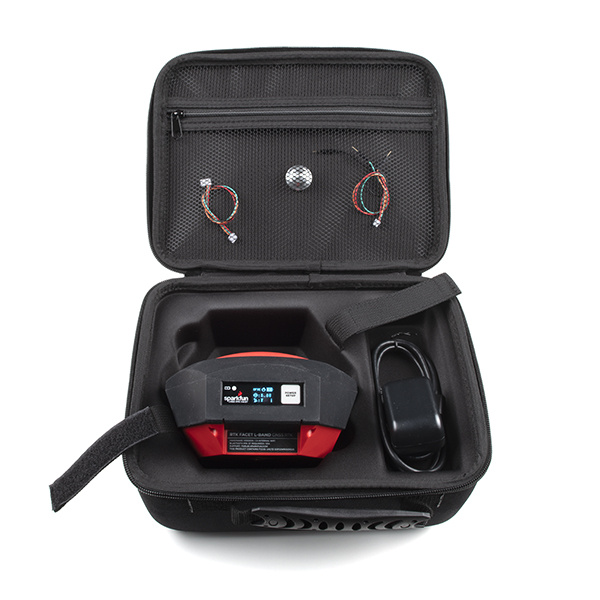
SparkFun RTK Facet L-Band Hookup Guide
Introduction
Note: In July of 2025 u-blox announced the L-Band service to North America would be discontinued on December 31st, 2025. RTK Facet L-Band units will continue to work after this date as high precision devices, but they will need to switch to an internet based correction services to obtain an RTK Fix. Because of this change, the device has been retired. This information remains available for customers who own the device.
The RTK Facet L-Band from SparkFun is our most advanced GNSS receiver to date. It's your one stop shop for high precision geolocation and surveying needs. For basic users, it’s incredibly easy to get up and running and for advanced users, the RTK Facet L-Band is a flexible and powerful tool.
SparkFun RTK Facet L-Band
GPS-20000With just a few minutes of setup, the RTK Facet L-Band is the fastest product currently on the market to take centimeter grade measurements.
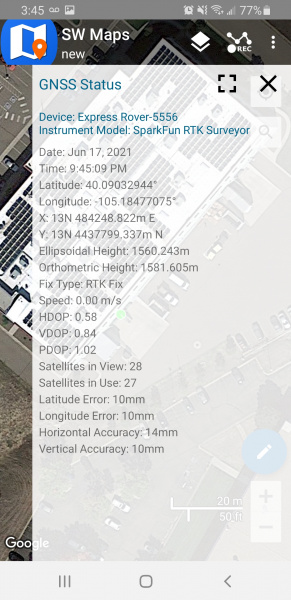
With just the press of a button, the RTK Facet L-Band is the fastest way to take centimeter-grade measurements. With built-in corrections, 14mm Real Time Kinematic fixes are less than a minute away. By connecting your phone to the RTK Facet L-Band over Bluetooth®, your phone or tablet can receive the NMEA output and work most GIS software. This is exactly how $10,000 surveying devices have been operating for the past decade - we just made it faster, more precise, and a lot more economical.
Required Materials
The RTK Facet L-Band has all you need built into one small unit. In addition, the RTK Facet L-Band Kit includes everything you might need as well. The only thing you need to add is your own tablet or cell phone (Andriod and iOS are supported).
No external radio link or RTCM corrections are needed. The RTK Facet L-Band utilizes corrections from u-blox's PointPerfect service broadcast from a geosynchronous Inmarsat satellite. The only setup required is a WiFi SSID and password. Once entered, the device will provision itself and periodically (once a month) update the decryption keys necessary to use the PointPerfect service. The price of the RTK Facet L-Band includes a 12-month subscription. Additional years of service can be purchased.
To charge the RTK Facet you will need a USB C cable and a power supply. These are included with the kit but any USB C port should charge the Facet at a maximum rate of 1A per hour.
Suggested Reading
GNSS RTK is an incredible feat of engineering that has been made easy to use by powerful GNSS receivers such as the ZED-F9P by u-blox (the receiver inside RTK Facet). The process of setting up an RTK system will be covered in this tutorial but if you want to know more about RTK here are some good tutorials to brush up on:
What is GPS RTK?
Getting Started with U-Center for u-blox
GPS-RTK2 Hookup Guide
Setting up a Rover Base RTK System
How to Build a DIY GNSS Reference Station
How RTK Facet L-Band Works
The SparkFun RTK Facet L-Band is unique in that it receives its corrections from u-blox's PointPerfect service broadcast from a geosynchronous Inmarsat satellite. No base station is needed, no external radio link, no internet connection or RTCM corrections are needed to achieve RTK fix. The RTK Facet L-Band does not require creating an account anywhere, does not require copy and pasting of keys, certificates, or any other materials. Everything is built into one unit and made to be as easy as possible to use.
What magic is this?
A normal RTK setup requires a Base and Rover. The Base sits still and provides RTCM corrections over a radio or internet link to a rover. These corrections aid the Rover in its location calculations allowing it to remove small ionospheric and tropospheric distortions. When it's all working, you can achieve 14mm X, Y, and Z accuracy. For many applications this works fine, but for a variety of applications a unit is often located far from cellular connectivity or a base station setup is not possible. For this reason, u-blox has built a large network of base stations across the contiguous 48 states of the USA. The correction data from these stations are aggregated into a series of correction feeds. Those feeds are then uplinked to, and broadcast from, a geosynchronous satellite operated by another company call Inmarsat. The satellite broadcasts at 1.55629GHz. This frequency is handy in that it is in the same band as the GNSS satellites: L-Band. L-Band is any frequency from 1 to 2 GHz. These frequencies have the ability to penetrate clouds, fog, and other natural weather phenomena making them particularly useful for location applications.
The single antenna atop the RTK Facet L-Band is a unique combination of elements designed to receive the GNSS signals (L1/L2) alongside the 1.55GHz PointPerfect corrections. These signals are sent to the ZED-F9P for classic GNSS position calculation (e.g. producing latitude, longitude, and altitude of the device), and to the NEO-D9S. The NEO-D9S is a satellite receiver who's sole purpose is to be tuned to a frequency (in our case ~1.55GHz) and output data. This data is the encrypted correction data in the SPARTN format. The RTK Facet L-Band receives these packets and passes them to the ZED-F9P. At startup, the ESP32 provides the ZED-F9P with decryption keys. With the packets and the keys, the ZED-F9P is able to decrypt the data and use it to correct its GNSS fix allowing the accuracy to increase from ~300mm to the RTK accuracy of 10 to 20mm.
It is fun to point out the GNSS satellites have a medium earth orbit, circling the earth every 12 hours, and have a orbit above the earth at approximately 22,200 kilometers (12,551 miles). Whereas the Inmarsat satellites broadcasting the PointPerfect correction values at ~1.5GHz are geosynchronous and therefore must be located much further out, at about 35,786 kilometers (22,236 miles).
Where can the RTK Facet L-Band operate?
USA Coverage Map of PointPerfect Corrections
From March 10th 2025, the u-blox PointPerfect service will only offered for the USA's contiguous 48 states. The EU L-Band service is being suspended on that date. Please see u-blox website for additional information. If L-Band coverage is not available in your area, the RTK Facet L-Band is still capable of better than 300mm accuracy off the shelf and 14mm accuracy when provided RTCM corrections using a standard Base/Rover setup.
How much does this cost?
The cost of a RTK Facet L-Band includes a 12 months subscription to u-blox's PointPerfect L-Band service. u-blox does not currently offer PointPerfect L-Band service to individuals. SparkFun formed a partnership with u-blox to allow SparkFun users to obtain L-Band service through SparkFun's account.
How do the 'keys' work?
One of our mantras at SparkFun is Don't Make Me Think based on a book by Steve Krug. The RTK Facet L-Band does not require creating an account anywhere, does not require copy and pasting of keys, certificates, or any other materials. The provisioning process is complicated, so we've designed the firmware within the RTK Facet L-Band to deal with everything. The only thing a user must provide is a 'Home' WiFi network ID and password. We use the term 'Home' but it is the network the device is mostly likely to be turned on around, for example the surveyor's office, school, or residence. Once these details are entered via WiFi or serial, the device will take care of everything else.
How do the L-Band keys work?

The correction data that is broadcast via Inmarsats is encrypted. The decryption keys expire every 28 days and two keys are provided during each update process. This means the RTK Facet L-Band can operate without any internet connectivity for a maximum of 56 days best case, 29 days worst case. Every time the device is powered on the RTK Facet L-Band will attempt to connect to its 'Home' WiFi. If successful, the keys will be automatically be updated and stored. The whole process takes lass than 10 seconds (worst case). The RTK Facet L-Band will show a series screens indicating what its doing but the device is designed to be used without concern or supervision.
What happens after 12 months?
The retail price of the RTK Facet L-Band includes 12 months of PointPerfect corrections. After 12 months the device will be unable to obtain keys and the device will operate as a normal, very high accuracy GNSS receiver. If additional PointPerfect corrections are needed they can be purchased for $600 per year by filling out the form here.
Can I get a unit without the subscription?
u-blox does not currently offer PointPerfect L-Band service to individuals. If you are interested in purchasing a large number of RTK Facet L-Bands, we can work with you to provide subscription-less units but it is up to your organization to confirm that L-Band service will be provided. The RTK Facet L-Band allows for a custom Device Profile Token. Once you have an account setup with u-blox, this token will need to be entered into all RTK Facet L-Band devices and they can provision through the normal PointPerfect API. Please contact SparkFun customer service for more information.
What are the down sides to L-band corrections?
Cons:
- RTK fix time using L-Band is 45 to 60 seconds as opposed to RTCM based RTK which can take a few seconds.
- Increased cost via subscription fees to u-blox.
- Accuracy varies from 30 to 60mm guaranteed with 14 to 20mm regularly seen.
Pros:
- High precision RTK fixes without any setup.
- Very easy to setup and just use. No base, no radio, no internet needed.
Hardware Overview
The RTK Facet L-Band is a fully enclosed, preprogrammed device. There are very few things to worry about or configure but we will cover the basics.
Power/Setup Button

The RTK Facet L-Band has one button used for both Power and Setup for in-field configuration changes. Pressing and holding the Power button will cause it to power on or off. Short pressing the button will cause the RTK Facet L-Band to change modes.
This device can be used in five modes:
- GNSS Positioning (~30cm accuracy) - also known as 'Rover'
- GNSS Positioning with RTK L-Band (1.4 to 6cm accuracy) - also known as 'Rover with L-Band RTK Fix'
- GNSS Positioning with RTK (1.4cm accuracy) - also known as 'Rover with RTK Fix'
- GNSS Base Station
- GNSS Base Station NTRIP Server
At Power On the device will enter Rover or Base mode; whichever state the device was in at the last power down. When the POWER/SETUP button is pressed momentarily, a menu is presented to change the RTK Facet L-Band to Rover or Base mode. The display will indicate the change with a small car or flag icon.
In Rover mode the RTK Facet L-Band will check if WiFi is available and update any L-Band keys needed (keys expire every 56 days). The device will automatically begin receiving and decrypting position correction data. Simultaneously, the RTK L-Band will receive L1 and L2 GNSS signals from the four constellations (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou). The device will calculate the position based on the combination of GNSS and correction signals. The receiver will quickly (within 60 seconds) obtain an RTK float, then fix. Similar to a standard grade GPS receiver, the RTK Facet L-Band will output industry standard NMEA sentences at 4Hz and broadcast them over any paired Bluetooth® device. The end user will need to parse the NMEA sentences using commonly available mobile apps, GIS products, or embedded devices (there are many open source libraries). Unlike standard grade GPS receivers that have 2500mm accuracy, the accuracy in this mode is approximately 14 to 60mm horizontal positional accuracy.
If the device is in Rover mode but L-Band is not available, regular RTCM based RTK is still available. When RTCM correction data is sent over Bluetooth® or into the radio port, the device will automatically enter Positioning with RTK mode. In this mode RTK Facet L-Band will receive L1/L2 signals from the antenna and correction data from a base station. The receiver will quickly (within a second) obtain an RTK float, then fix. The NMEA sentences will have increased accuracy of 14mm horizontal and 10mm vertical accuracy. The RTCM correction data is most easily obtained over the Internet using a free app on your phone (see SW Maps or Lefebure NTRIP) and sent over Bluetooth® to the RTK Facet L-Band but RTCM can also be delivered over an external cellular or radio link to a 2nd RTK Facet, Surveyor, Express, etc setup as a base station.
In Rover mode the RTK Facet L-Band will receive L1 and L2 GNSS signals from the four constellations (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou) and calculate the position based on these signals. Similar to a standard grade GPS receiver, the RTK Facet L-Band will output industry standard NMEA sentences at 4Hz and broadcast them over any paired Bluetooth® device. The end user will need to parse the NMEA sentences using commonly available mobile apps, GIS products, or embedded devices (there are many open source libraries). Unlike standard grade GPS receivers that have 2500mm accuracy, the accuracy in this mode is approximately 300mm horizontal positional accuracy.
In Base mode the device will enter Base Station mode. This is used when the device is mounted to a fixed position (like a tripod or roof). The RTK Facet L-Band will initiate a survey. After 60 to 120 seconds the survey will complete and the RTK Facet L-Band will begin transmitting RTCM correction data out the radio port. A base is often used in conjunction with a second RTK Facet L-Band (or RTK Surveyor, Express, Express Plus, etc) unit set to 'Rover' to obtain the 14mm accuracy. Said differently, the Base sits still and sends correction data to the Rover so that the Rover can output a really accurate position.
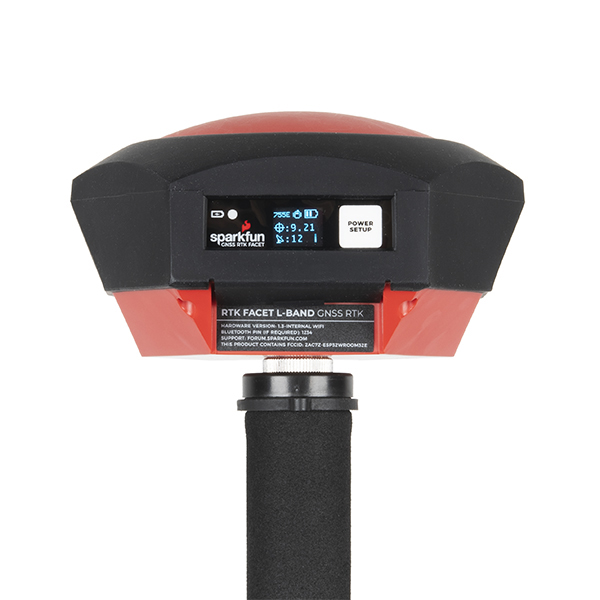
Power
](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/2/5/8/3/SparkFun_RTK_Facet_L-Band_Boot.jpg)
The Power button turns on and off the unit. Press and hold the power button until the display illuminates. Press and hold the power button at any time to turn the unit off.
The RTK Facet L-Band has a large, built-in 6000mAh lithium polymer battery that will enable over 25 hours of field use between charging. If more time is needed a common USB power bank can be attached boosting the field time to any amount needed.
Charge LED
The Charge LED is located on the front face. It will illuminate any time there is an external power source and will turn off when the internal battery is charged. With the unit fully powered down, charging takes approximately 6 hours from a 1A wall supply or 12 hours from a standard USB port. The RTK Facet L-Band can run while being charged but it increases the charge time. Using an external USB battery bank to run the device for extended periods or running the device on a permanent wall power source is supported.
Connectors
There are a variety of connectors protected by a dust flap.
USB
This USB C connector is used for four purposes:
- Charging the device
- Configuring the RTK Facet L-Band, and reprogramming the ESP32
- Updating the firmware of the ZED-F9P as needed
- Updating the firmware of the NEO-D9S as needed
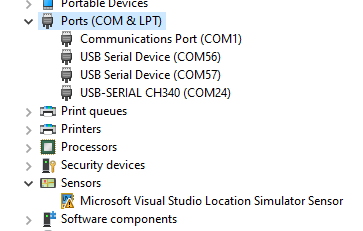
There is a USB hub built into the RTK Facet L-Band. When you attach the device to your computer it will enumerate as three COM ports.
In the image above, the USB-SERIAL CH340 is the ESP32 and the USB Serial Device is the ZED-F9P and the NEO-D9S.
Configuring the RTK Facet L-Band can be done over the USB-Serial CH340 COM port via serial text menu. Various debug messages are printed to this port at 115200bps and a serial menu can be opened to configure advanced settings. Configuring the ZED-F9P can be configured over the USB Serial Device port using u-center. It’s not necessary in normal operation but is handy for tailoring the receiver to specific applications. As an added perk, the ZED-F9P can be detected automatically by some mobile phones and tablets. If desired, the receiver can be directly connected to a compatible phone or tablet removing the need for a Bluetooth connection.
Radio
This port is used when an external cellular or radio link is needed. This port is not used if you transfer RTCM from your phone to the RTK Facet L-Band over Bluetooth.
This 4-pin JST connector can be used to allow RTCM correction data to flow into the device when it is acting as a rover or out of the device when it is acting as a base. The connector is a 4-pin locking 1.25mm JST SMD connector (part#: SM04B-GHS-TB, mating connector part#: GHR-04V-S). The RTK Facet L-Band comes with a cable to interface to this connector but additional cables can be purchased. You will most likely connect this port to one of our Serial Telemetry Radios if you don’t have access to a correction source on the internet. The pinout is 3.5-5.5V / TX / RX / GND from left to right as pictured. 3.5V to 5.5V is provided by this connector to power a radio with a voltage that depends on the power source. If USB is connected to the RTK Facet L-Band then voltage on this port will be 5V (+/-10%). If running off of the internal battery then voltage on this port will vary with the battery voltage (3.5V to 4.2V depending on the state of charge). This port is capable of sourcing up to 600mA and is protected by a PTC (resettable fuse). This port should not be connected to a power source.
Data
This port is used when an external system is connected such as a rover, car, timing equipment, camera triggers, etc. This port is not used if you transfer NMEA positional data to your phone from the RTK Facet L-Band over Bluetooth.
This 4-pin JST connector is used to output and input a variety of data to the RTK Facet L-Band. The connector is a 4-pin locking 1.25mm JST SMD connector (part#: SM04B-GHS-TB, mating connector part#: GHR-04V-S). The RTK Facet L-Band comes with a cable to interface to this connector but additional cables can be purchased.
Internally the Data connector is connected to a digital mux allowing one of four software selectable setups. See the Ports Menu for a description of each option.:
- NMEA - The TX pin outputs any enabled messages (NMEA, UBX, and RTCM) at a default of 460,800bps (configurable 9600 to 921600bps). The RX pin can receive RTCM for RTK and can also receive UBX configuration commands if desired.
- PPS/Trigger - The TX pin outputs the pulse-per-second signal that is accurate to 30ns RMS. The RX pin is connected to the EXTINT pin on the ZED-F9P allowing for events to be measured with incredibly accurate nano-second resolution. Useful for things like audio triangulation.
- I2C - The TX pin operates as SCL, RX pin as SDA on the I2C bus. This allows additional sensors to be connected to the I2C bus.
- GPIO - The TX pin operates as a DAC capable GPIO on the ESP32. The RX pin operates as a ADC capable input on the ESP32. This is useful for custom applications.
Most applications do not need to utilize this port and will send the NMEA position data over Bluetooth. This port can be useful for sending position data to an embedded microcontroller or single board computer. The pinout is 3.3V / TX / RX / GND. 3.3V from left to right as pictured, which is provided by this connector to power a remote device if needed. While the port is capable of sourcing up to 600mA, we do not recommend more than 300mA. This port should not be connected to a power source.
microSD
This slot accepts standard microSD cards up to 32GB formatted for FAT16 or FAT32. Logging any of 67 messages at up to 4Hz is supported for all constellations.
The following 67 messages are supported for logging:
| • NMEA-GSA | • NMEA-GST | • NMEA-GSV |
| • NMEA-RMC | • NMEA-VLW | • NMEA-VTG |
| • NMEA-ZDA | • NAV-CLOCK | • NAV-DOP |
| • NAV-EOE | • NAV-GEOFENCE | • NAV-HPPOSECEF |
| • NAV-HPPOSLLH | • NAV-ODO | • NAV-ORB |
| • NAV-POSECEF | • NAV-POSLLH | • NAV-PVT |
| • NAV-RELPOSNED | • NAV-SAT | • NAV-SIG |
| • NAV-STATUS | • NAV-SVIN | • NAV-TIMEBDS |
| • NAV-TIMEGAL | • NAV-TIMEGLO | • NAV-TIMEGPS |
| • NAV-TIMELS | • NAV-TIMEUTC | • NAV-VELECEF |
| • NAV-VELNED | • RXM-MEASX | • RXM-RAWX |
| • RXM-RLM | • RXM-RTCM | • RXM-SFRBX |
| • MON-COMMS | • MON-HW2 | • MON-HW3 |
| • MON-HW | • MON-IO | • MON-MSGPP |
| • MON-RF | • MON-RXBUF | • MON-RXR |
| • MON-TXBUF | • TIM-TM2 | • TIM-TP |
| • TIM-VRFY | • RTCM3x-1005 | • RTCM3x-1074 |
| • RTCM3x-1077 | • RTCM3x-1084 | • RTCM3x-1087 |
| • RTCM3x-1094 | • RTCM3x-1097 | • RTCM3x-1124 |
| • RTCM3x-1127 | • RTCM3x-1230 | • RTCM3x-4072-0 |
| • RTCM3x-4072-1 |
Qwiic
This 4-pin Qwiic connector exposes the I2C bus of the ESP32 WROOM module. Currently, there is no firmware support for adding I2C devices to the RTK Facet L-Band but support may be added in the future.
Antenna
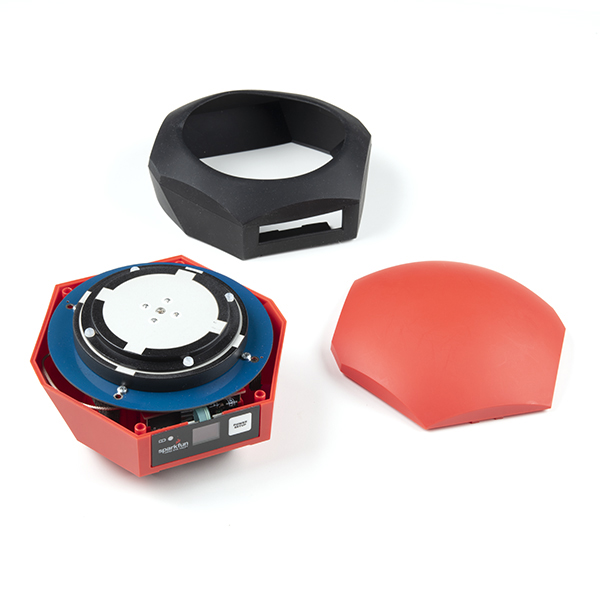

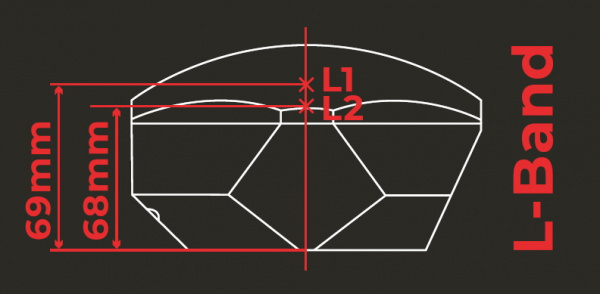
It's built in! Housed under the dome of the RTK Facet L-Band is a surveyor grade L1/L2/L-Band antenna. This antenna is a unique combination of elements designed to receive the GNSS signals (L1/L2) alongside the 1.55GHz PointPerfect corrections.
The built-in antenna has an antenna phase center (APC) of 69mm from the base of the device to the measuring point of the L1 antenna and an APC of 68mm to the measuring point of the L2 antenna.
Power
The RTK Facet L-Band has a built in 6000mAh battery and consumes approximately 240mA worst case with Bluetooth connection active and GNSS fully tracking. This will allow for around 25 hours of use in the field. If more time is needed in the field a standard USB power bank can be attached. If a 10,000mAh bank is attached one can estimate 56 hours of run time assuming 25% is lost to efficiencies of the power bank and charge circuit within RTK Facet L-Band.
The RTK Facet L-Band can be charged from any USB port or adapter. The charge circuit is rated for 1000mA so USB 2.0 ports will charge at 500mA and USB 3.0+ ports will charge at 1A.
To quickly view the state of charge, turn on the unit. The battery icon will indicate the following:
- 3 bars: >75% capacity remain
- 2 bars: >50% capacity remain
- 1 bar: >25% capacity remain
- 0 bars: <25% capacity remain
Hardware Overview - Advanced Features
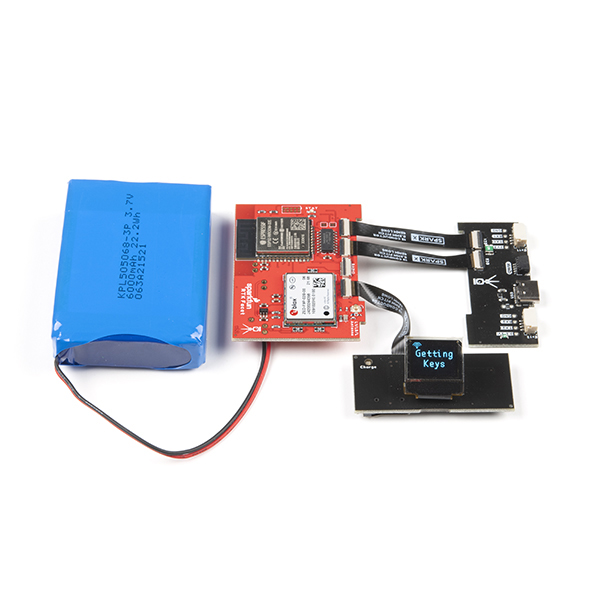

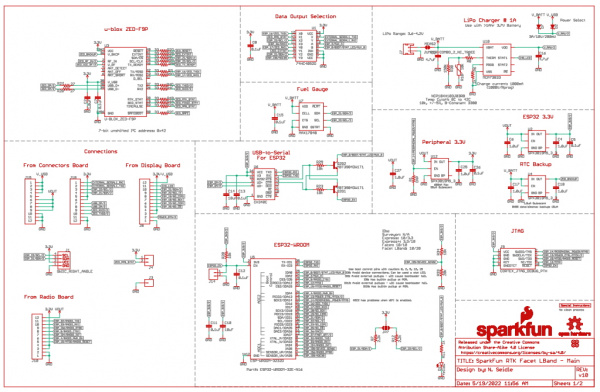
The RTK Facet L-Band is a hacker’s delight. Under the hood of the RTK Facet L-Band is an ESP32 WROOM connected to a ZED-F9P as well as some peripheral hardware (LiPo fuel gauge, microSD, etc). It is programmed in Arduino and can be tailored by the end user to fit their needs.
ZED-F9P GNSS Receiver
The ZED-F9P GNSS receiver is configured over I2C and uses two UARTs to output NMEA (UART1) and input/output RTCM (UART2). In general, the ESP32 harvests the data from the ZED-F9Ps UART1 for Bluetooth transmission and logging to SD.
NEO-D9S L-Band Receiver
The NEO-D9S is configured over I2C. The ESP32 sends decryption keys to the ZED-F9P at startup then harvests the encrypted PMP data from the NEO-D9S and sends the packets to the ZED-F9P over I2C.
ESP32
The ESP32 uses a standard USB to serial conversion IC (CH340) to program the device. You can use the ESP32 core for Arduino or Espressif’s IoT Development Framework (IDF).
The CH340 automatically resets and puts the ESP32 into bootload mode as needed. However, the reset pin of the ESP32 is brought out to an external 2-pin 0.1” footprint if an external reset button is needed.
LiPo and Charging
The RTK Facet L-Band houses a standard 6000mAh 3.7V LiPo. The charge circuit is set to 1A so with an appropriate power source, charging an empty battery should take a little over six hours. USB C on the RTK Facet L-Band is configured for 2A draw so if the user attaches to a USB 3.0 port, the charge circuit should operate near the 1A max. If a user attaches to a USB 2.0 port, the charge circuit will operate at 500mA. This charge circuit also incorporates a 42C upper temperature cutoff to insure the LiPo cannot be charged in dangerous conditions.
Fuel Gauge and Accelerometer
The MAX17048 is a simple to use fuel gauge IC that gives the user a statement of charge (SOC) that is basically a 0 to 100% report. The MAX17048 has a sophisticated algorithm to figure out what the SOC is based on cell voltage that is beyond the scope of this tutorial but for our purposes, allows us to reliably view the battery level when the unit is on.
The RTK Facet L-Band also incorporates a the LIS2DH12 triple-axis accelerometer to aid in leveling in the field.
Qwiic
An internal Qwiic connector is included in the unit for future expansion. Currently the stock RTK Facet L-Band does not support any additional Qwiic sensors or display but users may add support for their own application.
microSD
A microSD socket is situated on the ESP32 SPI bus. Any microSD up to 32GB is supported. RTK Facet L-Band supports RAWX and NMEA logging to the SD card. Max logging time can also be set (default is 24 hours) to avoid multi-gigabyte text files. For more information about RAWX and doing PPP please see this tutorial.
Data Port and Digital Mux
The 74HC4052 analog mux controls which digital signals route to the external Data port. This allows a variety of custom end user applications. The most interesting of which is event logging. Because the ZED-F9P has microsecond accuracy of the incoming digital signal, custom firmware can be created to triangulate an event based on the receiver's position and the time delay between multiple captured events. Currently, TM2 event logging is supported.
Additionally, this mux can be configured to connect ESP pin 26 (DAC capable) and pin 39 (ADC capable) for end user custom applications.
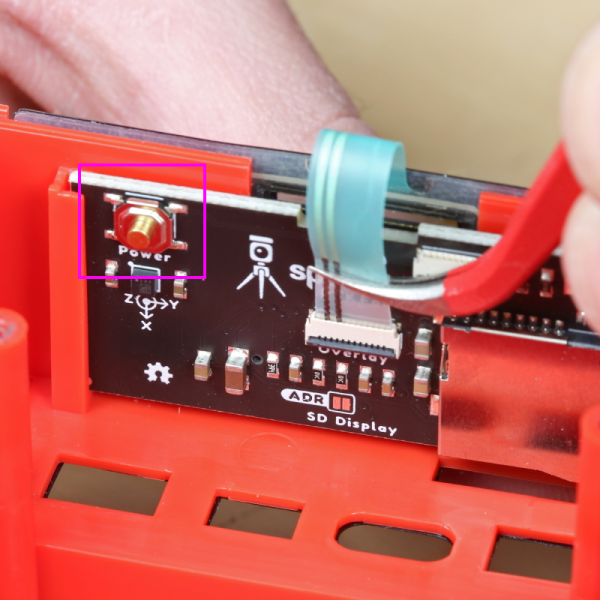
Internal Power Button
For normal operation, the power button on the outside of the device is used to turn on/off the unit. If the external power button ever fails or is suspect, an internal power button can be used to diagnose the problem.
The internal power button is located on the back of the display board.
Pressing and holding the internal power button for more than 2 seconds will turn on the device. Similarly, pressing and holding the button when the device is on will cause the device to power down.
Hardware Assembly
The RTK Facet L-Band was designed to work with low-cost, off the shelf equipment. The RTK Facet L-Band is designed to use corrections provided via u-blox's PointPerfect system, therefore, a Base/Rover setup is not needed. However, if the service is not available the RTK Facet L-Band can still be used in a traditional Base/Rover setup. Here we’ll describe how to assemble a Rover and Base.
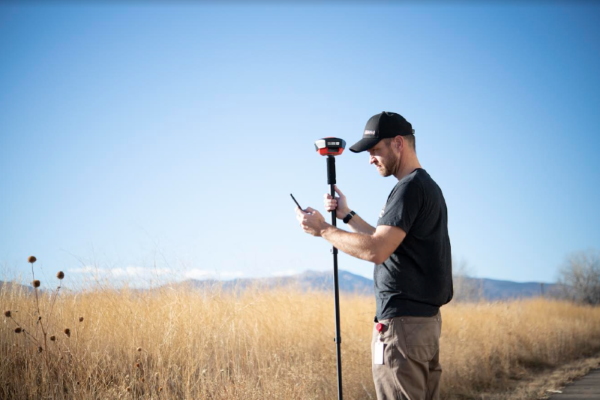
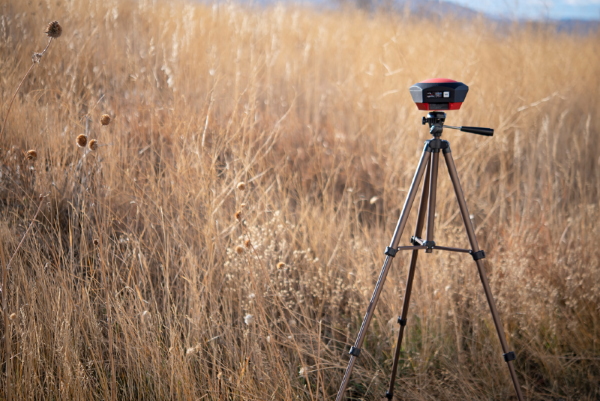
Surveying (Rover Mode)
Shown above is the most common RTK Rover setup. A monopole designed for cameras is used. The ¼” camera thread of the monopole is adapted to ⅝” 11-TPI and the RTK Facet L-Band is mounted on top. No radio is needed because RTCM correction data is provided by a phone over Bluetooth.
If you’re shopping for a monopole (aka monopod), get one that is 65” in length or greater to ensure that the antenna will be above your head. We’ve had good luck with the Amazon Basics brand.
If you prefer to mount your tablet or cell phone to the monopole be sure to get a clamp that is compatible with the diameter of your monopole and has a knob to increase clamp pressure. Our monopole is 27mm in diameter so a device clamp would need to be able to handle that diameter.
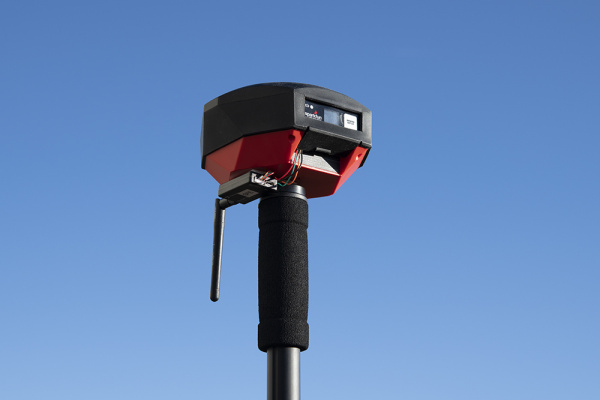
If you are receiving RTCM correction data over a radio link it’s recommended that you attach a radio to the bottom of the RTK Facet L-Band.
Picture hanging strips from 3M make a nice semi-permanent mount. Plug the 4-pin to 6-pin JST cable included with the RTK Facet L-Band from the Radio port to either of the Serial Telemetry Radios (shipped in pairs). We really love these radios because they are paired out of the box, either can send or receive (so it doesn't matter which radio is attached to base or rover) and they have remarkable range. We achieved over a mile range (nearly 1.5 miles or 2.4km) with the 100mW radios and a big 915MHz antenna on the base (see this tutorial for more info).
Temporary Base
A temporary or mobile base setup is needed when you are in the field too far away from a correction source and/or cellular reception. A 2nd RTK Facet L-Band is mounted to a tripod and it is configured to complete a survey-in (aka, locate itself), then begin broadcasting RTCM correction data. This data (~1000 bytes a second) is sent to the user's connected radio of choice. For our purposes, the 915MHz 100mW telemetry radios are used because they provide what is basically a serial cable between our base and rover.
Any tripod with a ¼” camera thread will work. The Amazon Basics tripod works well enough but is a bit light weight and rickety. The ¼” camera thread is adapted to ⅝” 11-TPI and the RTK Facet L-Band is attached on top.
Once the base has been setup with a clear view of the sky, turn on the RTK Facet L-Band. Once on, press the Setup button to put the device in Base mode. The display will show the Survey-In screen for 60-120 seconds. Once the survey is complete the display will show the 'Xmitting' display and begin producing RTCM correction data. You can verify this by viewing the LEDs on the telemetry radio (a small red LED will blink when serial data is received from the RTK Facet L-Band). The RTK Facet L-Band is designed to follow the u-blox recommended survey-in of 60s and a mean 3D standard deviation of 5m of all fixes. If a survey fails to achieve these requirements it will auto-restart after 10 minutes.
Note: A mobile base station works well for quick trips to the field. However, the survey-in method is not recommended for the highest accuracy measurements because the positional accuracy of the base will directly translate to the accuracy of the rover. Said differently, if your base's calculated position is off by 100cm, so will every reading your rover makes. If you’re looking for maximum accuracy consider installing a static base with fixed antenna. We were able to pinpoint the antenna on the top of SparkFun with an incredible accuracy +/-2mm of accuracy using PPP!
Bluetooth and NTRIP
The RTK Facet L-Band transmits full NMEA sentences over Bluetooth serial port profile (SPP) at 4Hz and 115200bps. This means that nearly any GIS application that can receive NMEA data over serial port (almost all do) can be used with the RTK Facet L-Band. As long as your device can open a serial port over Bluetooth (also known as SPP) your device can retrieve industry standard NMEA positional data.
Please see the SparkFun RTK Product Manual for step by step instructions.
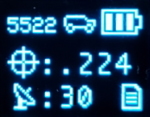
Display
The RTK Facet L-Band has a 0.96" high-contrast OLED display. While small, it packs various situational data that can be helpful in the field. Please see the SparkFun RTK Product Manual for a description of each display.
System Configuration
Out of the box, the SparkFun RTK products are exceptional GNSS receivers out-of-box and can be used with little or no configuration. Additionally, the line of RTK products from SparkFun are immensely configurable. Please see the SparkFun RTK Product Manual for detailed descriptions of all the available features on the RTK products.
Firmware Updates and Customization
The RTK Facet is open source hardware meaning you have total access to the firmware and hardware.
From time to time SparkFun will release new firmware for the RTK product line to add and improve functionality. We've made updating the firmware as easy as possible. Please see Updating RTK Firmware for a step by step tutorial.
Troubleshooting
If you need technical assistance and more information on a product that is not working as you expected, we recommend heading on over to the SparkFun Technical Assistance page for some initial troubleshooting.
If you don't find what you need there, the SparkFun Forums are a great place to find and ask for help. If this is your first visit, you'll need to create a Forum Account to search product forums and post questions.
Resources and Going Further
We hope you enjoy using the RTK Facet L-Band as much as we have!
Here are the pertinent technical documents for the RTK Facet L-Band:
- RTK Product Manual
- ZED-F9P Datasheet
- NEO-D9S Datasheet
- MAX17048 Fuel Gauge IC
- SparkFun RTK Facet GitHub Repo (contains the open source hardware electronics and enclosure)
- SparkFun RTK Firmware GitHub Repo (contains the firmware that runs SparkFun RTK products)
Check out these additional tutorials for your perusal: