Qwiic Accelerometer (MMA8452Q) Hookup Guide
Introduction
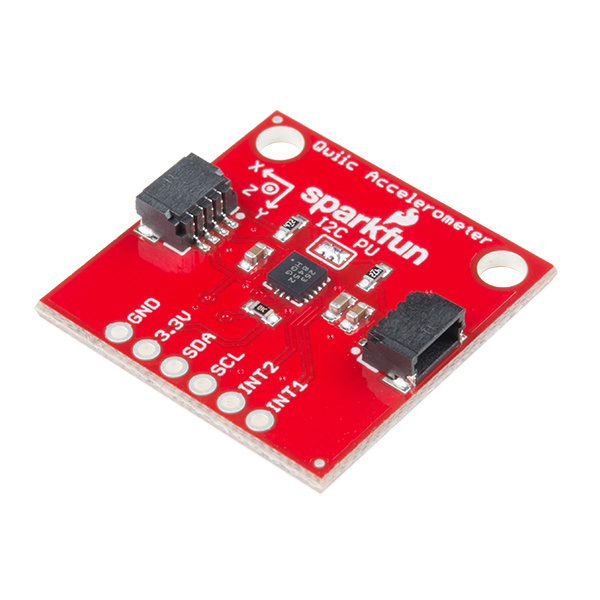
Freescale's MMA8452Q is a smart, low-power, three-axis, capacitive micro-machined accelerometer with 12 bits of resolution. It's perfect for any project that needs to sense orientation or motion. We've taken that accelerometer and stuck it on a Qwiic-Enabled breakout board, in order to make interfacing with the tiny, QFN package a bit easier. It's part of SparkFun's Qwiic system, so you won't have to do any soldering to figure out how things are oriented.
The MMA8452Q is a rock-solid, feature rich, 3-axis accelerometer. It supports three, selectable sensing ranges: ± 2g, 4g, or 8g. It also sports features like orientation detection, single and double-tap sensing, and low power modes. It's a digital sensor -- communicating over a Qwiic enabled I2C interface -- so you'll get reliable, noise-free data over a Qwiic enabled I2C port.
In this hookup guide, we'll connect our sensor up to our microcontroller of choice and read the X, Y, and Z accelerometer channels to figure out how we are accelerating in those directions. Then, we'll figure out how to use orientation detection to figure out what orientation the sensor is in.
Required Materials
To get started, you'll need a microcontroller to, well, control everything.
Particle Photon (Headers)
WRL-13774Raspberry Pi 3
DEV-13825Now to get into the Qwiic ecosystem, the key will be one of the following Qwiic shields to match your preference of microcontroller:
SparkFun Qwiic Shield for Photon
DEV-14477You will also need a Qwiic cable to connect the shield to your accelerometer, choose a length that suits your needs.
Qwiic Cable - 100mm
PRT-14427Qwiic Cable - 50mm
PRT-14426Qwiic Cable - 200mm
PRT-14428Qwiic Cable - 500mm
PRT-14429Suggested Reading
If you aren't familiar with the Qwiic system, we recommend reading here for an overview.
 |
| Qwiic Connect System |
We would also recommend taking a look at the following tutorials if you aren't familiar with them.