Experiment Guide for the SparkFun Tinker Kit
This Tutorial is Retired!
This tutorial covers concepts or technologies that are no longer current. It's still here for you to read and enjoy, but may not be as useful as our newest tutorials.
View the updated tutorial: Activity Guide for SparkFun Tinker Kit
Experiment 2: Reading a Potentiometer
Introduction
In this circuit you will work with a potentiometer. You will learn how to use a potentiometer to control the timing of a blinking LED by reading a sensor and storing it as a variable, then using it as your delay timing.
Parts Needed
You will need the following parts:
- 1x Breadboard
- 1x SparkFun RedBoard
- 1x LED
- 1x 330Ω Resistor
- 7x Jumper Wires
- 1x Potentiometer
Didn't Get the Tinker Kit?
If you are conducting this experiment and didn't get the Tinker Kit, we suggest using these parts:
Resistor 330 Ohm 1/6 Watt PTH - 20 pack
COM-11507Suggested Reading
Before continuing with this experiment, we recommend you be familiar with the concepts in the following tutorial:
Introducing the Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a resistance-based analog sensor that changes its internal resistance based on the rotation of its knob. The potentiometer has an internal voltage divider enabling you to read the change in voltage on the center pin with a microcontroller (the RedBoard). To hook up the potentiometer, attach the two outside pins to a supply voltage (5V in this circuit) and ground. It doesn’t matter which is connected where, as long as one is connected to power, and the other to ground. The center pin is then connected to an analog input pin so the RedBoard can measure the change in voltage. When you twist the knob, the sensor reading will change!
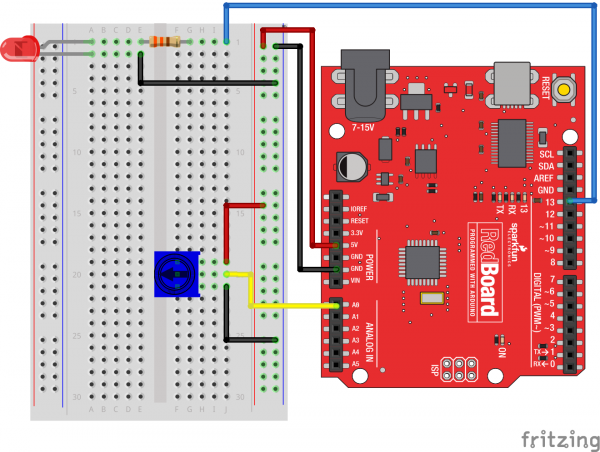
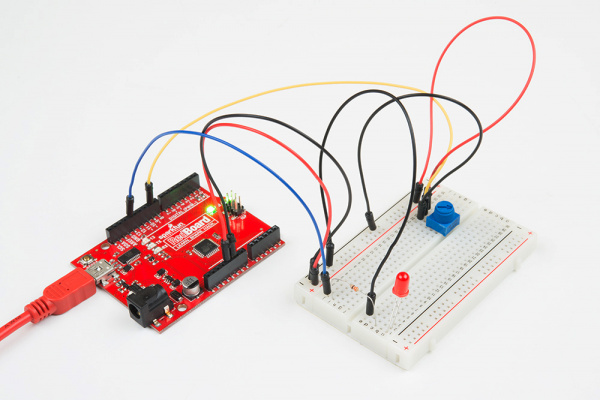
Hardware Hookup
Ready to start hooking everything up? Check out the wiring diagram and hookup table below to see how everything is connected.
| Polarized Components | Pay special attention to the component’s markings indicating how to place it on the breadboard. Polarized components can only be connected to a circuit in one direction. |
Wiring Diagram for the Experiment
Open the Sketch
Open the Arduino IDE software on your computer. Coding in the Arduino language will control your circuit.
You can type out or copy and paste the following code into the Arduino IDE. Hit upload, and see what happens!
language:cpp
/* SparkFun Tinker Kit
Example sketch 02
POTENTIOMETER
Measure the position of a potentiometer and use it to
control the blink rate of an LED. Turn the knob to make
it blink faster or slower!
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics,
with lots of help from the Arduino community.
This code is completely free for any use.
Visit http://learn.sparkfun.com/products/2 for SIK information.
Visit http://www.arduino.cc to learn about Arduino.
*/
//Create global variables (variables that can be used anywhere in our sketch)
// Here we're creating a variable called "sensorPin" of type "int"
// and initializing it to have the value "0," which is the analog input pin the pot is //conected to.
int sensorPin = 0;
// Variable for storing the pin number that the LED is connected to
int ledPin = 13;
// this function runs once when the sketch starts up
void setup()
{
//set ledPin (13) as an OUTPUT
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
// this function runs repeatedly after setup() finishes
void loop()
{
//create a local variable (variable that can only be used inside of loop() to store //a sensor value called sensorValue
int sensorValue;
//use the analogRead() function to read sensorPin and store the value in sensorValue
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Turn the LED on
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(sensorValue);
// Turn the LED off
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
//delay for the value of sensorValue
delay(sensorValue);
//loop back to the top
}
Code to Note
int sensorValue;
A “variable” is a placeholder for values that may change in your code. You must introduce, or "declare," variables before you use them; here you are declaring a variable called sensorValue, of type "int" (integer). Don't forget that variable names are case sensitive!
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
Use the analogRead() function to read the value on an analog pin. analogRead() takes one parameter, the analog pin you want to use ("sensorPin"), and returns a number ("sensorValue") between 0 (0 volts) and 1023 (3.3 volts).
delay(sensorValue);
Microcontrollers are very fast, capable of running thousands of lines of code each second. To slow it down so that we can see what it's doing, we'll often insert delays into the code. delay() counts in milliseconds; there are 1,000 ms in one second.
What You Should See
You should see the LED blink faster or slower in accordance with your potentiometer. If it isn't working, make sure you have assembled the circuit correctly and verified and uploaded the code to your board, or see the Troubleshooting section.
Troubleshooting
Sporadically Working
This is most likely due to a slightly dodgy connection with the potentiometer's pins. This can usually be conquered by holding the potentiometer down or moving the potentiometer circuit somewhere else on your breadboard.
Not Working
Make sure you haven’t accidentally connected the wiper (center pin), the resistive element in the potentiometer, to digital pin 0 rather than analog pin 0 (the row of pins beneath the power pins).
LED Not Lighting Up
LEDs will only work in one direction. Double check your connections.