Raspberry gPIo
Python (RPi.GPIO) Example
Follow along as we use the basic RPi.GPIO functions from the last page to create a simple example GPIO script.
1. Create a File
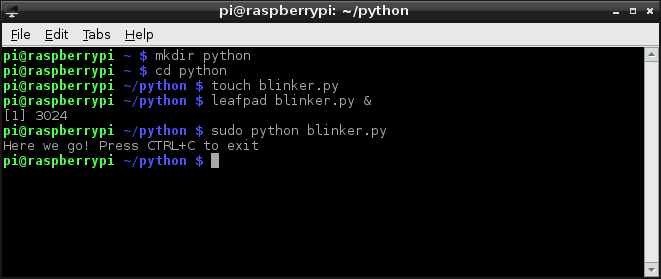
To begin, we need to create a Python file. You can do this through the GUI-based file explorer. Or, if you want a terminal-based solution, open up LXTerminal, and navigate to a folder you'd like the file to live (or create one). And create a new folder with these commands:
language:bash
mkdir python
Then move to the folder with the following command.
language:bash
cd python
Create a file -- we'll call ours "blinker" -- and terminate it with a .py extension.
language:bash
touch blinker.py
Then open it up in your favorite text editor. Nano works, as does Pi's default GUI text editor, Mousepad.
language:bash
mousepad blinker.py &
sudo apt-get install leafpad command. Once installed, you can specify the text editor to open up the file.
leafpad blinker.py &
That'll open up a blank text file (the "&" will open it in the background, leaving the terminal in place for future use). Time for some code!
2. Codify
Here's an example sketch that incorporates everything we learned on the last page. It does a little input and output, and even handles some PWM. This assumes you've set up the circuit as arranged on the Hardware Setup page.
language:Python
# External module imports
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
# Pin Definitons:
pwmPin = 18 # Broadcom pin 18 (P1 pin 12)
ledPin = 23 # Broadcom pin 23 (P1 pin 16)
butPin = 17 # Broadcom pin 17 (P1 pin 11)
dc = 95 # duty cycle (0-100) for PWM pin
# Pin Setup:
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Broadcom pin-numbering scheme
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # LED pin set as output
GPIO.setup(pwmPin, GPIO.OUT) # PWM pin set as output
pwm = GPIO.PWM(pwmPin, 50) # Initialize PWM on pwmPin 100Hz frequency
GPIO.setup(butPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # Button pin set as input w/ pull-up
# Initial state for LEDs:
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
pwm.start(dc)
print("Here we go! Press CTRL+C to exit")
try:
while 1:
if GPIO.input(butPin): # button is released
pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(dc)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
else: # button is pressed:
pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(100-dc)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.075)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.075)
except KeyboardInterrupt: # If CTRL+C is pressed, exit cleanly:
pwm.stop() # stop PWM
GPIO.cleanup() # cleanup all GPIO
After you've typed all of that in (don't forget your whitespace!) save.
Running the Script
The RPi.GPIO module requires administrator privileges, so you'll need to tag a sudo on to the front of your Python script call. To run your "blinker.py" script, type:
language:bash
sudo python blinker.py
With the code running, press the button to turn on the digital LED. The PWM-ing LED will invert its brightness when you press the button as well.
Press CTRL+C to cleanly exit the script.