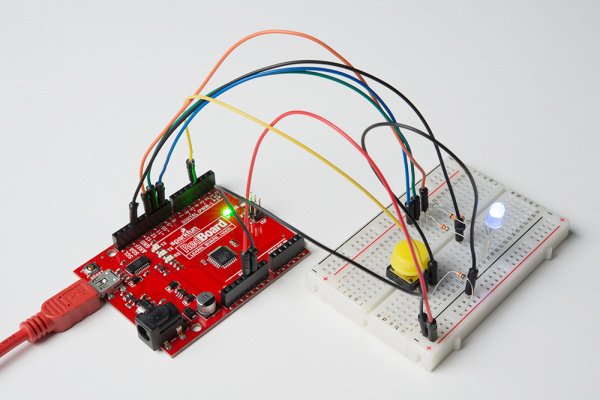
Hardware Hookup
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the wiring diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Wiring Diagram for the Experiment
Digital Input
Previously we've used the analog pins for input; now we'll use the digital pins for input as well. Because digital pins only know about HIGH and LOW signals, they're perfect for interfacing to pushbuttons and switches that also only have "on" and "off" states.
We'll connect one side of the pushbutton to ground, and the other side to a digital pin. When we press down on the pushbutton, the pin will be connected to ground, and therefore will be read as "LOW" by the RedBoard.
But wait -- what happens when you're not pushing the button? In this state, the pin is disconnected from everything, which we call "floating." What will the pin read as, then -- HIGH or LOW? It's hard to say, because there's no solid connection to either 5V or ground. The pin could read as either one.
To deal with this issue, we'll connect a small (10K, or 10,000 Ohm) resistance between the signal pin and 5V. This "pull-up" resistor will ensure that when you're NOT pushing the button, the pin will still have a weak connection to 5 volts, and therefore read as HIGH.
Open the Sketch
Open the Arduino IDE software on your computer. Coding in the Arduino language will control your circuit.
You can type out or copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/*
SparkFun Tinker Kit
Example sketch 05
PUSH BUTTONS
Use pushbuttons for digital input
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics,
with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
Visit http://learn.sparkfun.com/products/2 for SIK information.
Visit http://www.arduino.cc to learn about Arduino.
*/
// First we'll set up constants for the pin numbers.
// This will make it easier to follow the code below.
// pushbutton pin
const int buttonPin = 3;
//RGB LED pins
const int redPin = 11;
const int greenPin = 10;
const int bluePin = 9;
//create a variable to store a counter and set it to 0
int counter = 0;
void setup()
{
// Set up the pushbutton pins to be an input:
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
// Set up the RGB pins to be an outputs:
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin,OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// local variable to hold the pushbutton states
int buttonState;
//read the digital state of buttonPin with digitalRead() function and store the //value in buttonState variable
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
//if the button is pressed increment counter and wait a tiny bit to give us some //time to release the button
if (buttonState == LOW) // light the LED
{
counter++;
delay(150);
}
//use the if satement to check the value of counter. If counter is equal to 0 all //pins are off
if(counter == 0)
{
digitalWrite(redPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(greenPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(bluePin,LOW);
}
//else if counter is equal to 1, redPin is HIGH
else if(counter == 1)
{
digitalWrite(redPin,HIGH);
digitalWrite(greenPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(bluePin,LOW);
}
//else if counter is equal to 2 greenPin is HIGH
else if(counter ==2)
{
digitalWrite(redPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(greenPin,HIGH);
digitalWrite(bluePin,LOW);
}
//else if counter is equal to 3 bluePin is HIGH
else if(counter ==3)
{
digitalWrite(redPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(greenPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(bluePin,HIGH);
}
//else reset the counter to 0 (which turns all pins off)
else
{
counter =0;
}
}
Code to Note
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
The digital pins can be used as inputs as well as outputs. Before you do either, you need to tell the Arduino which direction you're going.
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
To read a digital input, you use the digitalRead() function. It will return HIGH if there's 3.3V present at the pin, or LOW if there's 0V present at the pin.
if (button1State == LOW)
Because we've connected the button to GND, it will read LOW when it's being pressed. Here we're using the "equivalence" operator ("==") to see if the button is being pressed.
What You Should See
You should see the LED turn on one color if you press the button. If you continue to press the button, the LED will change colors. (See the code to find out why!) If it isn't working, make sure you have assembled the circuit correctly and verified and uploaded the code to your board, or see the Troubleshooting section.
Troubleshooting
Light Not Turning On
The pushbutton is square, and because of this it is easy to put it in the wrong way. Give it a 90 degree twist and see if it starts working.
Underwhelmed
No worries; these circuits are all super stripped-down to make playing with the components easy, but once you throw them together the sky is the limit.