SparkFun gator:environment Hookup Guide
MakeCode Examples
Now that you have added the gator:environment extension to the Editor, lets start with some example code. Plug the micro:bit into your computer using an USB micro-B cable after you have assembled your hardware with the instructions from the previous section. The micro:bit should appear on your computer as a removable storage device.
To upload new code, this is where you will be copying the downloaded .hex file to later.
Block Functions
initialize gator:environment sensor
This block should be pretty self explanatory, it sets the sensor up to be used. You should use this within the on start block.
_____ value
This is a value block as indicated by the block's shape. There is a drop down menu with selectable options for the output value of the block. Below is a description of the available menu options:
degreeC- Reports temperature reading from BME280 in Celsius (°C).degreeF- Reports temperature reading from BME280 in Fahrenheit (°F).humidity- Reports humidity reading from BME280 in relative humidity (RH%).pressure- Reports pressure reading from BME280 in Pascals (Pa).eCO2- Reports equivalent CO2 reading from CCS811 in parts per million (ppm).TVOC- Reports equivalent TVOC reading from CCS811 in parts per billion (ppb).
Basic Read
Below, is a simple example of how to take simple measurements from the sensor. To use this example, there are multiple options for accessing the .hex file:
- Replicate the block functions from the display below to copy the example project. Then download the
.hexfile. - Expand the display widow to pull up the example project. Then download the
.hexfile. - Use this link to pull up the example project. Then download the
.hexfile. Download the
.hexfile from the button below or the link on the bottom of the display.
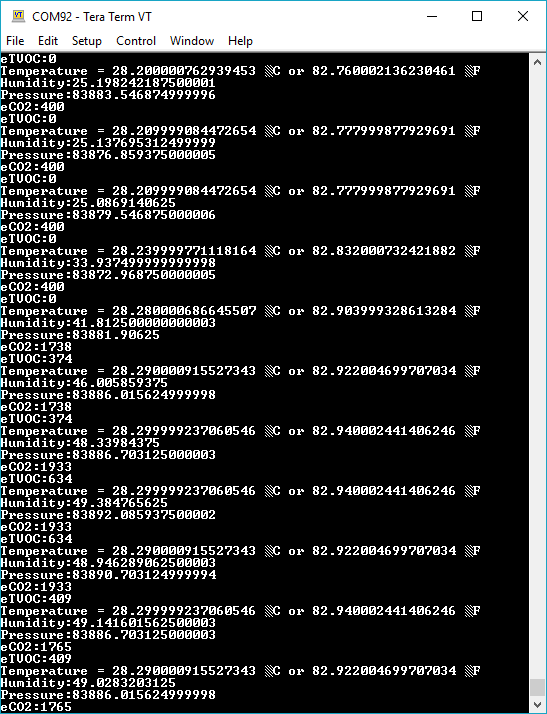
The output is redirected over the serial port to avoid conflicts on pins P0 and P1, which are also used for serial communication. To read the sensor values, pull up your favorite serial terminal emulator. Then, connect to the serial port that the micro:bit is on; the default baud rate is 115200 bps. Below, is an example of the sensor output for the example code.