DA16200 Thing Plus Hookup Guide
Hardware Assembly
Programming
The USB connection is utilized for programming, serial debug interface, and AT commands. Users only need to plug their DA16200 Thing Plus into a computer using a USB-C cable. Users will then be able to interact with the DA16200 module through a serial terminal.
Headers
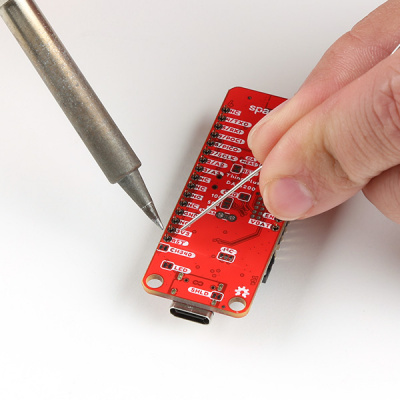
The pins for the DA16200 Thing Plus are broken out to 0.1"-spaced pins on the outer edges of the board. When selecting headers, be sure you are aware of the functionality you need. If you have never soldered before or need a quick refresher, check out our How to Solder: Through-Hole Soldering guide.
The Feather Stackable Header Kit is a great option as it allows users to stack shields (w/ Feather footprint) or it can be placed on the a breadboard; while, the pins are still accessible from the female/male headers.
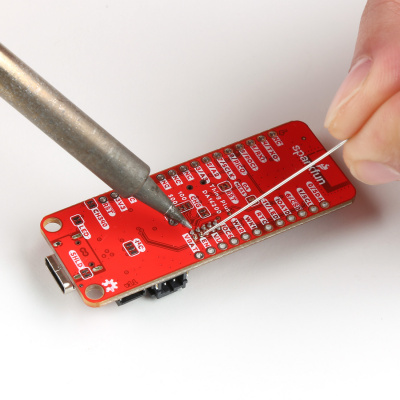
JTAG Header
If users wish to connect a debugger/programmer, they will need to solder a JTAG header. (Depending on the debugger/programmer customers utilize, an adapter may be necessary.)
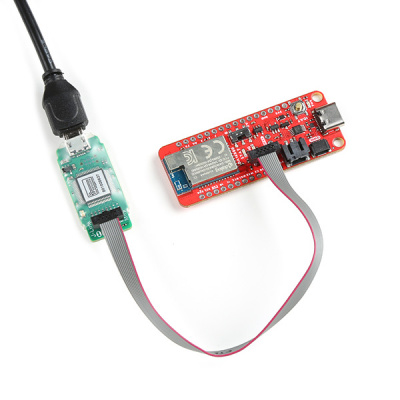
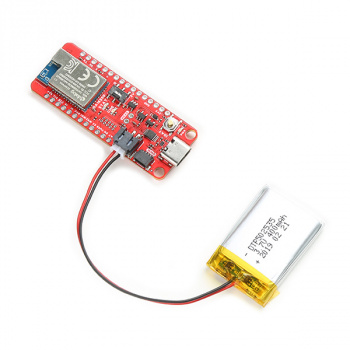
Battery
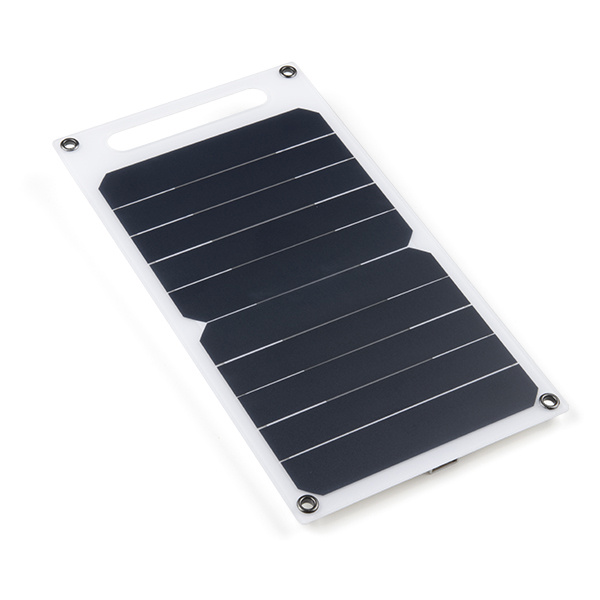
For remote applications, the DA16200 Thing Plus can be powered through its 2-pin JST battery connector. Additionally, users may be interested in utilizing a solar panel and USB-C cable to recharge their battery.
Solar Panel Charger - 10W
PRT-16835Note: DO NOT remove batteries by pulling on their wires. Instead, it is recommended that pair of dikes (i.e. diagonal wire cutters), pliers, or tweezers be used to pull on the JST connector housing, to avoid damaging the battery wiring.
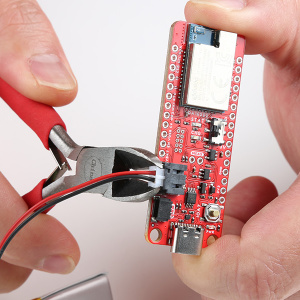
Using a pair of dikes to disconnect a battery. (Click to enlarge)
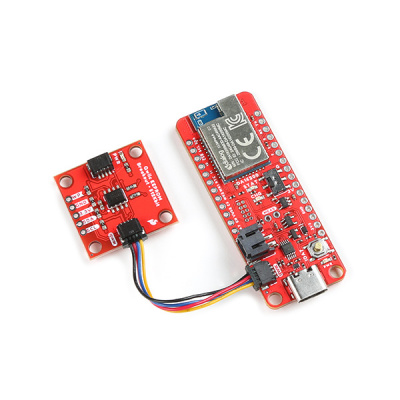
Qwiic Devices
The Qwiic system allows users to effortlessly prototype with a Qwiic compatible I2C device without soldering. Users can attach any Qwiic compatible sensor or board, with just a Qwiic cable.