Measure relative humidity and temperature with the RHT03 (a.k.a DHT22) low cost sensor on a single wire digital interface connected to an Arduino!
To follow along with this tutorial, you will need the following materials. You may not need everything though depending on what you have. Add it to your cart, read through the guide, and adjust the cart as necessary.
If you aren’t familiar with the following concepts, we recommend checking out these tutorials before continuing.
The pins of the RHT03 (DHT22) are labeled in the image below.
| Pin | RHT03 (DHT22) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Input Voltage between 3.3-6V DC |
| 2 | DAT | Data Output |
| 3 | N/C | Not Connected |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
Connect the RHT03 to your Arduino as shown below. Since we are using a 5V Arduino, we will be using 5V to power the sensor. If you are using a 3.3V Arduino, you will need to connect it to a 3.3V pin for your respective development board.
We’ve written an Arduino library to make reading the RHT03 a breeze. You will need to manually install the RHT03 Arduino library from the GitHub repository by downloading a *.zip. Once downloaded, click Sketch > Include Library > Add .ZIP Library... to have the Arduino IDE unzip the library into it's respective folder.
After installing the library, open the example from the Arduino IDE by clicking File > Examples > SparkFun RHT03 Arduino Library > RHT03-Example-Serial. Select the board that you are using (if you are using the RedBoard with the ATmega328P, select Arduino/Genuino Uno) and COM port that the board enumerated on and hit upload.
Open the serial monitor at 9600 baud to view the output. You should see the relative humidity and temperature in °F and °C. Try blowing some air at the sensor. The sensor should react to the water vapor contained in the exhaled air.
Looking for more examples? Check out the following tutorials to read the sensor with other development boards!
If you are using the ESP8266 with the RHT03 (DHT22), try checking out experiment 1 of the Internet of Things Experiment Guide to capture temperature and humidity data from a sensor and post it to our ThingSpeak channel.
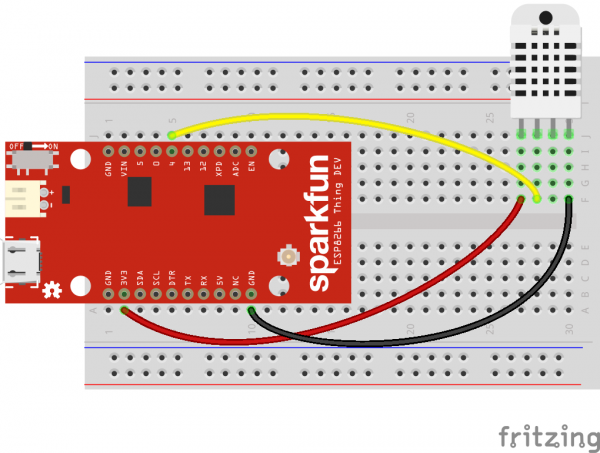 |
| ESP8266 Example |
If you are using the Particle Photon with the RHT03 (DHT22), try checking out experiment 6 of the SparkFun Inventor's Kit for Photon Experiment Guide to read the serial data with a photocell.
 |
| Particle Photon Example |
Now that you've successfully got your RHT03 up and running, it's time to incorporate it into your own project! For more information, check out the resources below:
Looking for more examples that monitor the environment? Check out the following tutorials.
learn.sparkfun.com | CC BY-SA 3.0 | SparkFun Electronics | Niwot, Colorado