Installing libmraa on Ubilinux for Edison
Install Libraries
Install Dependencies
We'll be using Debian's Advanced Package Manager to install the dependencies needed for libmraa. Log in as root (or use "su" or "sudo") on your Edison and type:
apt-get update
apt-get update will update your local cache of all currently available packages in the repository.
The first dependency of this install is the PCRE development files.
apt-cache search pcre
apt-cache search does just what it sounds like -- searches apt packages. Look through the list and you should see:
libpcre3-dev - Perl 5 Compatible Regular Expression Library - development files
Looks like the right thing.
apt-get install libpcre3-dev
Now that we are familiar with installing packages from apt, let's get everything else we need for the build:
apt-get install git
apt-get install cmake
apt-get install python-dev
apt-get install swig
Build and Install mraa
libmraa is not in apt so we'll have to compile it from source. Don't worry, it's easy:
git clone https://github.com/intel-iot-devkit/mraa.git
mkdir mraa/build && cd $_
cmake .. -DBUILDSWIGNODE=OFF
make
make install
cd
Important: Make sure you run the final command, "make install" with root or "sudo."
That DBUILDSWIGNODE flag turns off node.js support, which isn't available in the version of swig in apt. If you need node.js, you can compile a newer version of swig from source (3.01+).
Update Shared Library Cache
To use the library in C or C++ programs, we need to add it to our shared library cache. With root (or using "sudo"), open up the ld.so.conf file:
nano /etc/ld.so.conf
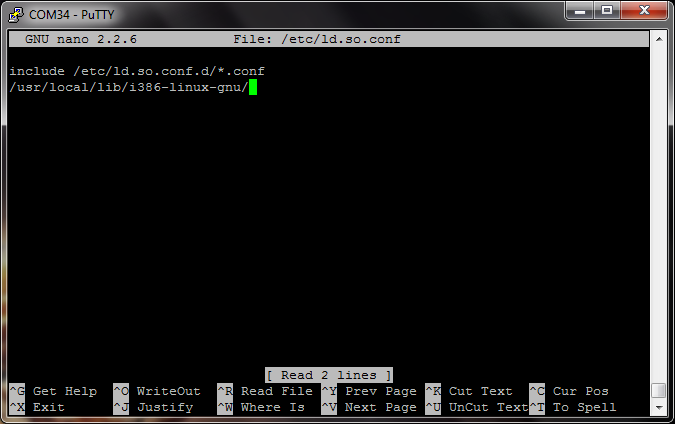
Scroll down to the bottom of the file and add:
/usr/local/lib/i386-linux-gnu/
Your ld.so.conf file should look like this:
Save and exit ('Crtl-x' and 'y' with nano). Type the command (using root or "sudo"):
ldconfig
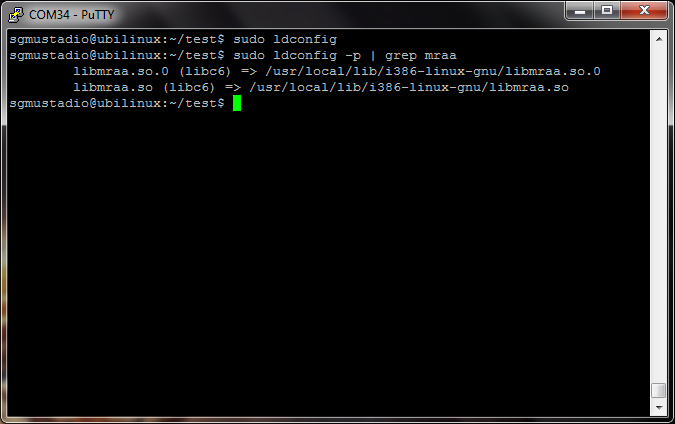
You can check to make sure that the cache was updated by typing the command:
ldconfig -p | grep mraa
You should see that the libraries have been included in the cache.
Export Library Path for Python
If you plan to use Python with mraa, you will need to export its location to the Python path. Enter the command:
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$(dirname $(find /usr/local -name mraa.py))
Note that this command lets us use the mraa module for this terminal session only. If we restart the Edison, we will have to retype the command.
Optional: You can modify the .bashrc file to run the commands automatically every time the Edison starts. Open the .bashrc file with your favorite editor. For example:
nano ~/.bashrc
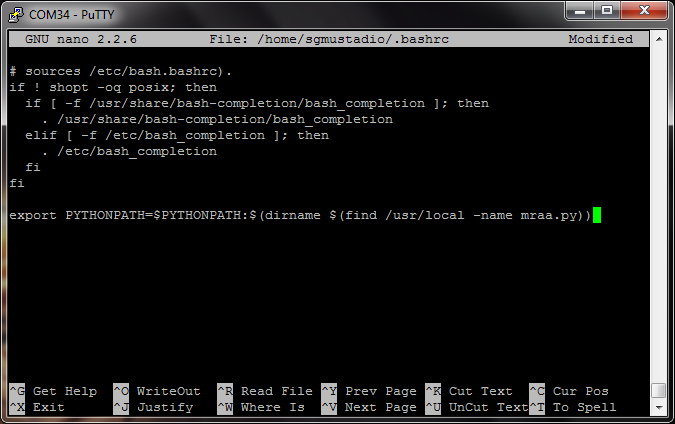
Scroll all the way down to the bottom of the file, and add the command from above in a new line.
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$(dirname $(find /usr/local -name mraa.py))
The bottom of your .bashrc file should look like the screenshot below.
Save and exit ('Crtl-x' and 'y' with nano).
Updating Sudoers File
This part is also optional. If you installed sudo, you might notice that PYTHONPATH is not updated properly when you try to run a Python script with "sudo." For example, you might get an error like "ImportError: No module named mraa."
Open up the sudoers file:
sudo visudo
Right under the first "Defaults" line, add the following:
Defaults env_keep += PYTHONPATH
Your sudoers file should look like the screenshot below.
Save and exit ('Crtl-x' and 'y' with nano). Reboot your Edison for this to take effect.