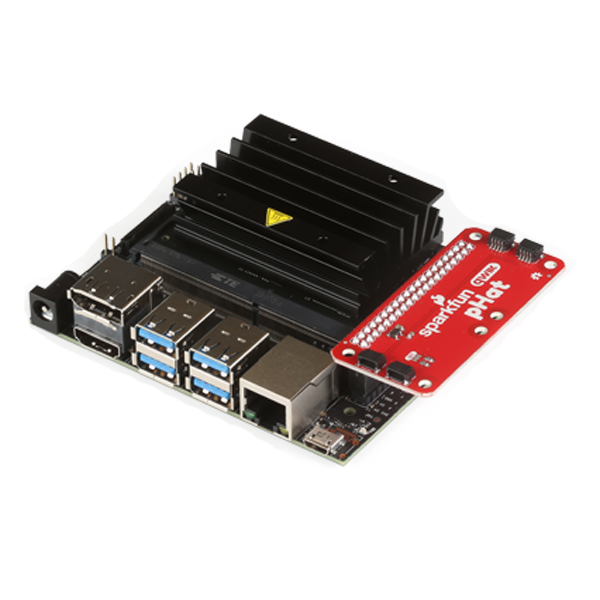
Qwiic pHAT for Raspberry Pi Hookup Guide
Introduction
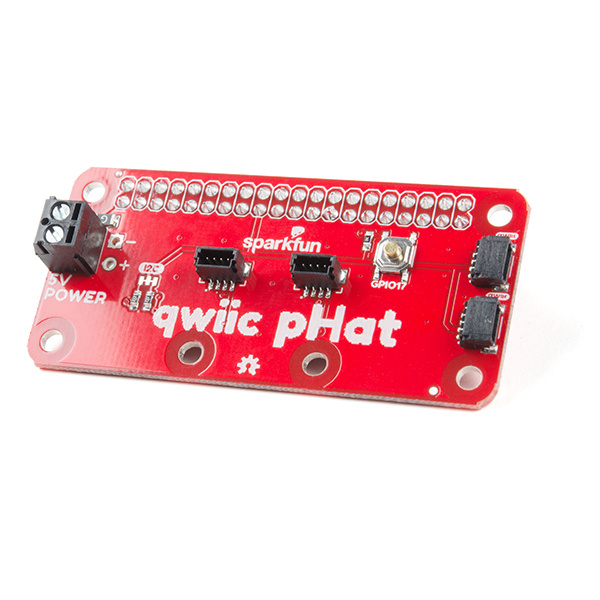
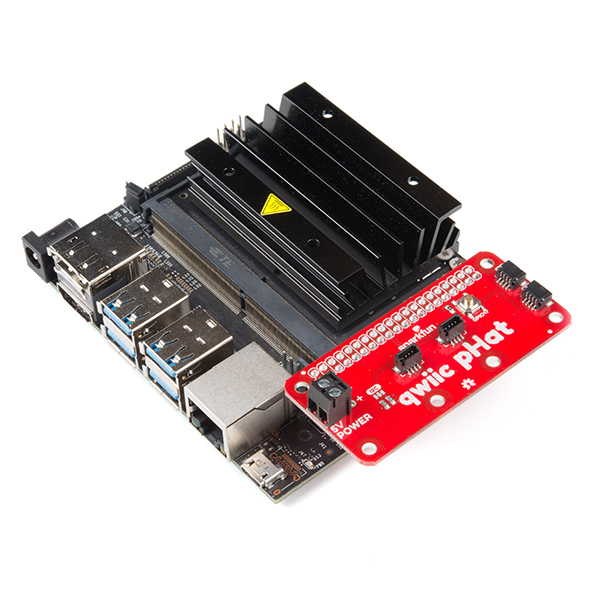
This Qwiic pHAT [v2.0 and v1.0] for Raspberry Pi is based on the Qwiic Hat. The board is the quickest and easiest way to utilize SparkFun's Qwiic ecosystem while still using that Raspberry Pi that you've come to know and love. This Qwiic pHAT connects the I2C bus (GND, 3.3V, SDA, and SCL) on your Raspberry Pi to an array of Qwiic connectors. Since the Qwiic system allows for daisy chaining (as long as your devices are on different addresses), you can stack as many sensors as you'd like to create a tower of sensing power!
SparkFun Qwiic pHAT for Raspberry Pi
DEV-15351Required Materials
To follow along with this tutorial, you will need the following materials. You may not need everything though depending on what you have. Add it to your cart, read through the guide, and adjust the cart as necessary.
Single Board Computer
You will need Raspberry Pi with 2x20 male headers installed. For those that are using an enclosure with the Raspberry Pi, you'll want to get two rows of 1x20 stackable headers in order to help extend the pins outside of the enclosure.
A Pi Zero W will also work but you will need to make sure to solder some male headers to it.
Or you could stack it on any single board computer (like the NVIDIA Jetson Nano) that utilizes the 40-pin Raspberry Pi header footprint.
NVIDIA Jetson Nano Developer Kit
DEV-15297
Google Coral Development Board
DEV-15318Qwiic Board
Now you probably didn't buy the Qwiic pHAT if you didn't have any Qwiic products to use with it, right? If you don't have any Qwiic products, the following might not be a bad place to start.
Finally, you'll need our handy Qwiic cables to easily connect sensors to your Qwiic pHAT. Below are a few options.
Qwiic Cable - 100mm
PRT-14427Qwiic Cable - 50mm
PRT-14426Qwiic Cable - 200mm
PRT-14428Qwiic Cable - 500mm
PRT-14429Required Setup Tools
As a desktop, these devices are required:
- USB Mouse
- USB Keyboard
- HDMI monitor/TV/adapted VGA
- 5V Power Supply
Suggested Reading
If you aren't familiar with the Qwiic system, we recommend reading here for an overview.
| Qwiic Connect System |
We would also recommend taking a look at the following tutorials if you aren't familiar with them.
I2C
Serial Terminal Basics
Hardware Overview
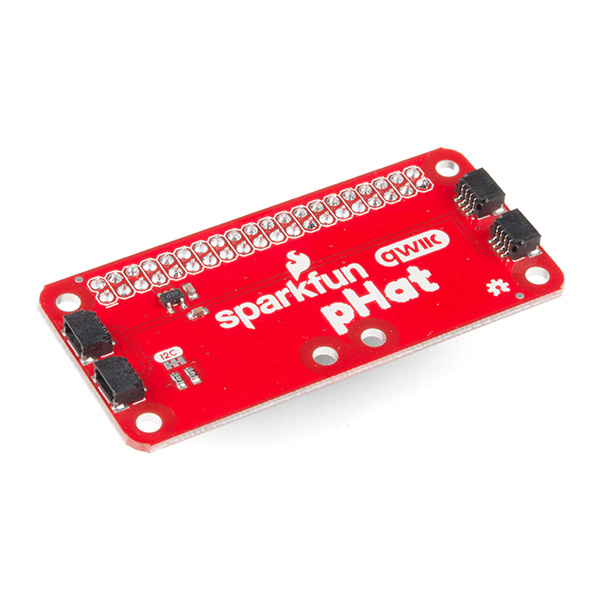
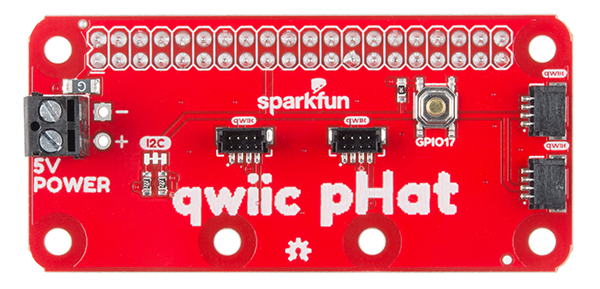
There are two pHAT versions out in the wild! Overall, they function the same to Qwiic-ly connect your I2C devices to your single board computer. However, there are small differences between the two boards. Click on one of the images below to explore the hardware for your respective Qwiic pHAT.
 |
 |
| Qwiic pHAT v2.0 | Qwiic pHAT v1.0 |
Qwiic pHAT v2.0
I2C Pins
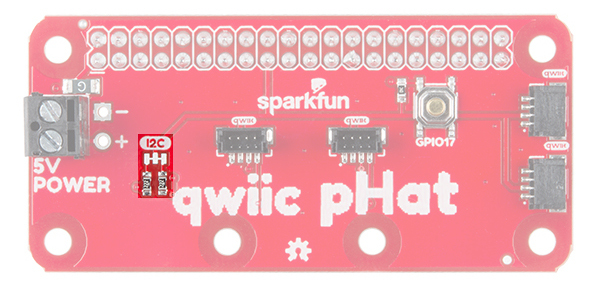
The Qwiic pHAT has 4x Qwiic connect ports, all on the same I2C bus. There are two vertical Qwiic connectors located at the center and two horizontal connectors on the right side.
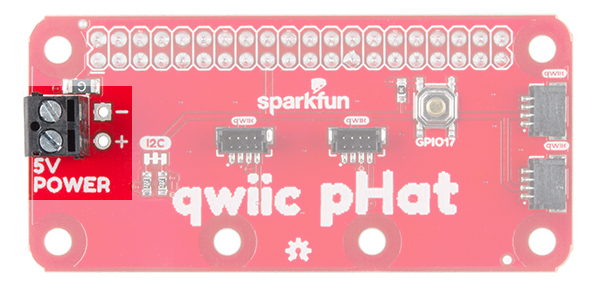
5V Power
If you need to power a device with 5V, we have broken out the Raspberry Pi's 5V and GND pins on the side with a screw terminal. Depending on your project, you can also solder to the PTH pads.
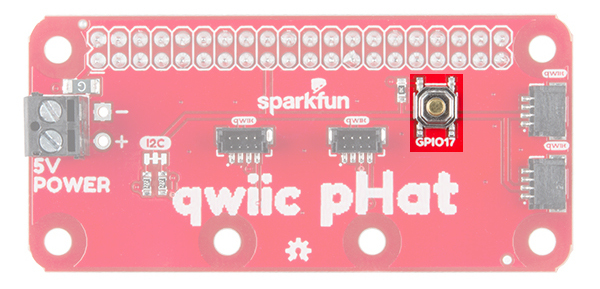
General Purpose Button
Included on the board is a general purpose button connected to GPIO17. You can use the button however you would like but we found it useful to shutdown or reboot a Raspberry Pi with a Python script.
Jumpers
There are built-in pull-up resistors on board. If necessary, you can cut the traces to disable depending on the number of boards connected to the I2C bus.
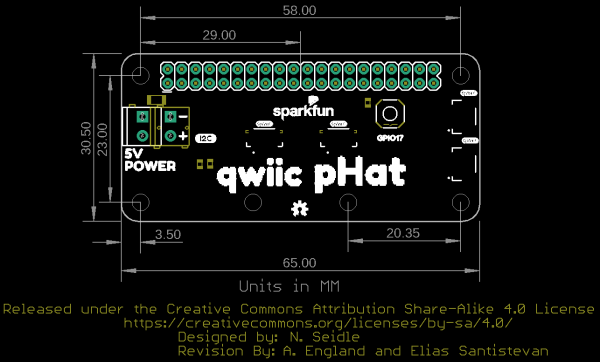
Board Dimensions
The board is about 65.00mm x 30.50mm. There are six mounting holes on the board. Two pairs of mounting holes were optimized to easily mount Qwiic devices that have the standard 1.0"x1.0" sized board.
Qwiic pHAT v1.0
I2C Pins
The Qwiic pHAT has 4x Qwiic connect ports, all on the same I2C bus. A 3.3V regulator is included to regulate voltage down for any Qwiic boards connected.
Jumpers
There are built-in pull-up resistors on board. If necessary, you can cut the traces to disable depending on the number of boards connected to the I2C bus.
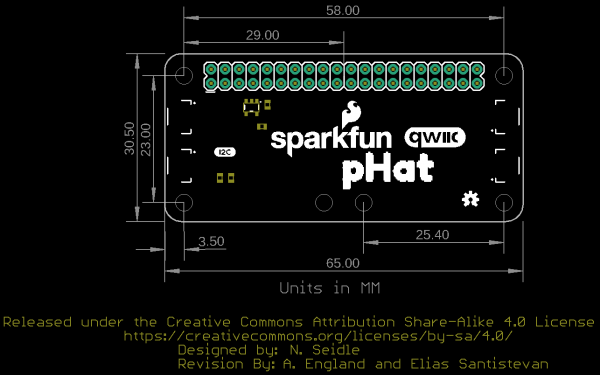
Board Dimensions
The board is about 65.00mm x 30.50mm. There are six mounting holes on the board.
Hardware Assembly
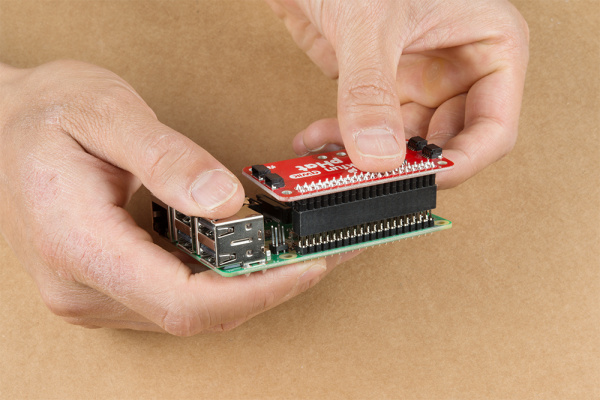
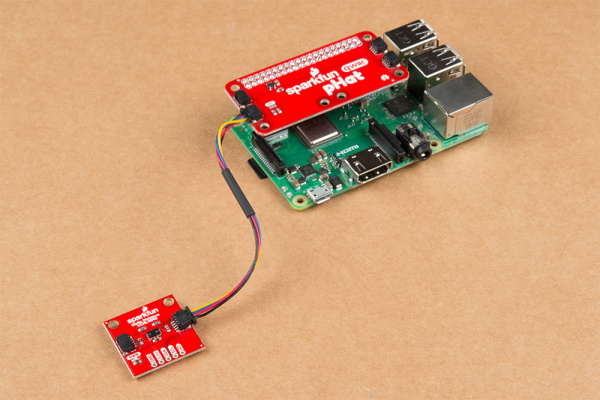
To get started with your Qwiic pHAT, simply plug it into the headers on the Raspberry Pi with the letters facing you. We'll use the Qwiic pHAT v1.0 in the following images to connect a Qwiic device.
Once the pHAT is plugged in, you can start plugging in any Qwiic enabled sensors.
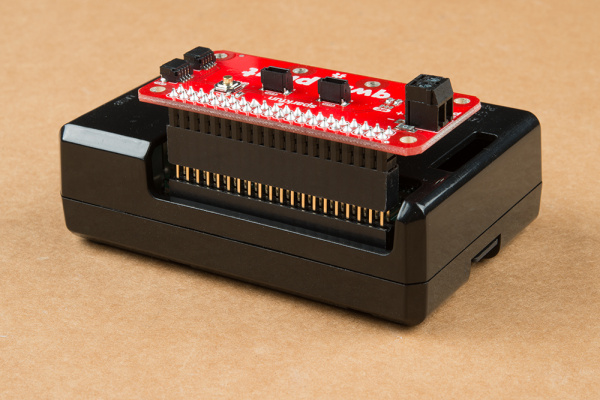
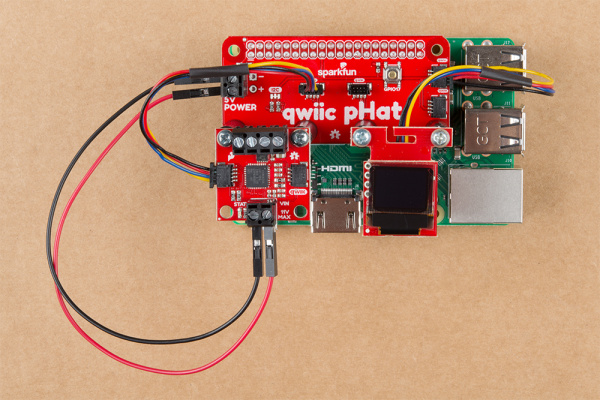
Standoffs and Mounting Holes
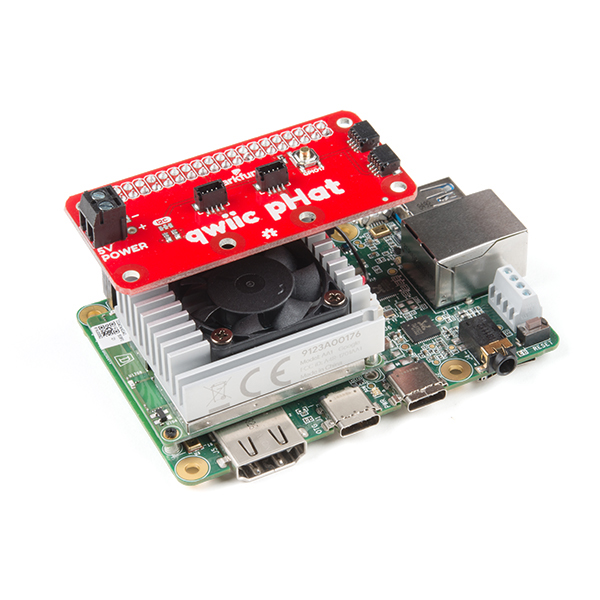
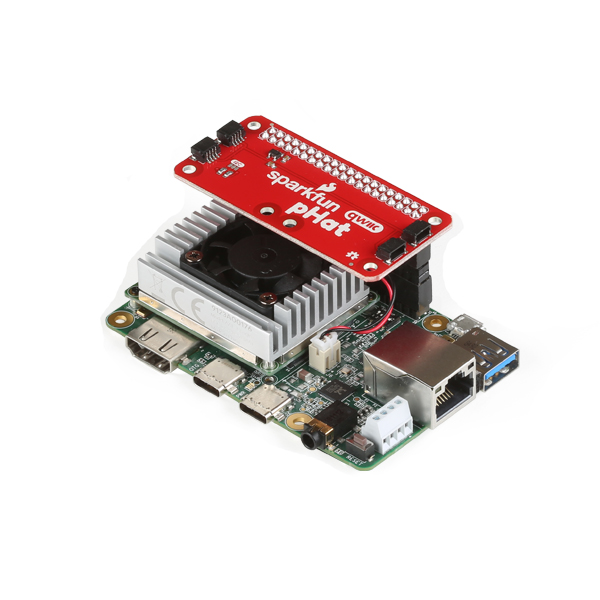
Depending on your project, you can mount a qwiic enabled board on the mounting holes using standoffs. Below are two images showing Qwiic devices mounted on each version of the Qwiic pHAT.
 |
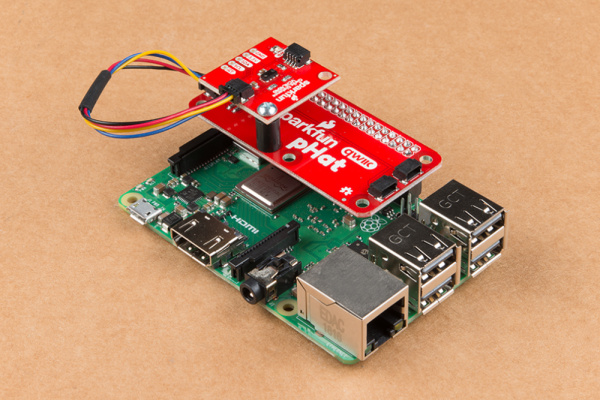 |
| Qwiic Devices Mounted on v2.0 | Qwiic Device Mounted on v1.0 |
Stackable Headers
When placing a Raspberry Pi and the pHat in an enclosure (like the Pi Tin), we noticed that the pHAT was not fully inserted in Pi's header pins. You will need an additional pair of stackable headers for a secure connection depending on your enclosure. Otherwise, the original Qwiic HAT would be better if you need to using the boards in an enclosure.
Getting an OS
We recommend checking out the Raspberry Pi 4 Hookup Guide to install the operating system to flash the image to your microSD card for detailed instructions.
Raspberry Pi 4 Kit Hookup Guide
If you're starting from scratch with a blank microSD card, you'll want to install Raspbian. If you've already got a working Raspbian system, skip ahead to the next section. Be patient — each of these steps can take a while depending on the speed of your microSD card.
- Download an Image — Download your favorite Linux distribution. For beginners, we recommend getting NOOBS image.
- Flashing the Image — Follow the instructions from the Raspberry Pi 4 Kit Hookup Guide to flash your microSD card. You can also follow the official Raspberry Pi installation instructions.
Configuring the Pi
The peripherals are not turned on by default. For those using Qwiic-enabled devices, you will want to enable I2C port. There are two methods to adjust the settings. This is outlined in our Raspberry Pi I2C tutorial.
Raspberry Pi SPI and I2C Tutorial
We've included the following instructions from the tutorial. To enable it, follow the steps below.
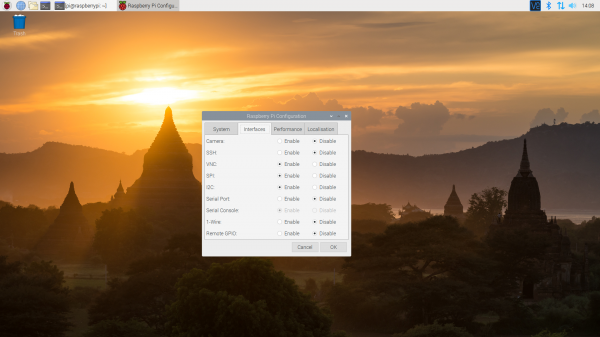
Raspberry Pi Configuration via Desktop GUI
You can use the Desktop GUI by heading to the Pi Start Menu > Preferences > Raspberry Pi Configuration.
A window will pop up with different tabs to adjust settings. What we are interested is the Interfaces tab. Click on the tab and select Enable for I2C. At this point, you can enable additional interfaces depending on your project needs. Click on the OK button to same.
We recommend restarting your Pi to ensure that the changes to take effect. Click on the Pi Start Menu > Preferences > Shutdown. Since we just need to restart, click on the Restart button.
 |
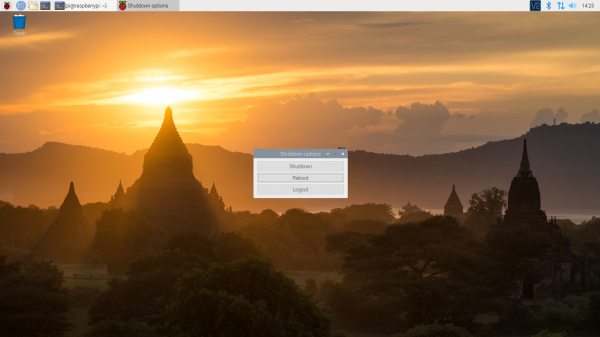 |
| Shutdown | Turn Off, Restart, Log Off |
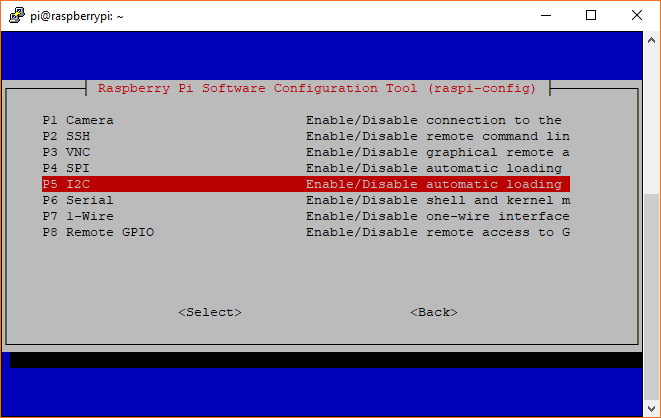
raspi-config Tool via Terminal
Again, we can use raspi-config to enable it.
- Run
sudo raspi-config. - Use the down arrow to select
5 Interfacing Options - Arrow down to
P5 I2C. - Select
yeswhen it asks you to enable I2C - Also select
yesif it asks about automatically loading the kernel module. - Use the right arrow to select the
<Finish>button. - Select
yeswhen it asks to reboot.
The system will reboot. When it comes back up, log in and enter the following command
language:bash
ls /dev/*i2c*
The Pi should respond with
language:bash
/dev/i2c-1
Which represents the user-mode I2C interface.
Scanning for I2C Devices
The best place to start would be to scan for an I2C device on the bus.
Configuration
Like the SPI peripheral, I2C is not turned on by default. Again, we can use raspi-config to enable it.
- Run
sudo raspi-config. - Use the down arrow to select
5 Interfacing Options - Arrow down to
P5 I2C. - Select
yeswhen it asks you to enable I2C - Select
OKand thenFinish
Once you return to terminal, enter this command:
language:bash
ls /dev/*i2c*
The Pi should respond with:
language:bash
/dev/i2c-1
Which represents the user-mode I2C interface.
Utilities
There is a set of command-line utility programs that can help get an I2C interface working. You can get them with the apt package manager. Enter the following command.
language:bash
sudo apt-get install -y i2c-tools
In particular, the i2cdetect program will probe all the addresses on a bus, and report whether any devices are present. Enter the following command in the command line. The -y flag will disable interactive mode so that you do not have to wait for confirmation. The 1 indicates that we are scanning for I2C devices on I2C bus 1 (e.g. i2c-1).
language:bash
i2cdetect -y 1
You will get an output from your Raspberry Pi similar to the output below.
language:bash
pi@raspberrypi:~/$ i2cdetect -y 1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: 60 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
This map indicates that there is a peripheral at address 0x60. Your address may vary depending on what is connected to the I2C bus. For advanced users, you can try to read and write its registers using the i2cget, i2cset and i2cdump commands.
Resources and Going Further
For more information, check out the resources below:
- Qwiic pHAT V2.0
- Qwiic pHAT V1.0
Now that you have your Qwiic pHAT ready to go, it's time to check out some of Qwiic enabled products.
But I Already Have Sensors!
If you already have a handful of SparkFun sensors and parts? SparkFun has been putting our standard GND/VCC/SDA/SCL pinout on all our I2C boards for many years. This makes it possible to attach a Qwiic Adapter that will get your SparkFun I2C sensor or actuator onto the Qwiic system.
Here is the list of the boards that have the standard I2C pinout and will work with the Qwiic adapter board:
- 9DoF Stick IMU - LSM9DS1
- 9DoF IMU - MPU-9250
- 6DoF IMU - LSM303C
- 6DoF IMU - LSM6DS3
- Triple Axis Accelerometer - LIS3DH
- Triple Axis Magnetometer - MAG3110
- Triple Axis Magnetometer - MLX90393
- Compass Module - HMC6343
- Atmospheric Sensor - BME280
- Barometric Pressure Sensor - MS5803-14BA
- Barometric Pressure Sensor - T5403
- Humidity and Temperature Sensor - Si7021
- Digital Temperature Sensor - TMP102
- Particle Sensor - MAX30105
- Air Quality Sensor - CCS811
- ToF Range Finder - VL6180
- Haptic Motor Driver - DRV2605L
- Micro OLED Display
- RGB and Gesture Sensor - APDS-9960
- RGB Light Sensor - ISL29125
- LED Driver - LP55231
- DAC Breakout - MCP4725
- 16 Output I/O Expander - SX1509
- Battery Babysitter - BQ24075
Looking for inspiration? Check out this related tutorials to use I2C devices on a Raspberry Pi:
Raspberry Pi SPI and I2C Tutorial
Or try taking advantage of the general purpose button on the Qwiic pHAT v2.0!