Flex Sensor Hookup Guide
Flex Sensor Overview
Before we get to circuit-building and Arduino-programming, here's a quick rundown of the flex sensor's important electrical characteristics.
How it Works
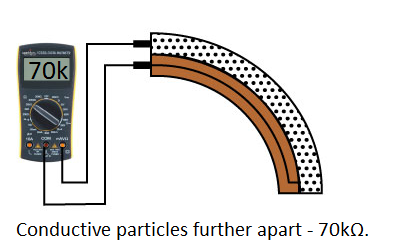
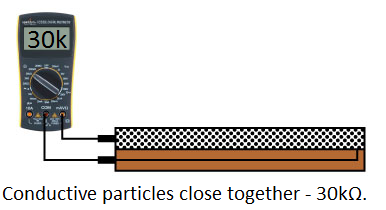
One side of the sensor is printed with a polymer ink that has conductive particles embedded in it. When the sensor is straight, the particles give the ink a resistance of about 30k Ohms. When the sensor is bent away from the ink, the conductive particles move further apart, increasing this resistance (to about 50k-70K Ohms when the sensor is bent to 90°, as in the diagram below).
When the sensor straightens out again, the resistance returns to the original value. By measuring the resistance, you can determine how much the sensor is being bent.
The flex sensor is designed to be flexed in just one direction – away from the ink – as demonstrated in the image below.
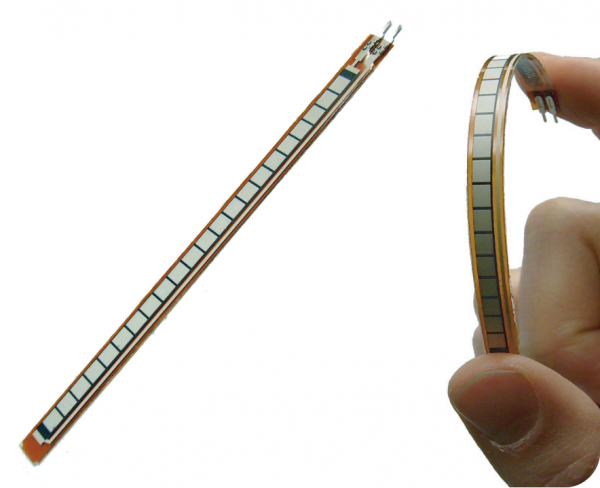
Flex sensor bend direction (from SpectraSymbol Datasheet).
Bending the sensor in the other direction will not produce any reliable data, and may damage the sensor. Also take care not to bend the sensor close to the base, as they have a tendency to kink and fail.