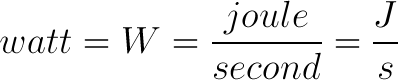Electric Power
Wattage
Energy is measured in terms of joules (J). Since power is a measure of energy over a set amount of time, we can measure it in joules per second. The SI unit for joules per second is the watt abbreviated as W.
It’s very common to see "watts" preceded by one of the standard SI prefixes: microwatts (µW), miliwatt (mW), kilowatt (kW), megawatt (MW), and gigawatts (GW), are all common depending on the situation.
| Prefix Name | Prefix Abbreviation | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Nanowatt | nW | 10-9 |
| Microwatt | µW | 10-6 |
| Milliwatt | mW | 10-3 |
| Watt | W | 100 |
| Kilowatt | kW | 103 |
| Megawatt | MW | 106 |
| Gigawatt | GW | 109 |
Microcontrollers, like the Arduino will usually operate in the the µW or mW range. Laptop and desktop computers operate in the standard watt power range. Energy consumption of a house is usually in the kilowatt range. Large stadiums might operate at the megawatt scale. And gigawatts come into play for large-scale power stations and time machines.