SparkFun Environmental Sensor Breakout - BME68x (Qwiic) Hookup Guide
Hardware Overview
The heart of these breakout boards, Bosch's BME680 Gas Sensor, integrates four sensors (gas, pressure, temperature and humidity) into a tiny package. The BME68x measures just 3mm x 3mm x 0.93 mm and was specifically designed for applications that depend on a small footprint and low power consumption. This makes the BME68x a great choice for remote or mobile environmental sensing applications. We will highlight some of the unique aspects of the BME68x in this section but for a full overview of the sensor package, check out the datasheets:
BME688 Note: The BME688 is a drop in replacement for the BME680; with the added gas scanning functionality and support for AI algorithms. The parameters in highlighted in yellow, only apply to the BME688 sensor.
How does the gas scanner work? The gas sensor takes measurements with different sensitivities during one gas scan. In doing so, it can generate a profile (or fingerprint) for different gas mixtures. This can be modified and optimized with BME AI-Studio.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage |
|
| Operational Modes |
Sleep (Default) and Forced (low power; single measurement) Parallel (Gas sensor heater operates in parallel to TPH measurement) |
| Interface | I²C and SPI |
| I²C Address |
BME680: 0x77 (Default) or 0x76 BME688: 0x76 (Default) or 0x77 |
Average current consumption |
2.1 µA at 1 Hz humidity and temperature 3.1 µA at 1 Hz pressure and temperature 3.7 µA at 1 Hz humidity, pressure and temperature 90 µA at ULP mode for p/h/T & air quality 0.9 mA at LP mode for p/h/T & air quality 3.9 mA in standard gas scan mode |
Humidity Parameters |
Range: 10 to 90 %RH Absolute Accuracy: ±3 %RH (from 20 - 80 %RH) Resolution: 0.008 %RH |
| Pressure Parameters |
Range: 300 to 1100 hPa (30,000 - 110,000 Pa or approx. 4.35 - 15.95 PSI) Absolute Accuracy: ±0.6 hPa Resolution: 0.18 Pa |
| Temperature Parameters |
Range: 0°C to 65°C (32°F to 149°F) Absolute Accuracy: ±(0.5 - 1.0)°C Resolution: 0.01°C |
| Gas Sensor Parameters |
F1 score for H₂S scanning: 0.92 Standard scan speed: 10.8 s / scan Sensor-to-sensor deviation: +/- 15% +/- 15 Output data processing:
|
Power
The BME68x accepts a supply voltage between 1.71 to 3.6V. Power can be supplied to the board either through one of the Qwiic connectors or the dedicated 3.3V and GND pins broken out on either side of the board.
Qwiic and I2C Interface
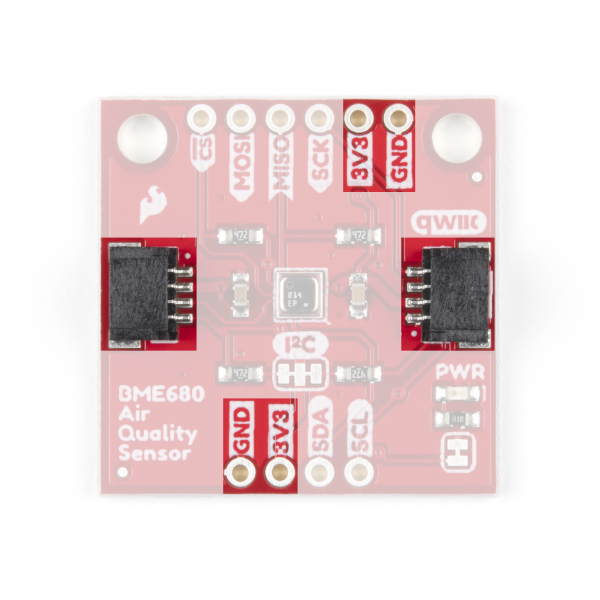
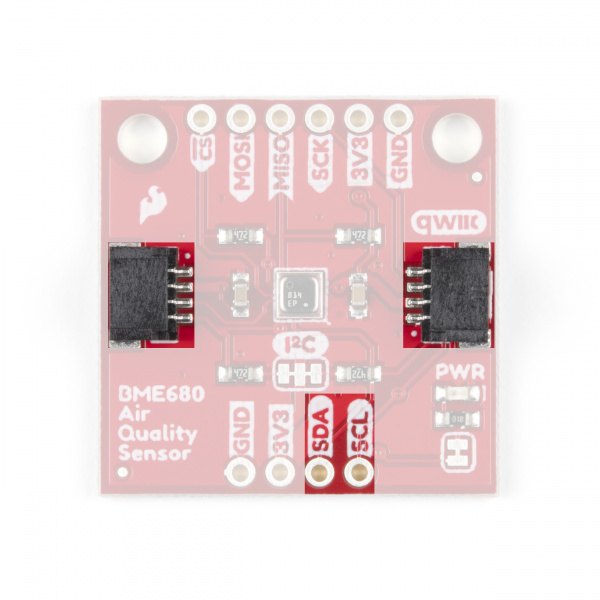
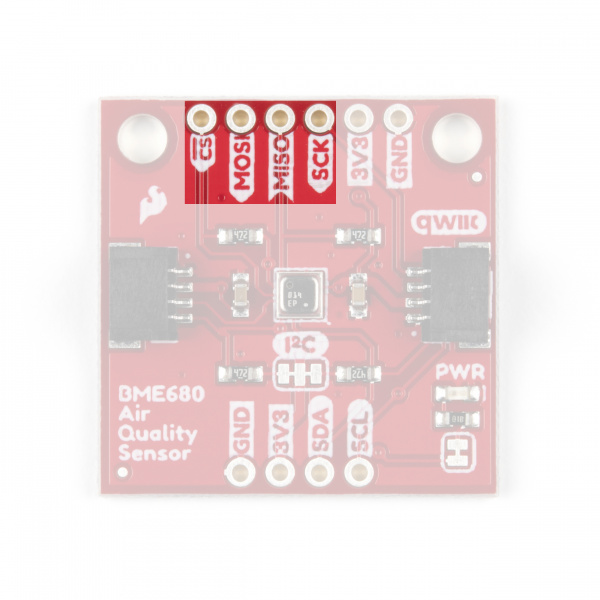
The SparkFun Environmental Sensor - BME68x (Qwiic) communicates over I2C by default. We have routed the BME68x's I2C pins to two Qwiic connectors as well as broken them out to 0.1"-spaced the header pins highlighted below.
- BME680: 0x77
- BME688: 0x76
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
If you would prefer to communicate with your BME68x via SPI, we have broken those pins out as well to standard 0.1"-spade header pins. Communicating over SPI requires more connections than I2C but is more versatile and can be faster. It is particularly helpful if you need to use more than two BME68x's in your circuit or if you have other devices using the same I2C addresses.
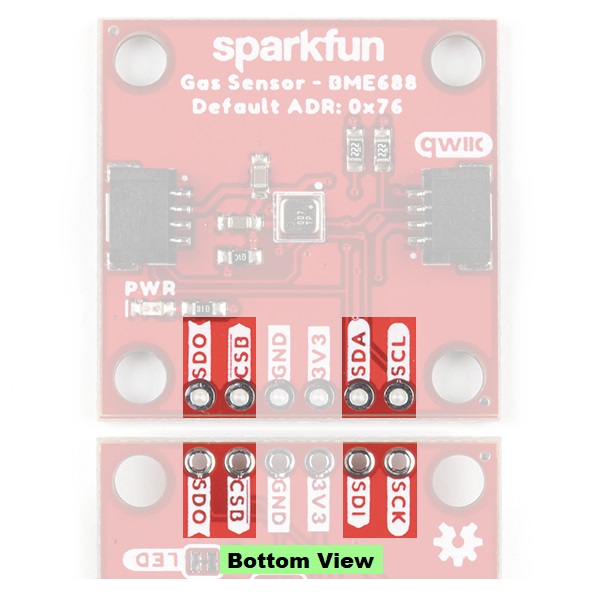
CSB and ADR (leave floating) jumpers. *See the CSB Jumper section, below, for more information.COPI/CIPO or SDI/SDO labels for SPI pins. SparkFun has joined with other members of OSHWA in a resolution to move away from using "Master" and "Slave" to describe signals between the controller and the peripheral. Check out this page for more on our reasoning behind this change. You can also see OSHWA's resolution here.
On the BME688 Qwiic board, the CS (chip select) pin is labeled with a CSB silkscreen, as annotated in the BME688 datasheet.
Solder Jumpers
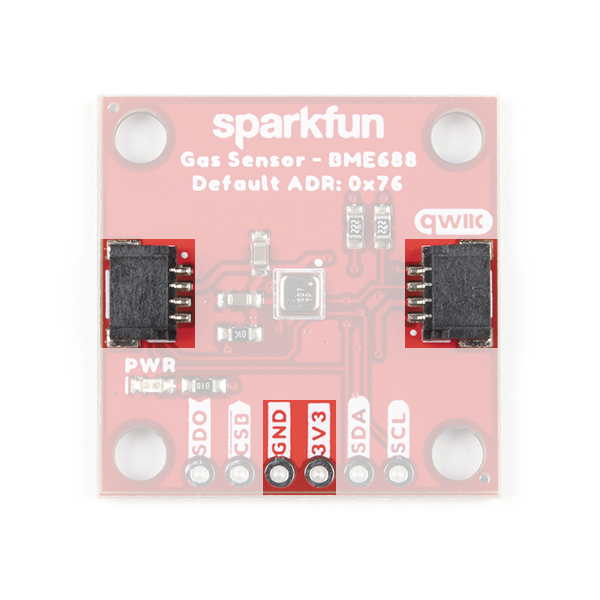
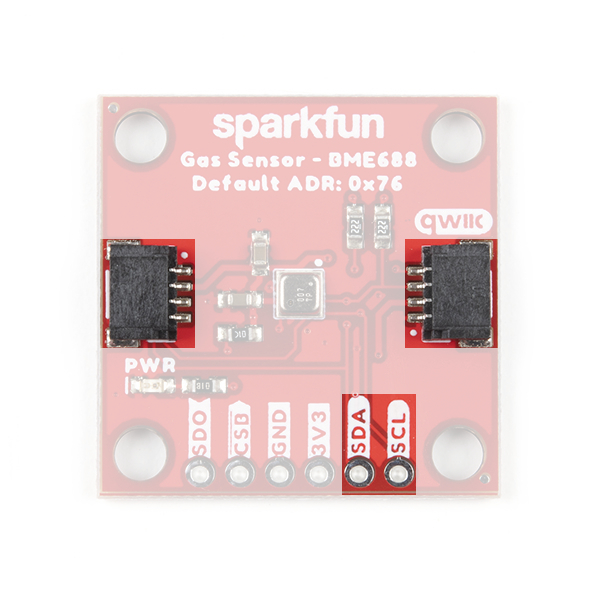
The SparkFun Environmental Sensor - BME680 (Qwiic) has three solder jumpers which can be modified to alter the functionality of the sensor. While, the SparkFun Environmental Sensor - BME688 (Qwiic) has four solder jumpers which can be modified to alter the functionality of the sensor.
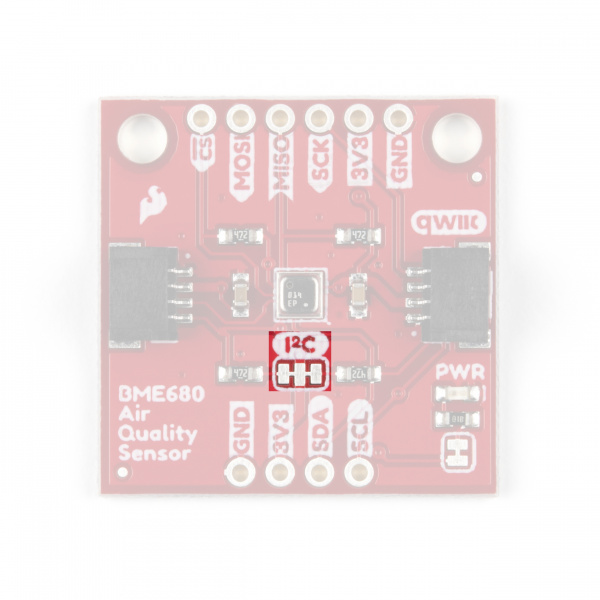
I2C Pull-Up Jumper
On the BME680 Qwiic board, the SDA/SDI and SCL/SCK pins are pulled to VDDIO (3.3V) through a pair of 4.7kΩ (2.2kΩ on the BME688) resistors. The jumper is normally closed so to disable the pull-up resistors, simply sever the traces between the three pads using a hobby knife.
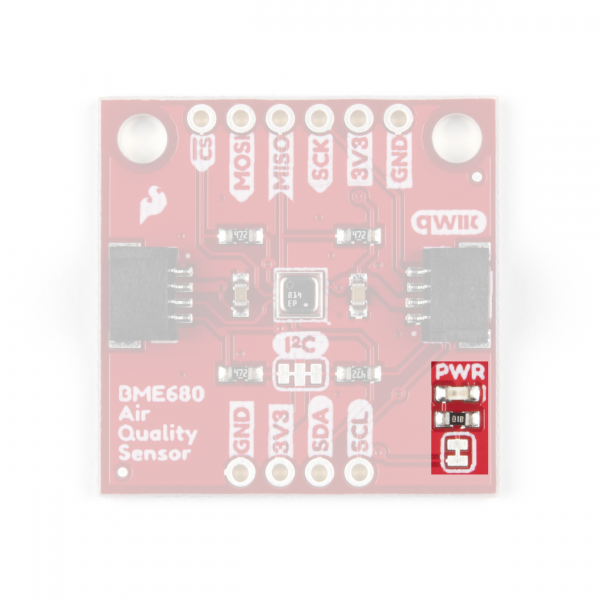
Power LED Jumper
This jumper connects the power LED to 3.3V via a 1K Ohm resistor. This jumper is normally closed so to disable the power LED, sever the trace between the two pads. This is particularly helpful for reducing the total current draw of your breakout for low-power applications.
I2C Address Jumper
This jumper sets the 7-Bit unshifted I2C address of the BME680 and is open by default. The default address is 0x77 and can be adjusted to 0x76 by closing this jumper.
This jumper sets the 7-Bit unshifted I2C address of the BME688 and sets the default address to 0x76 and can be adjusted to 0x77 by cutting and soldering the jumper over to the 0x77 pad.
CSB Jumper
This jumper only applies to the BME688 Qwiic board. The CSB pin is pulled up to VDDIO in order to configure the board for I2C communication by default. In order to communicate with the sensor over SPI, the CSB jumper must be cut along with the ADR jumper (leave floating). Once the CSB pin has been pulled low during SPI communication, the sensor will communicate over SPI until there is a power reset.
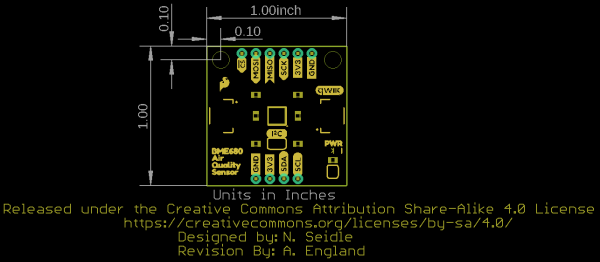
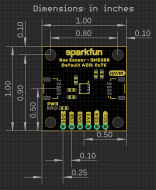
Board Dimensions
This breakout fits the Qwiic standard sizing for breakouts. It is a 1"x1" square with two mounting holes that fit a 4-40 screw.
Now that we have a thorough understanding of the hardware and features on the Environmental Sensor - BME680 (Qwiic), it's time to hook it up and start taking measurements.